C Program For Detecting Loop In A Linked List
Last Updated :
03 Mar, 2023
Given a linked list, check if the linked list has loop or not. Below diagram shows a linked list with a loop.
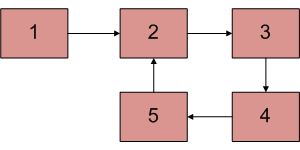
Solution: Floyd’s Cycle-Finding Algorithm
Approach: This is the fastest method and has been described below:
- Traverse linked list using two pointers.
- Move one pointer(slow_p) by one and another pointer(fast_p) by two.
- If these pointers meet at the same node then there is a loop. If pointers do not meet then linked list doesn’t have a loop.
The below image shows how the detectloop function works in the code:

Implementation of Floyd’s Cycle-Finding Algorithm:
C
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
int detectLoop(struct Node* list)
{
struct Node *slow_p = list, *fast_p = list;
while (slow_p && fast_p && fast_p->next) {
slow_p = slow_p->next;
fast_p = fast_p->next->next;
if (slow_p == fast_p) {
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 20);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 15);
push(&head, 10);
head->next->next->next->next = head;
if (detectLoop(head))
printf("Loop found");
else
printf("No Loop");
return 0;
}
|
Complexity Analysis:
- Time complexity: O(n).
Only one traversal of the loop is needed.
- Auxiliary Space:O(1).
There is no space required.
How does above algorithm work?
Please See : How does Floyd’s slow and fast pointers approach work?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Aup0kOWoMVg
Please refer complete article on Detect loop in a linked list for more details!
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...