Calculate height of Binary Tree using Inorder and Level Order Traversal
Last Updated :
31 Jan, 2023
Given inorder traversal and Level Order traversal of a Binary Tree. The task is to calculate the height of the tree without constructing it.
Example:
Input : Input: Two arrays that represent Inorder
and level order traversals of a
Binary Tree
in[] = {4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22};
level[] = {20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14};
Output : 4
The binary tree that can be constructed from the
given traversals is:
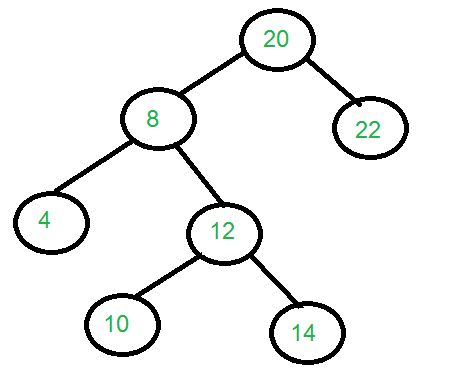
We can clearly see in the above image that the
height of the tree is 4.
The approach to calculating height is similar to the approach discussed in the post Constructing Tree from Inorder and Level Order Traversals.
Let us consider the above example.
in[] = {4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22};
level[] = {20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14};
In a Levelorder sequence, the first element is the root of the tree. So we know ’20’ is root for given sequences. By searching ’20’ in Inorder sequence, we can find out all elements on the left side of ‘20’ are in left subtree and elements on right are in the right subtree. So we know below structure now.
20
/ \
/ \
{4, 8, 10, 12, 14} {22}
Let us call {4, 8, 10, 12, 14} as left subarray in Inorder traversal and {22} as right subarray in Inorder traversal.
In level order traversal, keys of left and right subtrees are not consecutive. So we extract all nodes from level order traversal which are in left subarray of Inorder traversal. To calculate the height of the left subtree of the root, we recur for the extracted elements from level order traversal and left subarray of inorder traversal. In the above example, we recur for the following two arrays.
// Recur for following arrays to
// calculate the height of the left subtree
In[] = {4, 8, 10, 12, 14}
level[] = {8, 4, 12, 10, 14}
Similarly, we recur for the following two arrays and calculate the height of the right subtree.
// Recur for following arrays to calculate
// height of the right subtree
In[] = {22}
level[] = {22}
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int search(int arr[], int strt, int end, int value)
{
for (int i = strt; i <= end; i++)
if (arr[i] == value)
return i;
return -1;
}
int getHeight(int in[], int level[], int start,
int end, int& height, int n)
{
if (start > end)
return 0;
int getIndex = search(in, start, end, level[0]);
if (getIndex == -1)
return 0;
int leftCount = getIndex - start;
int rightCount = end - getIndex;
int* newLeftLevel = new int[leftCount];
int* newRightLevel = new int[rightCount];
int lheight = 0, rheight = 0;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = start; j < getIndex; j++) {
if (level[i] == in[j]) {
newLeftLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = getIndex + 1; j <= end; j++) {
if (level[i] == in[j]) {
newRightLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
if (leftCount > 0)
lheight = getHeight(in, newLeftLevel, start,
getIndex - 1, height, leftCount);
if (rightCount > 0)
rheight = getHeight(in, newRightLevel,
getIndex + 1, end, height, rightCount);
height = max(lheight + 1, rheight + 1);
delete[] newRightLevel;
delete[] newLeftLevel;
return height;
}
int main()
{
int in[] = { 4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22 };
int level[] = { 20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14 };
int n = sizeof(in) / sizeof(in[0]);
int h = 0;
cout << getHeight(in, level, 0, n - 1, h, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
class GFG
{
static int height;
static int search(int arr[], int strt,
int end, int value)
{
for (int i = strt; i <= end; i++)
if (arr[i] == value)
return i;
return -1;
}
static int getHeight(int in[], int level[],
int start, int end, int n)
{
if (start > end)
return 0;
int getIndex = search(in, start, end, level[0]);
if (getIndex == -1)
return 0;
int leftCount = getIndex - start;
int rightCount = end - getIndex;
int []newLeftLevel = new int[leftCount];
int []newRightLevel = new int[rightCount];
int lheight = 0, rheight = 0;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = start; j < getIndex; j++)
{
if (level[i] == in[j])
{
newLeftLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = getIndex + 1; j <= end; j++)
{
if (level[i] == in[j])
{
newRightLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
if (leftCount > 0)
lheight = getHeight(in, newLeftLevel, start,
getIndex - 1, leftCount);
if (rightCount > 0)
rheight = getHeight(in, newRightLevel,
getIndex + 1, end, rightCount);
height = Math.max(lheight + 1, rheight + 1);
newRightLevel=null;
newLeftLevel=null;
return height;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int in[] = {4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22};
int level[] = {20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14};
int n = in.length;
height = 0;
System.out.println(getHeight(in, level, 0, n - 1, n));
}
}
|
Python3
def search(arr, start, end, value):
for i in range(start, end + 1):
if arr[i] == value:
return i
return -1
def getHeight(inOrder, levelOrder,
start, end, height, n):
if start > end:
return 0
getIndex = search(inOrder, start, end, levelOrder[0])
if getIndex == -1:
return 0
leftCount = getIndex - start
rightCount = end - getIndex
newLeftLevel = [None for _ in range(leftCount)]
newRightLevel = [None for _ in range(rightCount)]
lheight, rheight, k = 0, 0, 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(start, getIndex):
if levelOrder[i] == inOrder[j]:
newLeftLevel[k] = levelOrder[i]
k += 1
break
k = 0
for i in range(n):
for j in range(getIndex + 1, end + 1):
if levelOrder[i] == inOrder[j]:
newRightLevel[k] = levelOrder[i]
k += 1
break
if leftCount > 0:
lheight = getHeight(inOrder, newLeftLevel, start,
getIndex - 1, height, leftCount)
if rightCount > 0:
rheight = getHeight(inOrder, newRightLevel,
getIndex + 1, end, height, rightCount)
height = max(lheight + 1, rheight + 1)
return height
if __name__=='__main__':
inOrder = [4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22]
levelOrder = [20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14]
n, h = len(inOrder), 0
print(getHeight(inOrder, levelOrder, 0, n - 1, h, n))
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG
{
static int height;
static int search(int []arr, int strt,
int end, int value)
{
for (int i = strt; i <= end; i++)
if (arr[i] == value)
return i;
return -1;
}
static int getHeight(int []In, int []level,
int start, int end, int n)
{
if (start > end)
return 0;
int getIndex = search(In, start, end, level[0]);
if (getIndex == -1)
return 0;
int leftCount = getIndex - start;
int rightCount = end - getIndex;
int []newLeftLevel = new int[leftCount];
int []newRightLevel = new int[rightCount];
int lheight = 0, rheight = 0;
int k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = start; j < getIndex; j++)
{
if (level[i] == In[j])
{
newLeftLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = getIndex + 1; j <= end; j++)
{
if (level[i] == In[j])
{
newRightLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
if (leftCount > 0)
lheight = getHeight(In, newLeftLevel, start,
getIndex - 1, leftCount);
if (rightCount > 0)
rheight = getHeight(In, newRightLevel,
getIndex + 1, end, rightCount);
height = Math.Max(lheight + 1, rheight + 1);
newRightLevel = null;
newLeftLevel = null;
return height;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int []In = {4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22};
int []level = {20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14};
int n = In.Length;
height = 0;
Console.WriteLine(getHeight(In, level, 0, n - 1, n));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var height = 0;
function search(arr, strt, end, value)
{
for (var i = strt; i <= end; i++)
if (arr[i] == value)
return i;
return -1;
}
function getHeight(In, level, start, end, n)
{
if (start > end)
return 0;
var getIndex = search(In, start, end, level[0]);
if (getIndex == -1)
return 0;
var leftCount = getIndex - start;
var rightCount = end - getIndex;
var newLeftLevel = Array(leftCount);
var newRightLevel = Array(rightCount);
var lheight = 0, rheight = 0;
var k = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (var j = start; j < getIndex; j++)
{
if (level[i] == In[j])
{
newLeftLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
k = 0;
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (var j = getIndex + 1; j <= end; j++)
{
if (level[i] == In[j])
{
newRightLevel[k] = level[i];
k++;
break;
}
}
}
if (leftCount > 0)
lheight = getHeight(In, newLeftLevel, start,
getIndex - 1, leftCount);
if (rightCount > 0)
rheight = getHeight(In, newRightLevel,
getIndex + 1, end, rightCount);
height = Math.max(lheight + 1, rheight + 1);
newRightLevel = null;
newLeftLevel = null;
return height;
}
var In = [4, 8, 10, 12, 14, 20, 22];
var level = [20, 8, 22, 4, 12, 10, 14];
var n = In.length;
height = 0;
document.write(getHeight(In, level, 0, n - 1, n));
</script>
|
Output:
4
Time Complexity: O(n^2)
In the worst case, the time complexity of the above algorithm will be O(n^2). The search() function takes O(n) time and getHeight() is called n times.
Space Complexity: O(n)
The space complexity of the above algorithm will be O(n). The auxiliary space used by the program is O(n) which is used to store the Level Order Traversal array.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...