Bucket Sort – Data Structures and Algorithms Tutorials
Last Updated :
27 Mar, 2024
Bucket sort is a sorting technique that involves dividing elements into various groups, or buckets. These buckets are formed by uniformly distributing the elements. Once the elements are divided into buckets, they can be sorted using any other sorting algorithm. Finally, the sorted elements are gathered together in an ordered fashion.
Bucket Sort Algorithm:
Create n empty buckets (Or lists) and do the following for every array element arr[i].
- Insert arr[i] into bucket[n*array[i]]
- Sort individual buckets using insertion sort.
- Concatenate all sorted buckets.
How does Bucket Sort work?
To apply bucket sort on the input array [0.78, 0.17, 0.39, 0.26, 0.72, 0.94, 0.21, 0.12, 0.23, 0.68], we follow these steps:
Step 1: Create an array of size 10, where each slot represents a bucket.
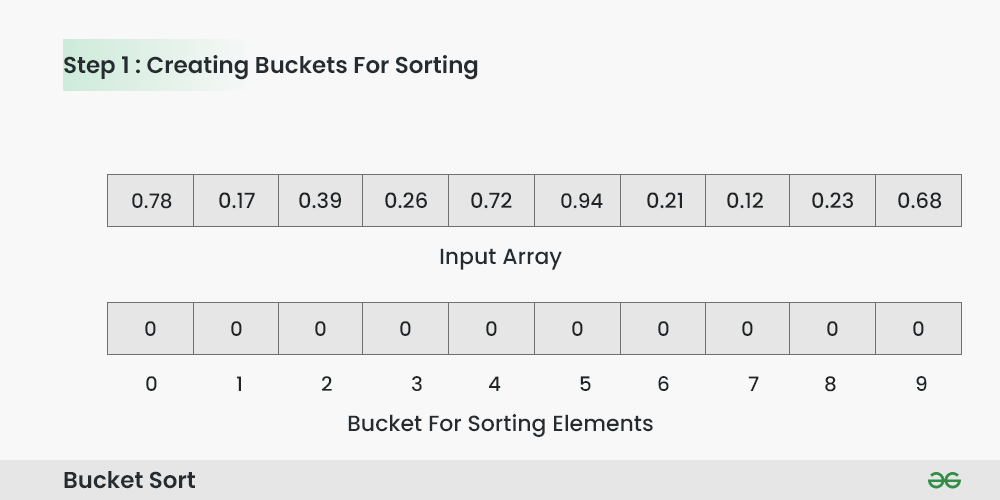
Creating Buckets for sorting
Step 2: Insert elements into the buckets from the input array based on their range.
Inserting elements into the buckets:
- Take each element from the input array.
- Multiply the element by the size of the bucket array (10 in this case). For example, for element 0.23, we get 0.23 * 10 = 2.3.
- Convert the result to an integer, which gives us the bucket index. In this case, 2.3 is converted to the integer 2.
- Insert the element into the bucket corresponding to the calculated index.
- Repeat these steps for all elements in the input array.
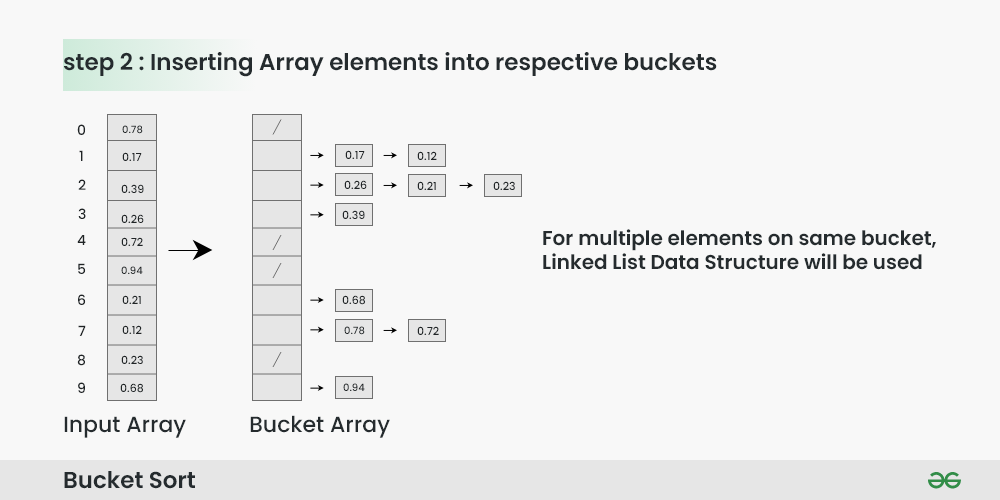
Inserting Array elements into respective buckets
Step 3: Sort the elements within each bucket. In this example, we use quicksort (or any stable sorting algorithm) to sort the elements within each bucket.
Sorting the elements within each bucket:
- Apply a stable sorting algorithm (e.g., Bubble Sort, Merge Sort) to sort the elements within each bucket.
- The elements within each bucket are now sorted.
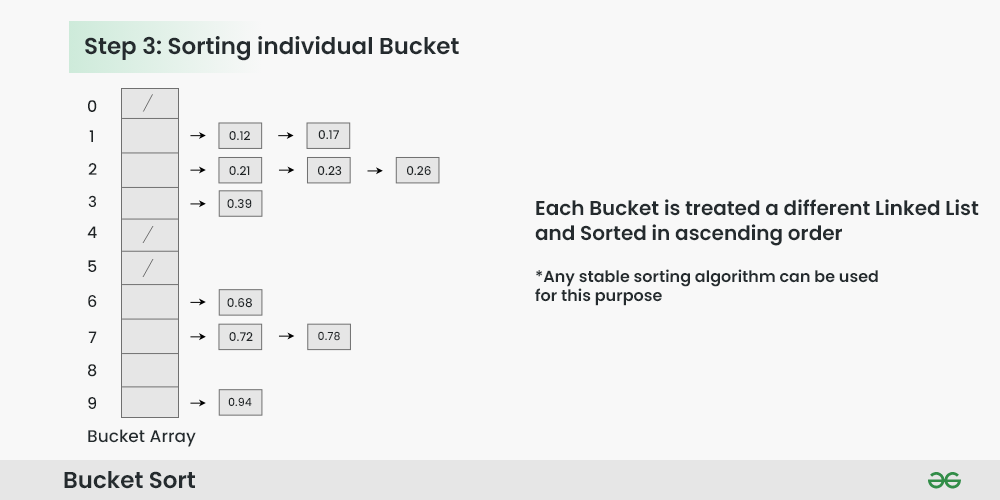
Sorting individual bucket
Step 4: Gather the elements from each bucket and put them back into the original array.
Gathering elements from each bucket:
- Iterate through each bucket in order.
- Insert each individual element from the bucket into the original array.
- Once an element is copied, it is removed from the bucket.
- Repeat this process for all buckets until all elements have been gathered.
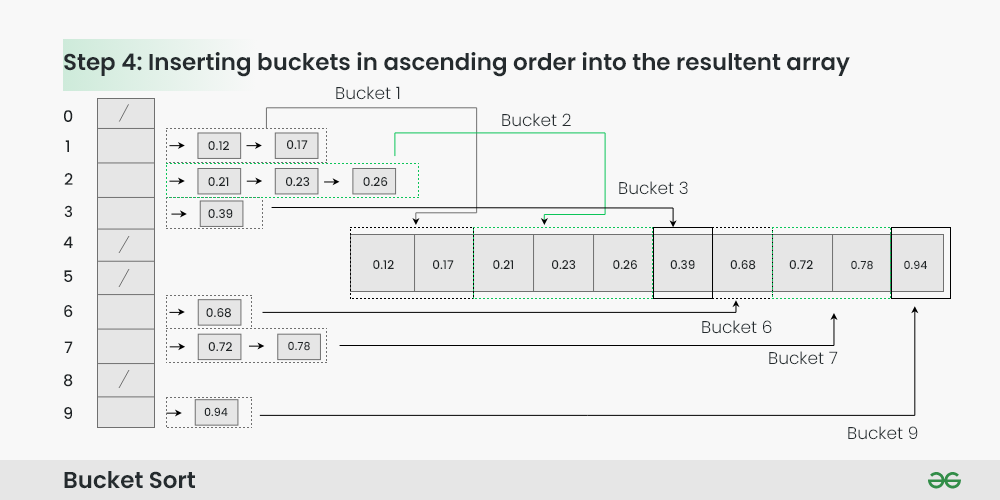
Inserting buckets in ascending order into the resultant array
Step 5: The original array now contains the sorted elements.
The final sorted array using bucket sort for the given input is [0.12, 0.17, 0.21, 0.23, 0.26, 0.39, 0.68, 0.72, 0.78, 0.94].
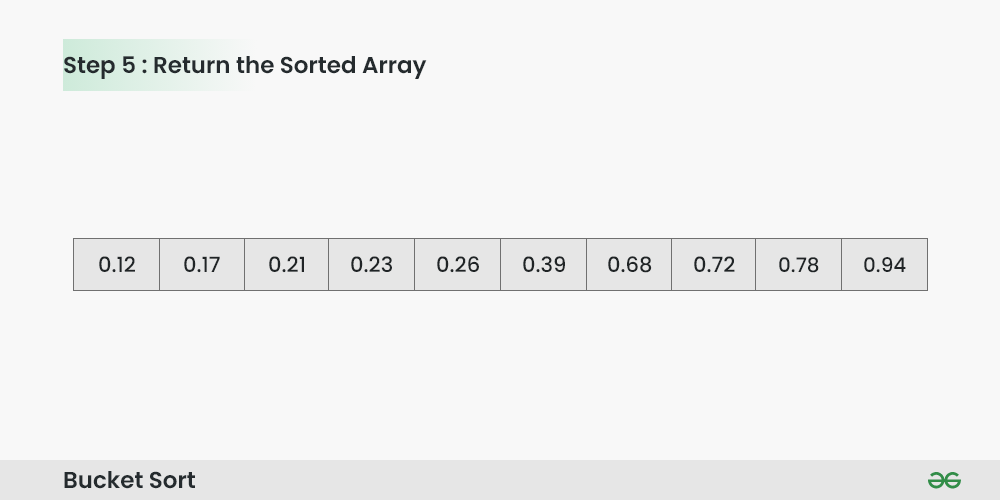
Return the Sorted Array
Implementation of Bucket Sort Algorithm:
Below is the implementation for the Bucket Sort:
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// Insertion sort function to sort individual buckets
void insertionSort(vector<float>& bucket) {
for (int i = 1; i < bucket.size(); ++i) {
float key = bucket[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && bucket[j] > key) {
bucket[j + 1] = bucket[j];
j--;
}
bucket[j + 1] = key;
}
}
// Function to sort arr[] of size n using bucket sort
void bucketSort(float arr[], int n) {
// 1) Create n empty buckets
vector<float> b[n];
// 2) Put array elements in different buckets
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int bi = n * arr[i];
b[bi].push_back(arr[i]);
}
// 3) Sort individual buckets using insertion sort
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
insertionSort(b[i]);
}
// 4) Concatenate all buckets into arr[]
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < b[i].size(); j++) {
arr[index++] = b[i][j];
}
}
}
// Driver program to test above function
int main() {
float arr[] = {0.897, 0.565, 0.656, 0.1234, 0.665, 0.3434};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
bucketSort(arr, n);
cout << "Sorted array is \n";
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
// Insertion sort function to sort individual buckets
public static void insertionSort(List<Float> bucket) {
for (int i = 1; i < bucket.size(); ++i) {
float key = bucket.get(i);
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && bucket.get(j) > key) {
bucket.set(j + 1, bucket.get(j));
j--;
}
bucket.set(j + 1, key);
}
}
// Function to sort arr[] of size n using bucket sort
public static void bucketSort(float[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
// 1) Create n empty buckets
List<Float>[] buckets = new ArrayList[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
buckets[i] = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 2) Put array elements in different buckets
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int bi = (int) (n * arr[i]);
buckets[bi].add(arr[i]);
}
// 3) Sort individual buckets using insertion sort
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
insertionSort(buckets[i]);
}
// 4) Concatenate all buckets into arr[]
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < buckets[i].size(); j++) {
arr[index++] = buckets[i].get(j);
}
}
}
// Driver program to test above function
public static void main(String[] args) {
float[] arr = {0.897f, 0.565f, 0.656f, 0.1234f, 0.665f, 0.3434f};
bucketSort(arr);
System.out.println("Sorted array is:");
for (float num : arr) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
}
}
def insertion_sort(bucket):
for i in range(1, len(bucket)):
key = bucket[i]
j = i - 1
while j >= 0 and bucket[j] > key:
bucket[j + 1] = bucket[j]
j -= 1
bucket[j + 1] = key
def bucket_sort(arr):
n = len(arr)
buckets = [[] for _ in range(n)]
# Put array elements in different buckets
for num in arr:
bi = int(n * num)
buckets[bi].append(num)
# Sort individual buckets using insertion sort
for bucket in buckets:
insertion_sort(bucket)
# Concatenate all buckets into arr[]
index = 0
for bucket in buckets:
for num in bucket:
arr[index] = num
index += 1
arr = [0.897, 0.565, 0.656, 0.1234, 0.665, 0.3434]
bucket_sort(arr)
print("Sorted array is:")
print(" ".join(map(str, arr)))
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class Program
{
// Insertion sort function to sort individual buckets
static void InsertionSort(List<float> bucket)
{
for (int i = 1; i < bucket.Count; ++i)
{
float key = bucket[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && bucket[j] > key)
{
bucket[j + 1] = bucket[j];
j--;
}
bucket[j + 1] = key;
}
}
// Function to sort arr[] of size n using bucket sort
static void BucketSort(float[] arr)
{
int n = arr.Length;
// 1) Create n empty buckets
List<float>[] buckets = new List<float>[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
buckets[i] = new List<float>();
}
// 2) Put array elements in different buckets
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int bi = (int)(n * arr[i]);
buckets[bi].Add(arr[i]);
}
// 3) Sort individual buckets using insertion sort
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
InsertionSort(buckets[i]);
}
// 4) Concatenate all buckets into arr[]
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < buckets[i].Count; j++)
{
arr[index++] = buckets[i][j];
}
}
}
// Driver program to test above function
static void Main(string[] args)
{
float[] arr = { 0.897f, 0.565f, 0.656f, 0.1234f, 0.665f, 0.3434f };
BucketSort(arr);
Console.WriteLine("Sorted array is:");
foreach (float num in arr)
{
Console.Write(num + " ");
}
}
}
function insertionSort(bucket) {
for (let i = 1; i < bucket.length; ++i) {
let key = bucket[i];
let j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && bucket[j] > key) {
bucket[j + 1] = bucket[j];
j--;
}
bucket[j + 1] = key;
}
}
function bucketSort(arr) {
let n = arr.length;
let buckets = Array.from({length: n}, () => []);
// Put array elements in different buckets
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
let bi = Math.floor(n * arr[i]);
buckets[bi].push(arr[i]);
}
// Sort individual buckets using insertion sort
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
insertionSort(buckets[i]);
}
// Concatenate all buckets into arr[]
let index = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < buckets[i].length; j++) {
arr[index++] = buckets[i][j];
}
}
}
let arr = [0.897, 0.565, 0.656, 0.1234, 0.665, 0.3434];
bucketSort(arr);
console.log("Sorted array is:");
console.log(arr.join(" "));
OutputSorted array is
0.1234 0.3434 0.565 0.656 0.665 0.897
Complexity Analysis of Bucket Sort Algorithm:
Time Complexity: O(n2),
- If we assume that insertion in a bucket takes O(1) time then steps 1 and 2 of the above algorithm clearly take O(n) time.
- The O(1) is easily possible if we use a linked list to represent a bucket.
- Step 4 also takes O(n) time as there will be n items in all buckets.
- The main step to analyze is step 3. This step also takes O(n) time on average if all numbers are uniformly distributed.
Auxiliary Space: O(n+k)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...