C Program for Binary Search
Last Updated :
26 Sep, 2023
In this article, we will understand the Binary search algorithm and how to write binary search programs in C. We will see both iterative and recursive approaches and how binary search is able to reduce the time complexity of the search operation as compared to linear search.
What is Binary Search?
Binary Search is an interval searching algorithm used to search for an item in the sorted list. It works by repeatedly dividing the list into two equal parts and then searching for the item that is the part where it can possibly exist.
Unlike linear search, there are a few conditions for applying binary search:
- The list must be sorted.
- Random access to the list member.
It means that we cannot apply the binary search in unsorted or liked data structures.
Algorithm for Binary Search in C
Let 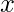 be the element we are searching for and the array is sorted in the ascending order.
be the element we are searching for and the array is sorted in the ascending order.
- Compare
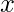 with the middle element of the array.
with the middle element of the array.
- If
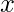 matches with the middle element, we return the index of the middle element.
matches with the middle element, we return the index of the middle element.
- Else if
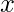 is greater than the middle element, it means that
is greater than the middle element, it means that 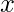 can only lie in the right half subarray after the middle element. So we repeat steps 1 and 2 for the right half subarray and leave the left half subarray from the algorithm
can only lie in the right half subarray after the middle element. So we repeat steps 1 and 2 for the right half subarray and leave the left half subarray from the algorithm
- Else if
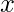 is smaller than the middle element, it means that
is smaller than the middle element, it means that 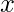 can only lie in the left half subarray before the middle element. So, we repeat steps 1 and 2 for the left half subarray.
can only lie in the left half subarray before the middle element. So, we repeat steps 1 and 2 for the left half subarray.
- We will keep doing that till we find
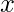 or there is no element left in the subarray being considered.
or there is no element left in the subarray being considered.
As we can see, the binary search ignores the half elements of the subarray after each pass. Due to this, it is able to reduce the time required for searching the element in the array as compared to linear search.
Binary Search Program in C (Recursive)
The following C program implements the binary search algorithm using recursion:
C
#include <stdio.h>
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{
if (r >= l) {
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == x)
return mid;
if (arr[mid] > x) {
return binarySearch(arr, l, mid - 1, x);
}
return binarySearch(arr, mid + 1, r, x);
}
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int x = 10;
int index = binarySearch(arr, 0, size - 1, x);
if (index == -1) {
printf("Element is not present in array");
}
else {
printf("Element is present at index %d", index);
}
return 0;
}
|
OutputElement is present at index 3
Complexity Analysis of Binary Search(Recursive)
Time Complexity: O(log n)
Auxiliary Space: O(log n), where n is the number of elements in the array.
Binary Seach Program in C (Iterative)
C
#include <stdio.h>
int binarySearch(int arr[], int l, int r, int x)
{
while (l <= r) {
int m = l + (r - l) / 2;
if (arr[m] == x) {
return m;
}
if (arr[m] < x) {
l = m + 1;
}
else {
r = m - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
int main(void)
{
int arr[] = { 2, 3, 4, 10, 40 };
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
int x = 24;
int result = binarySearch(arr, 0, size - 1, x);
if (result == -1) {
printf("Element is not present in array");
}
else {
printf("Element is present at index %d", result);
}
return 0;
}
|
OutputElement is not present in array
Complexity Analysis of Binary Search (Iterative)
Time Complexity: O(log n), where n is the number of elements in the array.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Please refer complete article on Binary Search for more details!
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...