Boundary Extraction of image using MATLAB
Last Updated :
14 Mar, 2022
The boundary of the image is different from the edges in the image. Edges represent the abrupt change in pixel intensity values while the boundary of the image is the contour. As the name boundary suggests that something whose ownership changes, in the image when pixel ownership changes from one surface to another, the boundary comes into the picture. Edge is basically the boundary line but the boundary is the line or location dividing the two surfaces.
Types of boundary extraction techniques
There are two types of boundaries in binary images.
- Inner boundary: It is the difference between the original image and the eroded image. The eroded image is the shrunk image when erosion is applied to the original image. On taking the difference between the original image and the eroded version, we get the inner boundary of the image. The inner boundary is the part of the main surface separating the other surface. Erosion shrinks the white portion thus the boundary is the part of the white surface itself.
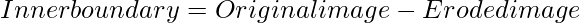
- Outer boundary: It is the difference between dilated image and an original image. The dilated image is the expanded image when dilation is applied to the original image. Dilation increases the white portion of the image. On taking the difference between dilated and original versions of the image we get the boundary which is the lost art of the black surface of the original image.
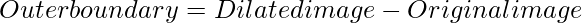
What are imerode() and imdilate()?
Erosion and Dilation both are morphological operations.
- imerode(): imerode( ) is the Matlab in-built function for erosion. imerode(I,SE) erodes the grayscale, binary, or packed binary image.
Syntax:
J = imerode(I,SE)
- imdilate( ): imdilate( ) is the MatLab in-built function for dilation.It dilates the grayscale, binary, or packed binary image I using the structuring element SE.
Syntax:
J = imdilate(I,SE)
Example 1:
Matlab
k=imread("1.png");
k=rgb2gray(k);
SE=strel('disk',2,0);
k1=imerode(k,SE);
k2= k-k1;
imtool(k);
imtool(k2);
|
Output:

Figure: Original image and Inner boundary image

figure: Original image

figure: Inner boundary image
Code Explanation:
- First of all, the image is read by imread( ) inbuilt function.
- Image is the colored logo of GFG, we convert it into grayscale.
- The structuring element is created for morphological operations.
- Image is eroded using imerode() inbuilt function.
- The eroded image is subtracted from the original image.
- Both images are displayed.
Example 2:
Matlab
k=imread("1.png");
k=rgb2gray(k);
SE=strel('disk',2,0);
k1=imdilate(k,SE);
k2= k1-k;
imtool(k);
imtool(k2);
|
Output:

figure: Original image and Outer boundary image

figure: Original image

figure: Outer boundary image
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...