Cow dung and agricultural waste have been used as fuel to cook food in many villages since ancient times. However, it is not an effective source of energy to use as a fuel since its efficiency is extremely poor, which means that the energy generated by them is extremely low and generates a lot of smoke while burning. This smoke is hazardous to both the environment and the person preparing the meal. It is known that a large volume of farm waste and cow manure is produced in an area. So, is there a method to turn them into a form that we can use as a source of energy? The answer is Yes, we can convert it to biogas by establishing a biogas plant.
What is Biomass?
The dead elements of plants and trees, as well as animal feces, are referred to as biomass. Biomass is organic matter that is used as a fuel to generate energy. Wood, agricultural waste (crop leftovers), and cow dung are all examples of biomass.
Another way that solar energy presents itself is through biomass. This is because all the plants and trees that generate biomass, such as wood, grew using the sun’s energy.
Even animal wastes (such as cow manure) are produced by cattle that developed by ingesting plant food produced with the aid of sunshine energy. Because biomass fuels such as wood, agricultural waste, and cow dung are all plant and animal products, they are referred to as such (or biofuels).
Biomass is a renewable energy source since it is derived from plants (or animals) that can be reproduced indefinitely.
Different Ways of Extracting Energy from Biomass:
The various methods of biomass extraction can be broadly be classified as:
Solid fuel combustion: The simplest way of extracting energy from biomass can be done directly by the combustion of solid matter. Many of the developing countries especially in rural areas obtain most of their energy needs by burning wood, animal dung, and other biomass. But burning can be inefficient.
Gasification: Gasification can be defined as a process that exposes a solid fuel to high temperatures and limited oxygen, in order to produce a gaseous fuel. Gasification is the mixture of gases like carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen, and methane. Gasification has many advantages over burning solid fuel. One of the resultant gases, like methane, can be treated similarly as natural gas and used for the same purposes.
Paralysis: Paralysis is an old technology that involves heating the biomass to drive off the volatile matter, leaving behind the black residue known as charcoal. It has double the energy density of its original material. The charcoal will be half the weight of the original biomass, which contains the same amount of energy that makes the fuel more transportable. The charcoal also burns at a higher temperature than the original biomass, making it more useful for the manufacturing processes.
Digestion: Biomass digestion works under the action of anaerobic bacteria, these microorganisms live at the bottom of swamps or sometimes in other places where there is no air, consuming dead organic matter to produce among other things like methane and hydrogen. We can put these bacteria to work for us, by feeding the organic matter such as human sewage or animal dung into tanks called digesters and adding these bacteria, we can collect the emitted gas that can be used as an energy source.
Fermentation: Compared to the above, fermentation isn’t a new idea. Producing the fuel from biomass by the process of fermentation is just an extension of this old process. And a wide range of plants or its material can now be used, from sugar cane to wood fiber. For example, the waste from the wheat mill has been used to produce ethanol by fermentation then it is mixed with diesel to produce ‘dishelm’.
Anaerobic Digestion: Anaerobic Digestion can be defined as a biochemical degradation process that converts the complex organic material, such as animal manure, into methane and other byproducts. The anaerobic digester device promotes the decomposition of manure into simple organics and gaseous biogas products. The biogas can be formed by the activity of anaerobic bacteria. And microbial growth, as well as biogas production, are very slow at ambient temperatures. The biogas comprises about 60% methane, 40% carbon dioxide, and 0.2 to 0.4% of hydrogen sulfide.
Biogas Plant
The biogas plant is a dome-shaped building. Organic material, such as waste food waste, lipids, sludge, cow dung, and so on, is combined with water and fed into the digester via the entrance depicted in the image. The digester is a sealed room where organic matter is decomposed anaerobically.
After a few days, the organic matter decomposes entirely, releasing gases such as methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and hydrogen sulfide. These gases are then pulled through pipes from the storage tank above the digester and sent to surrounding centers for usage via decentralization pathways.
Construction of a Biogas Plant:
The biogas plant is a brick and cement structure having the following parts:
- Digester: The digester is a closed chamber that has no oxygen and hence inside the chamber the digester anaerobic oxidation takes place.
- Gas Tank: After anaerobic oxidation in the digester the gases are released into the gas tank.
- Mixing Tank: Cow dung and farm waste are mixed by adding some water to the mixing tank.
Working of a Biogas Plant:
To extract biogases and manure from the biogas plant following steps takes place as discussed below using multiple figures:
Step 1:
To make a biogas plant firstly, a hole is drilled into the soil and such a type of arrangement will be formed.
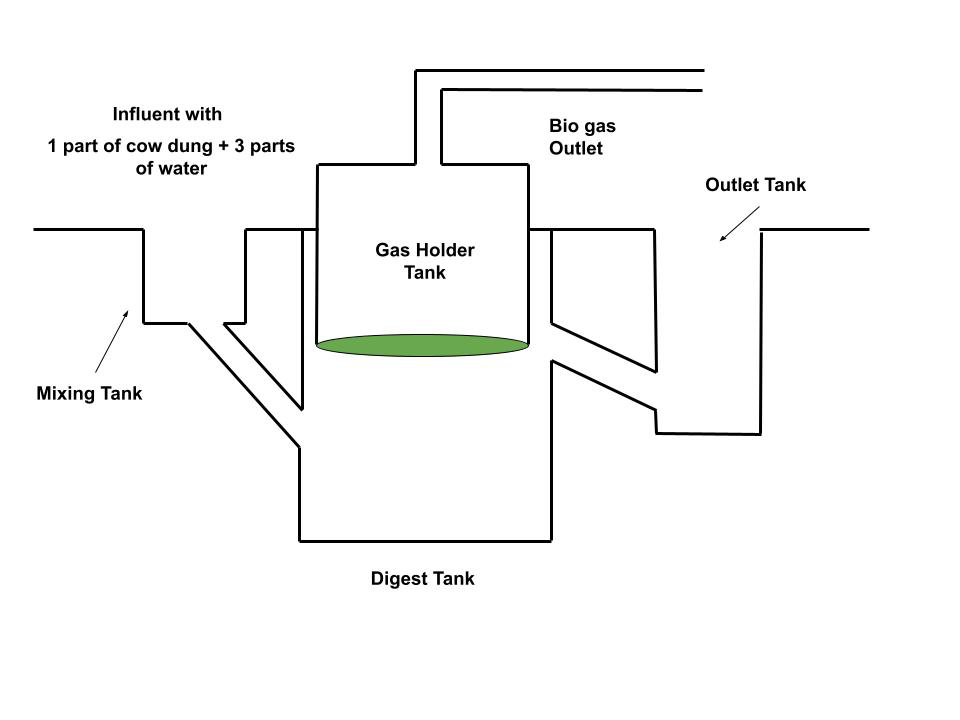
Step 2:
Now some part of cow dung and farm waste is taken and three parts of water mixed to this part. They are mixed very well in the mixing tank and the slurry of the mixture fed into the mouth of the digester.
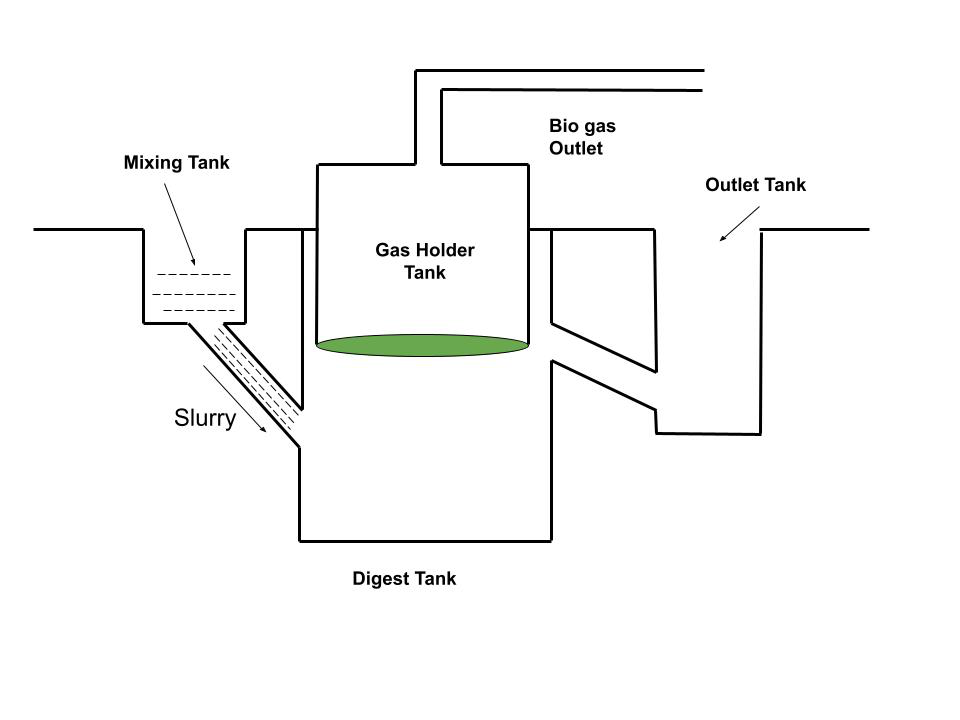
Step 3:
When the mixture of cow dung and water is known as slurry moves into the digester, the microorganisms get an environment of non-oxygen so they start decomposing the organic matter into simpler substances.
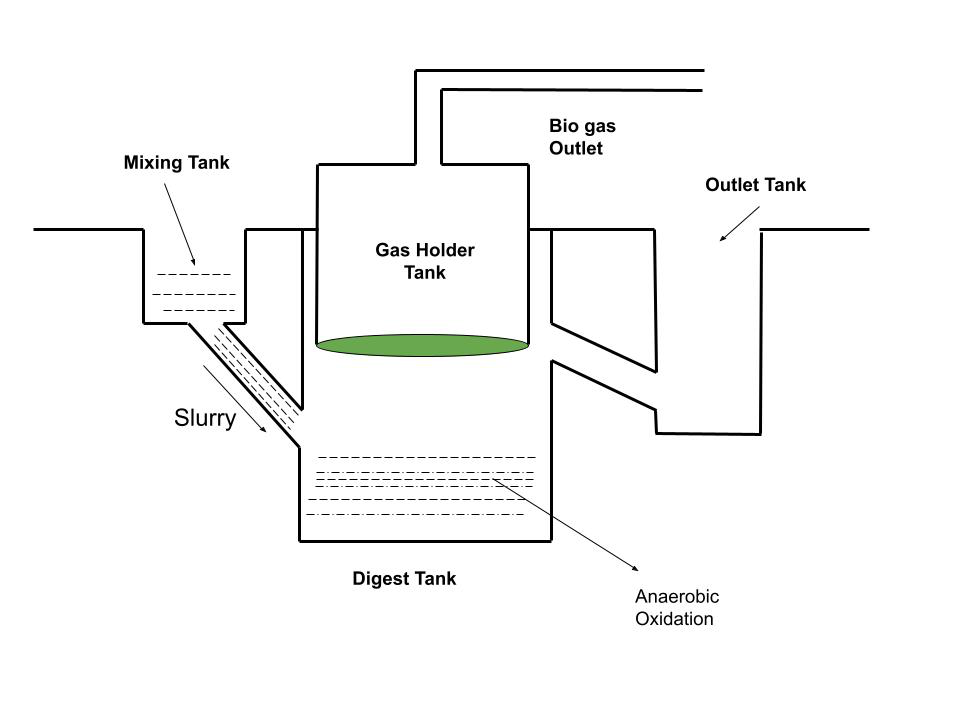
Step 4:
The decomposition process takes some days of time. After decomposition gases like methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen, and hydrogen sulfide on a whole called Bio-gas are sent to the gas tank.
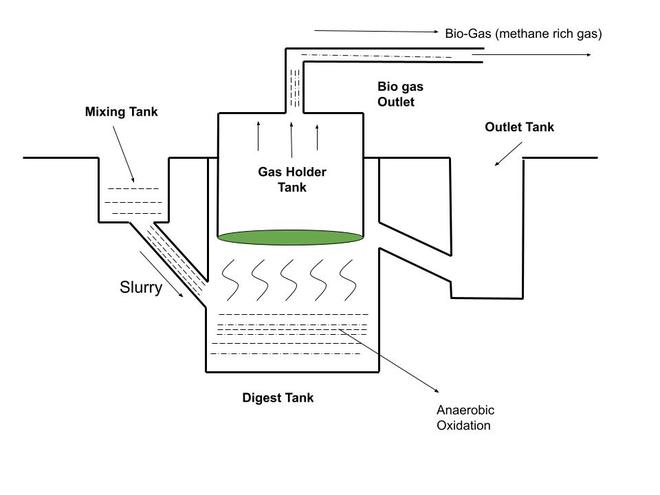
Step 5:
Biogas is highly rich in methane constituting around 75 % of biogas. As this process continues after some days the slurry which gets left out after the decomposition is very rich in nitrogen and phosphorous.
Step 6:
This slurry is taken out then it is supplied to the farm as “manure”.
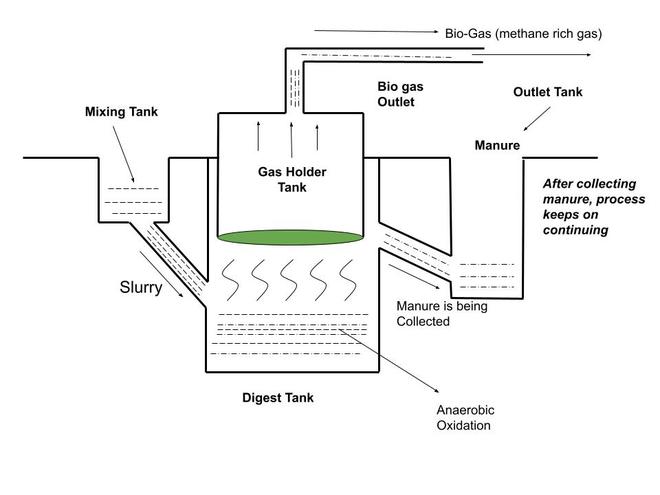
It can that by setting up a biogas plant and feeding the cow dung and farm-based to this plant we are getting a very good source of fuel i.ebiogas. Additionally, we also get the source of manure which is very rich in nitrogen and phosphorous.
Advantages of Biogas
- Since India has a very high rural population, the fuel will be easily available.
- This fuel burns without the smoke.
- The slurry residue is used as manure on the farm.
- It is Environment friendly.
- Excellent fuel quality with reasonable heating efficiency.
- Many countries like India subsidized the biogas plants too.
Disadvantages of Biogas
- The fuel has less heating capacity compares to other resources.
- As biogas consists of carbon dioxide, methane, hydrogen, and hydrogen sulfide, it can corrode the parts of the biogas plant.
- it can’t be constructed easily because cow dung is mostly available in villages only.
Sample Problems
Problem 1: Why charcoal is better than fuel and wood?
Solution:
There are several reasons where we can say charcoal is better than charcoal. They are:
- Charcoal has a very high calorific value than wood i.e the amount of heat produced by charcoal is much higher than wood.
- Charcoal doesn’t produce smoke, whereas wood and fuel produce smoke and cause pollution.
- Charcoal is much convenient to use than wood.
Problem 2: List two advantages and two disadvantages of using cow dung?
Solution:
Advantages
- Cow dung gives clean fuel which is called Biogas.
- Used dung can be used as manure for the farms.
Disadvantages
- Cow dung produces a lot of smokes which can lead to pollution.
- Cow dung contains important elements like nitrogen and phosphorous, which is getting wasted after burning them.
Problem 3: What are the ways to make biofuels?
Solution:
Ethanol and Biodiesel are two types of biofuels. By fermentation process ethanol is produced on Biomass and used in producing biological crops. Whereas Biodiesel is used in combination with gasoline for machines.
Problem 4: What are the inputs and outputs of the Biogas Plant?
Solution:
A biogas plant is used mainly to produce biogas which is a very pure form of gas. Now let’s look into the inputs and outputs of the biogas plant:
Inputs: Cow dung and farm waste.
Outputs: Biogas and manure.
Problem 5: List some uses of Biogas?
Solution:
The uses of Biogas are listed below:
- Biogas is comparatively very cheaper than other common fuels.
- There is no storage problem of gas because it is directly supplied from the plant through pipelines.
- In biogas, even the residue is very useful because it used as manure in farms
- It is used for lighting and for generating electricity.
- At last, biogas burns without smoke. Hence, it doesn’t cause any air pollution.
Problem 6: What are all the elements present in the produced biogas?
Solution:
After the process of anaerobic oxidation, the biogas is produced and taken through pipes. The biogas majorly consists of methane element constituting 75% and thereafter carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide with minimal contributions.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...