Program to multiply two matrices
Last Updated :
19 Mar, 2024
Given two matrices, the task is to multiply them. Matrices can either be square or rectangular:
Examples:
(Square Matrix Multiplication)
Input: mat1[m][n] = { {1, 1}, {2, 2} }
mat2[n][p] = { {1, 1}, {2, 2} }
Output: result[m][p] = { {3, 3}, {6, 6} }
(Rectangular Matrix Multiplication)
Input: mat1[3][2] = { {1, 1}, {2, 2}, {3, 3} }
mat2[2][3] = { {1, 1, 1}, {2, 2, 2} }
Output: result[3][3] = { {3, 3, 3}, {6, 6, 6}, {9, 9, 9} }
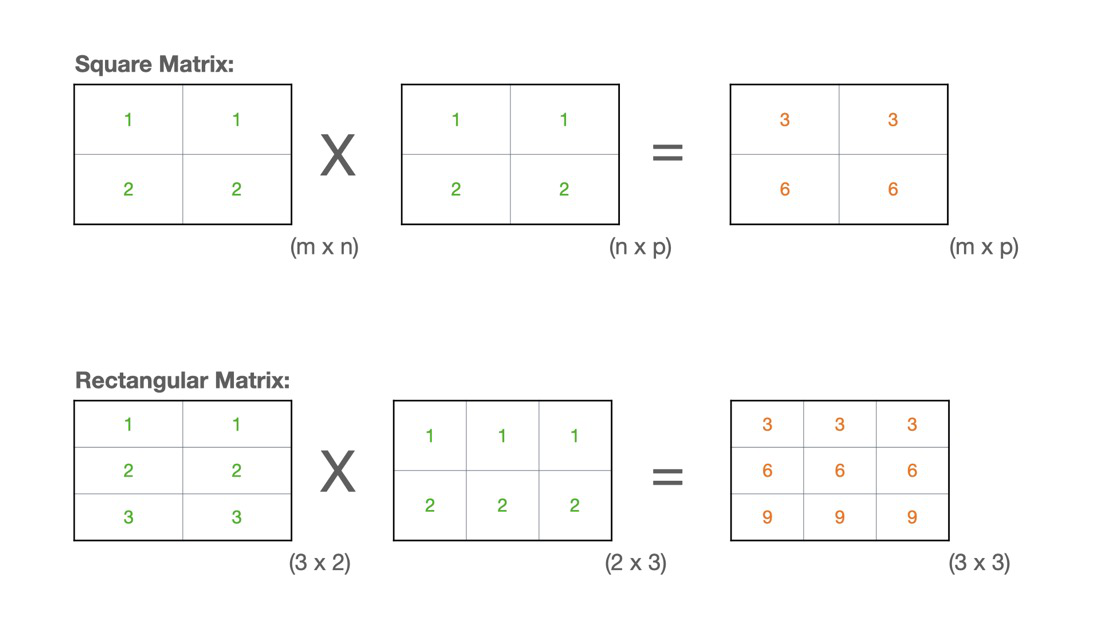
Multiplication of two Square or Rectangular Matrices:
- The number of columns in Matrix-1 must be equal to the number of rows in Matrix-2.
- Output of multiplication of Matrix-1 and Matrix-2, results with equal to the number of rows of Matrix-1 and the number of columns of Matrix-2 i.e. rslt[R1][C2]
Below is the implementation of the multiplication of two matrices:
C++
// C++ program to multiply two matrices
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Edit MACROs here, according to your Matrix Dimensions for
// mat1[R1][C1] and mat2[R2][C2]
#define R1 2 // number of rows in Matrix-1
#define C1 2 // number of columns in Matrix-1
#define R2 2 // number of rows in Matrix-2
#define C2 2 // number of columns in Matrix-2
void mulMat(int mat1[][C1], int mat2[][C2])
{
int rslt[R1][C2];
cout << "Multiplication of given two matrices is:\n";
for (int i = 0; i < R1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < C2; j++) {
rslt[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < R2; k++) {
rslt[i][j] += mat1[i][k] * mat2[k][j];
}
cout << rslt[i][j] << "\t";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// R1 = 4, C1 = 4 and R2 = 4, C2 = 4 (Update these
// values in MACROs)
int mat1[R1][C1] = { { 1, 1 },
{ 2, 2 } };
int mat2[R2][C2] = { { 1, 1 },
{ 2, 2 } };
if (C1 != R2) {
cout << "The number of columns in Matrix-1 must "
"be equal to the number of rows in "
"Matrix-2"
<< endl;
cout << "Please update MACROs according to your "
"array dimension in #define section"
<< endl;
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// Function call
mulMat(mat1, mat2);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Manish Kumar (mkumar2789)
// C program to multiply two matrices
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Edit MACROs here, according to your Matrix Dimensions for
// mat1[R1][C1] and mat2[R2][C2]
#define R1 2 // number of rows in Matrix-1
#define C1 2 // number of columns in Matrix-1
#define R2 2 // number of rows in Matrix-2
#define C2 2 // number of columns in Matrix-2
void mulMat(int mat1[][C1], int mat2[][C2])
{
int rslt[R1][C2];
printf("Multiplication of given two matrices is:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < R1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < C2; j++) {
rslt[i][j] = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < R2; k++) {
rslt[i][j] += mat1[i][k] * mat2[k][j];
}
printf("%d\t", rslt[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
// R1 = 4, C1 = 4 and R2 = 4, C2 = 4 (Update these
// values in MACROs)
int mat1[R1][C1] = { { 1, 1 },
{ 2, 2 } };
int mat2[R2][C2] = { { 1, 1 },
{ 2, 2 } };
if (C1 != R2) {
printf("The number of columns in Matrix-1 must be "
"equal to the number of rows in "
"Matrix-2\n");
printf("Please update MACROs value according to "
"your array dimension in "
"#define section\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// Function call
mulMat(mat1, mat2);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Manish Kumar (mkumar2789)
// C++ program to multiply two matrices
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static int R1 = 2; // number of rows in Matrix-1
static int C1 = 2; // number of columns in Matrix-1
static int R2 = 2; // number of rows in Matrix-2
static int C2 = 2; // number of columns in Matrix-2
// This function multiplies mat1[][]
// and mat2[][], and stores the result
// in res[][]
static void mulMat(int[][] mat1, int[][] mat2)
{
// To store result
int[][] rslt = new int[R1][C2];
System.out.println(
"Multiplication of given two matrices is:");
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < R1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < C2; j++) {
rslt[i][j] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < R2; k++)
rslt[i][j] += mat1[i][k] * mat2[k][j];
System.out.print(rslt[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int[][] mat1 = { { 1, 1 },
{ 2, 2 } };
int[][] mat2 = { { 1, 1 },
{ 2, 2 } };
if (C1 != R2) {
System.out.println(
"The number of columns in Matrix-1 must be equal to the number of rows in Matrix-2");
System.out.println(
"Please update the global variables according to your array dimension");
}
else {
// Function call
mulMat(mat1, mat2);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by shruti456rawal
// C# program to multiply two matrices
using System;
class GFG {
static int R1 = 2; // number of rows in Matrix-1
static int C1 = 2; // number of columns in Matrix-1
static int R2 = 2; // number of rows in Matrix-2
static int C2 = 2; // number of columns in Matrix-2
// This function multiplies mat1[][]
// and mat2[][], and stores the result
// in res[][]
static void mulMat(int[, ] mat1, int[, ] mat2)
{
// To store result
int[, ] rslt = new int[R1, C2];
Console.WriteLine(
"Multiplication of given two matrices is:");
int i, j, k;
for (i = 0; i < R1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < C2; j++) {
rslt[i, j] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < R2; k++)
rslt[i, j] += mat1[i, k] * mat2[k, j];
Console.Write(rslt[i, j] + "\t");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main()
{
int[, ] mat1 = { { 1, 1 },
{ 2, 2 } };
int[, ] mat2 = { { 1, 1 },
{ 2, 2 } };
if (C1 != R2) {
Console.WriteLine(
"The number of columns in Matrix-1 must be equal to the number of rows in Matrix-2");
Console.WriteLine(
"Please update MACROs according to your array dimension in #define section");
}
else {
mulMat(mat1, mat2);
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi
var R1 = 2;
// number of rows in Matrix-1
var C1 = 2;
// number of columns in Matrix-1
var R2 = 2;
// number of rows in Matrix-2
var C2 = 2;
// number of columns in Matrix-2
// This function multiplies mat1[][]
// and mat2[][], and stores the result
// in res[][]
function mulMat(mat1, mat2)
{
// To store result
var rslt = Array(R1).fill(0).map(()=>new Array(C2).fill(0));
console.log("Multiplication of given two matrices is:");
var i = 0;
var j = 0;
var k = 0;
for (i = 0; i < R1; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < C2; j++)
{
rslt[i][j] = 0;
for (k = 0; k < R2; k++)
{
rslt[i][j] += mat1[i][k] * mat2[k][j];
}
console.log(rslt[i][j] + " ");
}
console.log("");
}
}
// Driver program
var mat1 = [[1, 1], [2, 2]];
var mat2 = [[1, 1], [2, 2]];
if (C1 != R2)
{
console.log("The number of columns in Matrix-1 must be equal to the number of rows in Matrix-2");
console.log("Please update the global variables according to your array dimension");
}
else
{
mulMat(mat1, mat2);
}
// This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi
# Python3 program to multiply two matrices
def mulMat(mat1, mat2, R1, R2, C1, C2):
# List to store matrix multiplication result
rslt = [[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0]]
for i in range(0, R1):
for j in range(0, C2):
for k in range(0, R2):
rslt[i][j] += mat1[i][k] * mat2[k][j]
print("Multiplication of given two matrices is:")
for i in range(0, R1):
for j in range(0, C2):
print(rslt[i][j], end=" ")
print("\n", end="")
# Driver code
if __name__ == '__main__':
R1 = 2
R2 = 2
C1 = 2
C2 = 2
# First matrix. M is a list
mat1 = [[1, 1],
[2, 2]]
# Second matrix. N is a list
mat2 = [[1, 1],
[2, 2]]
if C1 != R2:
print("The number of columns in Matrix-1 must be equal to the number of rows in " + "Matrix-2", end='')
print("\n", end='')
print("Please update MACROs according to your array dimension in #define section", end='')
print("\n", end='')
else:
# Call matrix_multiplication function
mulMat(mat1, mat2, R1, R2, C1, C2)
# This code is contributed by Aarti_Rathi
OutputMultiplication of given two matrices is:
3 3
6 6
Time complexity: O(R1 * C2 * R2) for given matrices mat1[R1][C1] and mat2[R2][C2]
Auxiliary space: O(R1 * C2)
Multiplication of Rectangular Matrices using Pointers in C/C++:
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
We use pointers in C/C++ to multiply matrices
Prerequisite: How to pass a 2D array as a parameter in C?
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program to multiply two
// rectangular matrices
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Multiplies two matrices mat1[][]
// and mat2[][] and prints result.
// (m1) x (m2) and (n1) x (n2) are
// dimensions of given matrices.
void multiply(int m1, int m2, int mat1[][2], int n1, int n2,
int mat2[][2])
{
int x, i, j;
int res[m1][n2];
for (i = 0; i < m1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++) {
res[i][j] = 0;
for (x = 0; x < m2; x++) {
*(*(res + i) + j) += *(*(mat1 + i) + x)
* *(*(mat2 + x) + j);
}
}
}
for (i = 0; i < m1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++) {
cout << *(*(res + i) + j) << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int mat1[][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 2, 2 } };
int mat2[][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 2, 2 } };
int m1 = 2, m2 = 2, n1 = 2, n2 = 2;
// Function call
multiply(m1, m2, mat1, n1, n2, mat2);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed
// by Akanksha Rai(Abby_akku)
// C program to multiply two rectangular matrices
#include <stdio.h>
// Multiplies two matrices mat1[][] and mat2[][]
// and prints result.
// (m1) x (m2) and (n1) x (n2) are dimensions
// of given matrices.
void multiply(int m1, int m2, int mat1[][m2], int n1,
int n2, int mat2[][n2])
{
int x, i, j;
int res[m1][n2];
for (i = 0; i < m1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++) {
res[i][j] = 0;
for (x = 0; x < m2; x++) {
*(*(res + i) + j) += *(*(mat1 + i) + x)
* *(*(mat2 + x) + j);
}
}
}
for (i = 0; i < m1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++) {
printf("%d ", *(*(res + i) + j));
}
printf("\n");
}
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int mat1[][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 2, 2 } };
int mat2[][2] = { { 1, 1 }, { 2, 2 } };
int m1 = 2, m2 = 2, n1 = 2, n2 = 2;
// Function call
multiply(m1, m2, mat1, n1, n2, mat2);
return 0;
}
// JAVA program to multiply two
// rectangular matrices
import java.io.*;
import java.lang.*;
import java.util.*;
// Multiplies two matrices mat1[][]
// and mat2[][] and prints result.
// (m1) x (m2) and (n1) x (n2) are
// dimensions of given matrices.
public class GFG {
public static void multiply(int m1, int m2,
int mat1[][], int n1,
int n2, int mat2[][])
{
int x, i, j;
int res[][] = new int[m1][n2];
for (i = 0; i < m1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++) {
res[i][j] = 0;
for (x = 0; x < m2; x++) {
res[i][j] += mat1[i][x] * mat2[x][j];
}
}
}
for (i = 0; i < m1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++) {
System.out.print(res[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int m1 = 2, m2 = 2, n1 = 2, n2 = 2;
int mat1[][] = new int[][] { { 1, 1 }, { 2, 2 } };
int mat2[][] = new int[][] { { 1, 1 }, { 2, 2 } };
// Function call
multiply(m1, m2, mat1, n1, n2, mat2);
}
}
// This code is contributed by ishankhandelwals.
// C# program to multiply two
// rectangular matrices
using System;
class Program {
// Driver code
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int m1 = 2, m2 = 2, n1 = 2, n2 = 2;
int[, ] mat1 = new int[, ] { { 1, 1 }, { 2, 2 } };
int[, ] mat2 = new int[, ] { { 1, 1 }, { 2, 2 } };
// Function call
multiply(m1, m2, mat1, n1, n2, mat2);
}
// Multiplies two matrices mat1[][]
// and mat2[][] and prints result.
// (m1) x (m2) and (n1) x (n2) are
// dimensions of given matrices.
static void multiply(int m1, int m2, int[, ] mat1,
int n1, int n2, int[, ] mat2)
{
int x, i, j;
int[, ] res = new int[m1, n2];
for (i = 0; i < m1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++) {
res[i, j] = 0;
for (x = 0; x < m2; x++) {
res[i, j] += mat1[i, x] * mat2[x, j];
}
}
}
for (i = 0; i < m1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++) {
Console.Write(res[i, j] + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}
// This code is contributed by Tapesh(tapeshdua420)
// JS program to multiply two
// rectangular matrices
// Multiplies two matrices mat1[][]
// and mat2[][] and prints result.
// (m1) x (m2) and (n1) x (n2) are
// dimensions of given matrices.
function multiply(m1, m2, mat1, n1, n2, mat2) {
let x, i, j;
let res = [[0, 0], [0, 0]];
for (i = 0; i < m1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++) {
// res[i][j] = 0;
for (x = 0; x < m2; x++) {
res[i][j] += (mat1[i][x] * mat2[x][j])
}
}
}
for (i = 0; i < m1; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < n2; j++) {
console.log(res[i][j]);
}
}
}
// Driver code
let mat1 = [[1, 1], [2, 2]];
let mat2 = [[1, 1], [2, 2]];
let m1 = 2, m2 = 2, n1 = 2, n2 = 2;
// Function call
multiply(m1, m2, mat1, n1, n2, mat2);
// This code is contributed by ishankhandelwals.
# Python program to multiply two
# rectangular matrices
# Multiplies two matrices mat1[][]
# and mat2[][] and prints result.
# (m1) x (m2) and (n1) x (n2) are
# dimensions of given matrices.
def multiply(m1, m2, mat1, n1, n2, mat2):
res = [[0 for x in range(n2)] for y in range(m1)]
for i in range(m1):
for j in range(n2):
res[i][j] = 0
for x in range(m2):
res[i][j] += mat1[i][x] * mat2[x][j]
for i in range(m1):
for j in range(n2):
print(res[i][j], end=" ")
print()
# Driver code
m1 = 2
m2 = 2
n1 = 2
n2 = 2
mat1 = [[1, 1], [2, 2]]
mat2 = [[1, 1], [2, 2]]
# Function call
multiply(m1, m2, mat1, n1, n2, mat2)
# This code is contributed by Tapesh(tapeshdua420)
Time complexity: O(N3)
Auxiliary Space: O(M1 * N2)
Related Article
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...