Blockchain Key Areas
Last Updated :
06 Aug, 2021
Blockchain is the backbone of technology Digital CryptoCurrency BitCoin. The blockchain is a distributed database of records of all transactions or digital events that have been executed and shared among participating parties. Each transaction is verified by the majority of participants of the system. It contains every single record of each transaction.
Technology such as blockchain or decentralized ledgers is a popular means of eliminating third-party requirements to validate transactions over peer-to-peer networks.
Each block in the blockchain consists of two parts:
- Header- A header contains the block number, previous block’s hash value to maintain chain integrity, the hash of the current block’s body to maintain the integrity of transaction data, combined with a timestamp, nonce, Blockchain address of the creator of the block, as well as other requested information.
- Body- There are one or more transactions in the body of the block.
The most well-known blockchain technology is bitcoin. Blockchain’s role in enabling Bitcoin determines the direction of the development. There are many areas for learning and expanding its application.
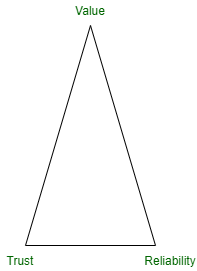
There are three things the Internet was not designed to do, and blockchain technology fixes them. Furthermore, these three things are:
- Value- Digital assets can be worth something with blockchain. Owners can control the value of a property. By using this technology, over the internet one can transfer unique assets without the need for an intermediary.
- Trust- Every business must trust its employees to contribute and hold each other accountable, while even in terms of internal workings, a business must believe in its ability to earn the trust of its customers and employees. Assigning ownership of a digital asset over a blockchain is a highly secure process and allows you to look at who holds control over that asset at any given time. Essentially, blockchain creates a permanent, secure, and unalterable record of what is owed. The integrity of the information is maintained by using advanced hash cryptography.
- Reliability- Thousands of computers worldwide share their workload on the blockchain. Localizing everything in one location provides reliability since there is only one point of failure if everything is located in one place. The decentralized architecture ensures that one point of failure cannot bring the entire system to a halt, but centralized infrastructure ensures that the entire system remains up and running.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...