C Program for Identity Matrix
Last Updated :
08 Jul, 2022
Introduction to Identity Matrix :
The dictionary definition of an Identity Matrix is a square matrix in which all the elements of the principal or main diagonal are 1’s and all other elements are zeros. In the below image, every matrix is an Identity Matrix.
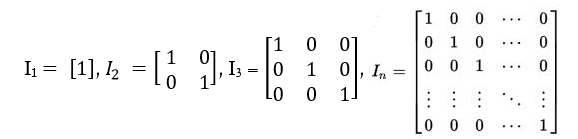
In linear algebra, this is sometimes called as a Unit Matrix, of a square matrix (size = n x n) with ones on the main diagonal and zeros elsewhere. The identity matrix is denoted by “ I “. Sometimes U or E is also used to denote an Identity Matrix.
A property of the identity matrix is that it leaves a matrix unchanged if it is multiplied by an Identity Matrix.
Examples:
Input : 2
Output : 1 0
0 1
Input : 4
Output : 1 0 0 0
0 1 0 0
0 0 1 0
0 0 0 1
The explanation is simple. We need to make all
the elements of principal or main diagonal as
1 and everything else as 0.
Program to print Identity Matrix :
The logic is simple. You need to the print 1 in those positions where row is equal to column of a matrix and make all other positions as 0.
C
#include<stdio.h>
int Identity(int num)
{
int row, col;
for (row = 0; row < num; row++)
{
for (col = 0; col < num; col++)
{
if (row == col)
printf("%d ", 1);
else
printf("%d ", 0);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int size = 5;
identity(size);
return 0;
}
|
Output:
1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0
0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 1
Time complexity: O(n2) where n is number of rows and columns of matrix
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...