Class 11 Notes Body Fluids and Circulation: Body liquids are the mode of transport of supplements, oxygen, and other significant substances in the body. They supply the cells with oxygen and nutrients and remove waste products, which are then excreted in the urine. As body temperature rises, blood flow to the skin increases, allowing heat from sweat to dissipate, thus maintaining a constant body temperature. There are several types of body fluids, including blood, lymph, cerebrospinal fluid, interstitial fluid, and various secretions. The most prominent among them is blood, which carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and immune cells to different tissues and organs. Blood also transports waste products, such as carbon dioxide and metabolic byproducts, to the appropriate organs for elimination.
Mainly, our body has two types of fluids-
- Intracellular Fluid– The fluid which is present inside the cell.
- Extracellular Fluid– The fluid which is present outside the cell is known as extracellular fluid. Example ( blood, lymph, etc)
The circulatory system comprises two main components: the cardiovascular system and the lymphatic system. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. The heart pumps oxygenated blood from the lungs to the rest of the body and returns deoxygenated blood back to the lungs for oxygenation. Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, while veins transport deoxygenated blood toward the heart.
Blood
Blood is a fluid connective tissue composed of a fluid network, plasma, and blood cells. It makes up about 30-35% of the extracellular fluid. It is a slightly antacid liquid with a pH of 7.4. The main components of blood are: the elements form (erythrocytes, leukocytes, thrombocytes) and plasma (water, proteins, minerals) Plasma is a straw-colored viscous fluid that makes up 55% of blood volume. It contains 90-92% water, 6-8% proteins (fibrinogen, albumins, and globulins), glucose, amino acids, and a limited amount of minerals like Na+, Ca2+, Cl– etc. Erythrocytes, leukocytes, and blood platelets form elements.
Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
Erythrocytes are the most abundant cells in the human body. The total number of red blood cells is between 5 and 5.5 million
- Red platelets are round with a flattish, indented focus, similar to doughnuts without an opening. Your medical care supplier can keep an eye on the size, shape, and soundness of your red platelets utilizing a blood test.
- Hemoglobin is the protein inside red platelets. It conveys oxygen. Red platelets likewise eliminate carbon dioxide from your body, carrying it to the lungs for you to breathe out.
- Red platelets are made in the bone marrow. They commonly live for around 120 days, and afterward, they bite the dust.
WBC (White Blood Cells)
Leukocytes or white blood cells. There are 6000-8000 WBC in each ml. There are two types of leukocytes: granulocytes and agranulocytes. Both are classified according to the presence or absence of granules in the white blood cells.
Granulocytes
Granulocytes are the most well-known type of white blood platelets. They contain chemical granules. The moment the contamination or aggravation enters the body, granulocytes rush to the area and release their granules to fight the disease. Granulocytes are sometimes referred to as granular leukocytes, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, or PMNs.
There are three specific types of granulocytes. They are neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils.
- Neutrophils: Neutrophils are the most common type of granulocyte and attack microscopic organisms. Each neutrophil can swallow up to 20 microorganisms during its lifetime.
- Eosinophils: These granulocytes are surprisingly sensitive in virtually every safe reaction. In any case, they also deter pests.
- Basophils: These granulocytes mainly fight unwanted reactions. They release the receptor (which carries the allergen out of the body) and the thinning blood heparin (which prevents it from thickening).
Function of Granulocytes
Granulocytes cooperate to free your collection of contamination or allergens. Each sort of granulocyte has its own mix of synthetics and proteins in its granules. Therefore, each type has an alternate capacity
Agranulocytes
Those that don’t have granules inside them are known as Agranulocyte. Monocytes and neutrophils are phagocytic cells, that destroy foreign organisms.
- Monocytes:Monocytes are one sort of agranulocyte. They are created in the bone marrow from monoblasts. Monoblasts are created from hematopoietic undifferentiated cells.
- Lymphocyte: Lymphocytes are one more sort of agranulocyte. They are additionally associated with battling specific diseases and destructive cells from the body. There are two sorts of lymphocytes in the body: T cells and B cells.
Functions of Agranulocytes
The capacity of agranulocytes is like that of granulocytes in that they intercede immunological reactions to unfamiliar microbes, harmful and cancer cells, and eliminate dead cells from the body. They do this by delivering antibodies and straightforwardly appending them to cells, as opposed to delivering granules.
Also Read: Difference between Granulocytes and Agranulocytes
Blood Platelets
Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, are small, colorless, disc-shaped cell fragments that circulate in the blood. They play a crucial role in hemostasis, the process of stopping bleeding and forming blood clots to repair damaged blood vessels.
Blood Groups
The most well-known blood group system is the ABO system, which categorizes blood into four main types: A, B, AB, and O.
- Blood Type A: People with blood type A have A antigens on the surface of their red blood cells and produce antibodies against type B antigens in their plasma. They can receive blood from individuals with blood types A and O (with A being preferable) and can donate blood to individuals with blood types A and AB.
- Blood Type B: Individuals with blood type B have B antigens on the surface of their red blood cells and produce antibodies against type A antigens in their plasma. They can receive blood from individuals with blood types B and O (with B being preferable) and can donate blood to individuals with blood types B and AB.
- Blood Type AB: People with blood type AB have both A and B antigens on the surface of their red blood cells but do not produce antibodies against either A or B antigens in their plasma. They can receive blood from individuals with all blood types (A, B, AB, and O), making them universal recipients. However, they can only donate blood to individuals with blood type AB.
- Blood Type O: Individuals with blood type O have neither A nor B antigens on the surface of their red blood cells but produce antibodies against both A and B antigens in their plasma. They are considered universal donors because their blood can be given to individuals with any blood type (A, B, AB, and O). However, people with blood type O can only receive blood from individuals with blood type O.
Rh System
Another important blood group system is the Rh system, which classifies blood into Rh-positive (+) or Rh-negative (-) based on the presence or absence of the Rh antigen on RBCs. Rh-positive individuals have the Rh antigen, while Rh-negative individuals lack it. Rh-positive blood can be given to Rh-positive and Rh-negative individuals, but Rh-negative blood should only be given to Rh-negative individuals.
Coagulation of Blood
It is a remarkable defense mechanism that prevents excessive bleeding when blood vessels are damaged. Understanding the intricacies of blood coagulation is essential for grasping the body’s remarkable ability to control and heal wounds effectively.
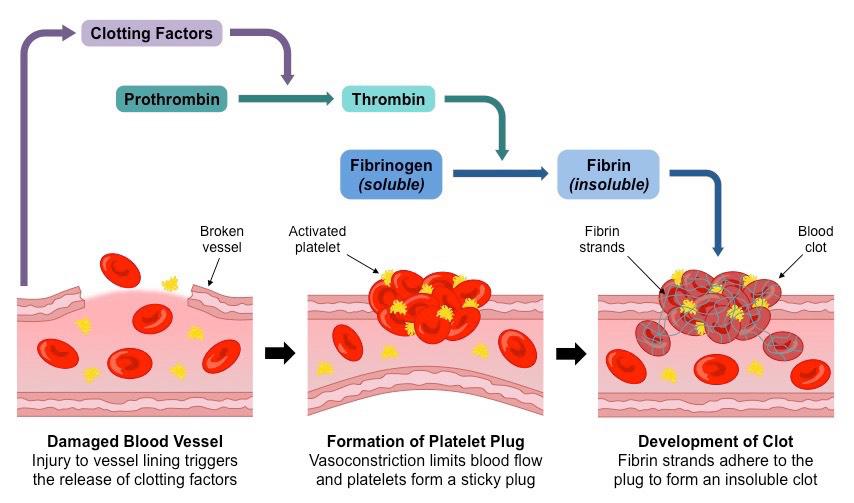
Events During Blood Clotting (Blood Coagulation)
How Does Fluid Move Around the Body?
Water travels through semi-permeable layers of cells and starts with one compartment of the body and then onto the next by a cycle called assimilation. Assimilation is fundamentally the dissemination of water from districts of higher fixation to locales of lower focus, along an osmotic inclination across a semipermeable membrane.
Lymph
Lymph is a clear-to-white fluid that circulates throughout the lymphatic system, a network of vessels, nodes, and organs that complements the circulatory system. Lymph plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance, immune function, and the transportation of nutrients and waste products within the body.
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic framework is a broad organization of vessels, hubs, and pipes that pass through practically all substantial tissues. It permits the flow of a liquid called lymph through the body, likewise as blood. They help in absorbing the food from the intestine, maintain the fluid levels, and provide immunity.
Human Circulatory System
Heart
The heart is roughly the size of a clenched fist and is divided into four chambers: two atria (the left atrium and right atrium) and two ventricles (the left ventricle and right ventricle). The atria receive blood returning to the heart, while the ventricles pump blood out of the heart.
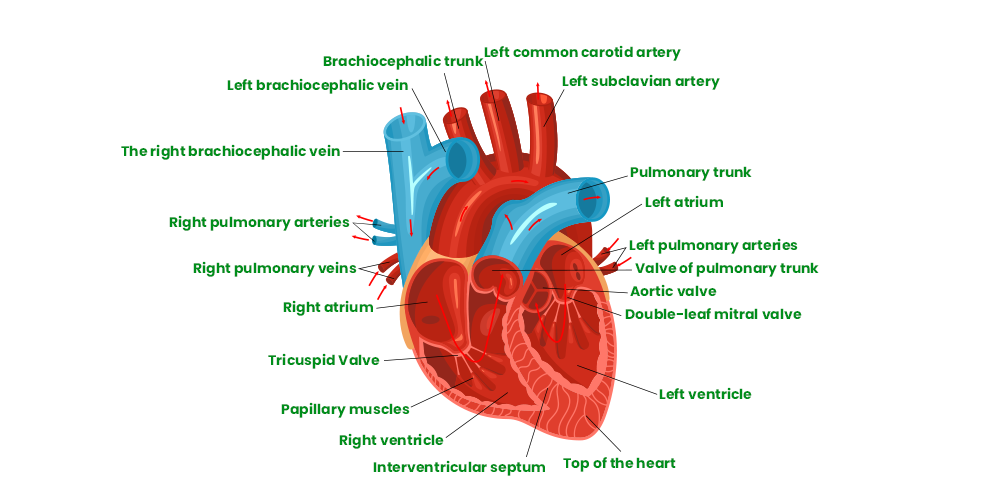
Structure of Human Heart
Function of Heart
The heart’s primary function is to circulate blood throughout the body. It acts as a pump, contracting rhythmically to propel blood into the blood vessels. The right side of the heart receives deoxygenated blood from the body and pumps it to the lungs for oxygenation, while the left side receives oxygenated blood from the lungs and pumps it to the rest of the body.
Heart Valves
To maintain proper blood flow, the heart has four valves that ensure unidirectional blood flow through the chambers. The valves are the tricuspid valve (between the right atrium and right ventricle), the pulmonary valve (between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery), the mitral valve (between the left atrium and left ventricle), and the aortic valve (between the left ventricle and aorta). These valves open and close in response to pressure changes, preventing backflow of blood.
Electrical Conduction
The heart has its own electrical conduction system that coordinates its contractions. The sinoatrial (SA) node, located in the right atrium, initiates the electrical impulses that regulate the heartbeat. The impulses then travel through the atria, causing them to contract. The impulses then pass through the atrioventricular (AV) node, located between the atria and ventricles, and continue down the specialized pathways called the bundle of His and Purkinje fibers, stimulating the ventricles to contract.
Double Circulation
Double circulation is a specialized cardiovascular system found in mammals and birds, including humans, that involves the circulation of blood through two separate circuits. This unique system allows for the efficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues while maintaining a high level of oxygenation in the blood.
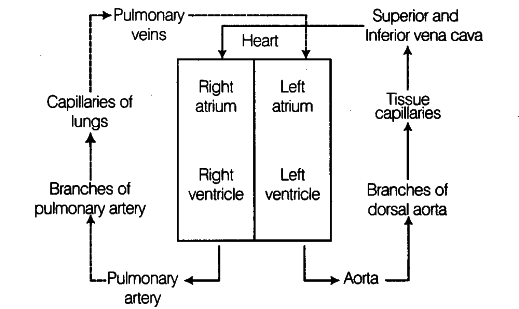
Blood Flow
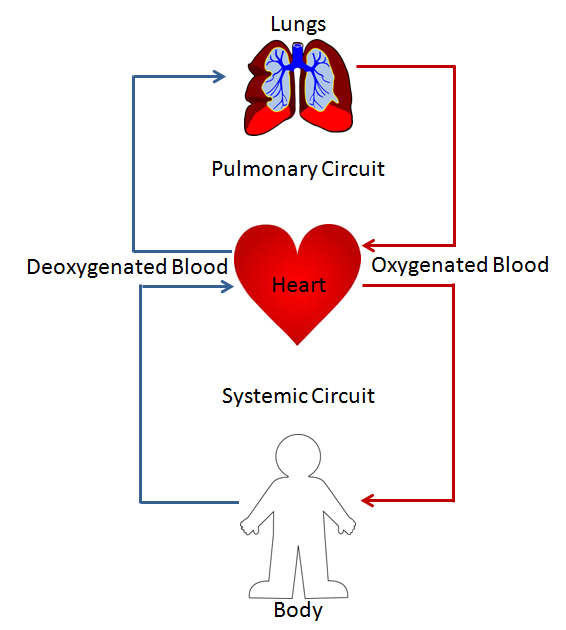
Systemic and Pulmonary Circulation
Cardiac Cycle and ECG
The cardiac cycle refers to the sequence of events that occur during one complete heartbeat. It includes diastole (relaxation phase) and systole (contraction phase) of both the atria and ventricles. During diastole, the heart chambers fill with blood, and during systole, the chambers contract, pumping blood out of the heart.
ECG stands for electrocardiogram. It is a non-invasive medical test that records the electrical activity of the heart. The test involves placing electrodes on the skin of the chest, arms, and legs, which detect and measure the electrical signals generated by the heart.
Regulation of Cardiac Activity
The regulation of cardiac activity is a complex process that ensures the heart functions efficiently, adapting to the body’s needs. This intricate system involves a combination of intrinsic mechanisms within the heart itself and extrinsic influences from the nervous and endocrine systems.
Cardiac Disorders
Cardiovascular infections are conditions that influence the capacity of your heart, for example,
- Unusual heart rhythms
- Aorta sickness
- Innate coronary illness
- Coronary conduit sickness
- Cardiovascular breakdown
- Heart muscle sickness (cardiomyopathy)
- Heart valve sickness
- Heart failure
FAQs on Body Fluids and Circulation
Q1: Which Cell is Known as Policemen of Blood?
Answer:
Monocytes are the macro policeman of blood and phagocytic in nature.
Q2: Where are the RBCs Formed in the Human Body?
Answer:
The bone marrow produces RBCs.
Q3: Which Respiratory Pigment is found in the RBCs?
Answer:
Haemoglobin is found in the RBCs.
Q4: What is the Lifespan of RBCs?
Answer:
RBCs live for around 120 days.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...