Program for Tower of Hanoi Algorithm
Last Updated :
16 Feb, 2023
Tower of Hanoi is a mathematical puzzle where we have three rods (A, B, and C) and N disks. Initially, all the disks are stacked in decreasing value of diameter i.e., the smallest disk is placed on the top and they are on rod A. The objective of the puzzle is to move the entire stack to another rod (here considered C), obeying the following simple rules:
- Only one disk can be moved at a time.
- Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the stacks and placing it on top of another stack i.e. a disk can only be moved if it is the uppermost disk on a stack.
- No disk may be placed on top of a smaller disk.
Examples:
Input: 2
Output: Disk 1 moved from A to B
Disk 2 moved from A to C
Disk 1 moved from B to C
Input: 3
Output: Disk 1 moved from A to C
Disk 2 moved from A to B
Disk 1 moved from C to B
Disk 3 moved from A to C
Disk 1 moved from B to A
Disk 2 moved from B to C
Disk 1 moved from A to C
Tower of Hanoi using Recursion:
The idea is to use the helper node to reach the destination using recursion. Below is the pattern for this problem:
- Shift ‘N-1’ disks from ‘A’ to ‘B’, using C.
- Shift last disk from ‘A’ to ‘C’.
- Shift ‘N-1’ disks from ‘B’ to ‘C’, using A.
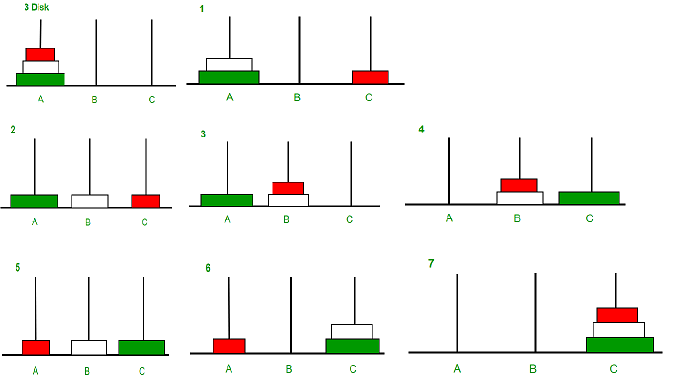
Image illustration for 3 disks
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Create a function towerOfHanoi where pass the N (current number of disk), from_rod, to_rod, aux_rod.
- Make a function call for N – 1 th disk.
- Then print the current the disk along with from_rod and to_rod
- Again make a function call for N – 1 th disk.
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void towerOfHanoi(int n, char from_rod, char to_rod,
char aux_rod)
{
if (n == 0) {
return;
}
towerOfHanoi(n - 1, from_rod, aux_rod, to_rod);
cout << "Move disk " << n << " from rod " << from_rod
<< " to rod " << to_rod << endl;
towerOfHanoi(n - 1, aux_rod, to_rod, from_rod);
}
int main()
{
int N = 3;
towerOfHanoi(N, 'A', 'C', 'B');
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
static void towerOfHanoi(int n, char from_rod,
char to_rod, char aux_rod)
{
if (n == 0) {
return;
}
towerOfHanoi(n - 1, from_rod, aux_rod, to_rod);
System.out.println("Move disk " + n + " from rod "
+ from_rod + " to rod "
+ to_rod);
towerOfHanoi(n - 1, aux_rod, to_rod, from_rod);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int N = 3;
towerOfHanoi(N, 'A', 'C', 'B');
}
}
|
Python3
def TowerOfHanoi(n, from_rod, to_rod, aux_rod):
if n == 0:
return
TowerOfHanoi(n-1, from_rod, aux_rod, to_rod)
print("Move disk", n, "from rod", from_rod, "to rod", to_rod)
TowerOfHanoi(n-1, aux_rod, to_rod, from_rod)
N = 3
TowerOfHanoi(N, 'A', 'C', 'B')
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void towerOfHanoi(int n, char from_rod,
char to_rod, char aux_rod)
{
if (n == 0) {
return;
}
towerOfHanoi(n - 1, from_rod, aux_rod, to_rod);
Console.WriteLine("Move disk " + n + " from rod "
+ from_rod + " to rod " + to_rod);
towerOfHanoi(n - 1, aux_rod, to_rod, from_rod);
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int N = 3;
towerOfHanoi(N, 'A', 'C', 'B');
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
$poles = array(array(), array(), array());
function TOH($n, $A="A", $B="B", $C="C"){
if ($n > 0){
TOH($n-1, $A, $C, $B);
echo "Move disk from rod $A to rod $C \n";
move($A, $C);
dispPoles();
TOH($n-1, $B, $A, $C);
}
else {
return;
}
}
function initPoles($n){
global $poles;
for ($i=$n; $i>=1; --$i){
$poles[0][] = $i;
}
}
function move($source, $destination){
global $poles;
if ($source=="A") $ptr1=0;
elseif ($source=="B") $ptr1 = 1;
else $ptr1 = 2;
if ($destination=="A") $ptr2 = 0;
elseif ($destination=="B") $ptr2 = 1;
else $ptr2 = 2;
$top = array_pop($poles[$ptr1]);
array_push($poles[$ptr2], $top);
}
function dispPoles(){
global $poles;
echo "A: [".implode(", ", $poles[0])."] ";
echo "B: [".implode(", ", $poles[1])."] ";
echo "C: [".implode(", ", $poles[2])."] ";
echo "\n\n";
}
$N = 3;
initPoles($N);
echo "Tower of Hanoi Solution for $numdisks disks: \n\n";
dispPoles();
TOH($N);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function towerOfHanoi(n, from_rod, to_rod, aux_rod)
{
if (n == 0)
{
return;
}
towerOfHanoi(n - 1, from_rod, aux_rod, to_rod);
document.write("Move disk " + n + " from rod " + from_rod +
" to rod " + to_rod+"<br/>");
towerOfHanoi(n - 1, aux_rod, to_rod, from_rod);
}
var N = 3;
towerOfHanoi(N, 'A', 'C', 'B');
</script>
|
Output
Move disk 1 from rod A to rod C
Move disk 2 from rod A to rod B
Move disk 1 from rod C to rod B
Move disk 3 from rod A to rod C
Move disk 1 from rod B to rod A
Move disk 2 from rod B to rod C
Move disk 1 from rod A to rod C
Time complexity: O(2N), There are two possibilities for every disk. Therefore, 2 * 2 * 2 * . . . * 2(N times) is 2N
Auxiliary Space: O(N), Function call stack space
Related Articles
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...