Basic Operations for Queue in Data Structure
Last Updated :
03 Jan, 2023
Basic Operations on Queue:
Some of the basic operations for Queue in Data Structure are:
- enqueue() – Insertion of elements to the queue.
- dequeue() – Removal of elements from the queue.
- peek() or front()- Acquires the data element available at the front node of the queue without deleting it.
- rear() – This operation returns the element at the rear end without removing it.
- isFull() – Validates if the queue is full.
- isEmpty() – Checks if the queue is empty.
- size(): This operation returns the size of the queue i.e. the total number of elements it contains.

Queue Data Structure
Operation 1: enqueue()
Inserts an element at the end of the queue i.e. at the rear end.
The following steps should be taken to enqueue (insert) data into a queue:
- Check if the queue is full.
- If the queue is full, return overflow error and exit.
- If the queue is not full, increment the rear pointer to point to the next empty space.
- Add the data element to the queue location, where the rear is pointing.
- return success.
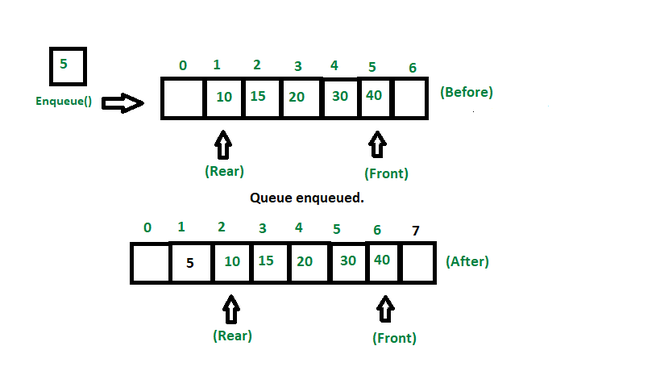
Enqueue representation
Below is the Implementation of the above approach:
C++
void queueEnqueue(int data)
{
if (capacity == rear) {
printf("\nQueue is full\n");
return;
}
else {
queue[rear] = data;
rear++;
}
return;
}
|
Java
void queueEnqueue(int data)
{
if (capacity == rear) {
System.out.println("\nQueue is full\n");
return;
}
else {
queue[rear] = data;
rear++;
}
return;
}
|
C
void enqueue(struct Queue* queue, int item)
{
if (isFull(queue))
return;
queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1) % queue->capacity;
queue->array[queue->rear] = item;
queue->size = queue->size + 1;
printf("%d enqueued to queue\n", item);
}
|
Python3
def EnQueue(self, item):
if self.isFull():
print("Full")
return
self.rear = (self.rear + 1) % (self.capacity)
self.Q[self.rear] = item
self.size = self.size + 1
print("% s enqueued to queue" % str(item))
|
C#
public void enqueue(int item)
{
if (rear == max - 1) {
Console.WriteLine("Queue Overflow");
return;
}
else {
ele[++rear] = item;
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
enqueue(element){
this.items.push(element);
}
</script>
|
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity: O(1)
Space Complexity: O(N)
Operation 2: dequeue()
This operation removes and returns an element that is at the front end of the queue.
The following steps are taken to perform the dequeue operation:
- Check if the queue is empty.
- If the queue is empty, return the underflow error and exit.
- If the queue is not empty, access the data where the front is pointing.
- Increment the front pointer to point to the next available data element.
- The Return success.
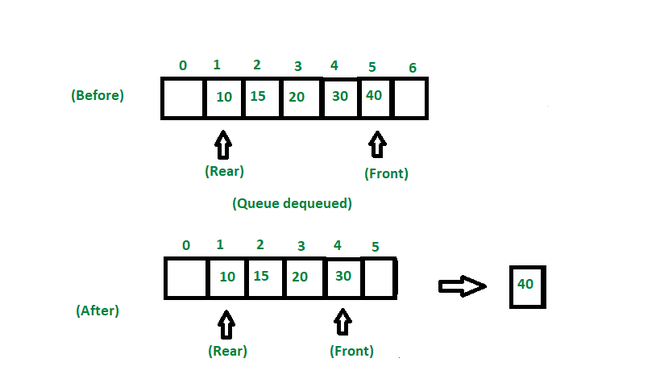
Dequeue operation
Below is the Implementation of above approach:
C++
void queueDequeue()
{
if (front == rear) {
printf("\nQueue is empty\n");
return;
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i < rear - 1; i++) {
queue[i] = queue[i + 1];
}
rear--;
}
return;
}
|
Java
void queueDequeue()
{
if (front == rear) {
System.out.println("\nQueue is empty\n");
return;
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i < rear - 1; i++) {
queue[i] = queue[i + 1];
}
rear--;
}
return;
}
|
C
int dequeue(struct Queue* queue)
{
if (isEmpty(queue)) {
printf("\nQueue is empty\n");
return;
}
int item = queue->array[queue->front];
queue->front = (queue->front + 1) % queue->capacity;
queue->size = queue->size - 1;
return item;
}
|
Python3
def DeQueue(self):
if self.isEmpty():
print("Queue is empty")
return
print("% s dequeued from queue" % str(self.Q[self.front]))
self.front = (self.front + 1) % (self.capacity)
self.size = self.size - 1
|
C#
public int dequeue()
{
if (front == rear + 1) {
Console.WriteLine("Queue is Empty");
return -1;
}
else {
int p = ele[front++];
return p;
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
dequeue(){
if(this.isEmpty()){
document.write("<br>Queue is empty<br>");
return -1;
}
return this.items.shift();
}
</script>
|
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity: O(1)
Space Complexity: O(N)
Operation 3: front()
This operation returns the element at the front end without removing it.
The following steps are taken to perform the front operation:
- If the queue is empty return the most minimum value.
- otherwise, return the front value.
Below is the Implementation of the above approach:
C++
int front(Queue* queue)
{
if (isempty(queue))
return INT_MIN;
return queue->arr[queue->front];
}
|
Java
int front(Queue queue)
{
if (isempty(queue))
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
return queue.arr[queue.front];
}
|
C
int front(struct Queue* queue)
{
if (isempty(queue))
return INT_MIN;
return queue->arr[queue->front];
}
|
Python3
def que_front(self):
if self.isempty():
return "Queue is empty"
return self.Q[self.front]
|
C#
public int front()
{
if (isempty())
return INT_MIN;
return arr[front];
}
|
Javascript
<script>
front(){
if(this.isEmpty())
return "No elements in Queue<br>";
return this.items[0];
}
<script>
|
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity: O(1)
Space Complexity: O(N)
Operation 4 : rear()
This operation returns the element at the rear end without removing it.
The following steps are taken to perform the rear operation:
- If the queue is empty return the most minimum value.
- otherwise, return the rear value.
Below is the Implementation of the above approach:
C++
int rear(Queue* queue)
{
if (isEmpty(queue))
return INT_MIN;
return queue->arr[queue->rear];
}
|
Java
int rear(Queue queue)
{
if (isEmpty(queue))
return Integer.MIN_VALUE;
return queue.arr[queue.rear];
}
|
C
int front(struct Queue* queue)
{
if (isempty(queue))
return INT_MIN;
return queue->arr[queue->rear];
}
|
Python3
def que_rear(self):
if self.isEmpty():
return "Queue is empty"
return self.Q[self.rear]
|
C#
public int front()
{
if (isempty())
return INT_MIN;
return arr[rear];
}
|
Javascript
<script>
rear(){
if(this.isEmpty())
return "No elements in Queue<br>";
return this.items[this.items.length-1];
}
<script>
|
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity: O(1)
Space Complexity: O(N)
Operation 5: isEmpty():
This operation returns a boolean value that indicates whether the queue is empty or not.
The following steps are taken to perform the Empty operation:
- check if front value is equal to -1 or not, if yes then return true means queue is empty.
- Otherwise return false, means queue is not empty
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
bool isEmpty()
{
if (front == -1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
|
Java
boolean isEmpty()
{
if (front == -1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
|
C#
bool isEmpty()
{
if (front == -1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
|
C
bool isEmpty(struct Queue* queue)
{
return (queue->size == 0);
}
|
Python3
def isEmpty(self):
return self.size == 0
|
Javascript
</script>
isEmpty(){
return this.items.length == 0;
}
</script>
|
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity: O(1)
Space Complexity: O(N)
Operation 6 : isFull()
This operation returns a boolean value that indicates whether the queue is full or not.
The following steps are taken to perform the isFull() operation:
- Check if front value is equal to zero and rear is equal to the capacity of queue if yes then return true.
- otherwise return false
Below is the Implementation of the above approach:
C++
bool isFull()
{
if (front == 0 && rear == MAX_SIZE - 1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
|
Java
boolean isFull()
{
if (front == 0 && rear == MAX_SIZE - 1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
|
C
bool isFull(struct Queue* queue)
{
return (queue->size == queue->capacity);
}
|
C#
public bool isFull(int item) { return (rear == max - 1); }
|
Python3
def isFull(self):
return self.size == self.capacity
|
Javascript
function isFull() {
if (front == 0 && rear == MAX_SIZE - 1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
|
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity: O(1)
Space Complexity: O(N)
Operation 7: size()
This operation returns the size of the queue i.e. the total number of elements it contains.
queuename.size()
Parameters :
No parameters are passed
Returns :
Number of elements in the container
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int sum = 0;
queue<int> myqueue;
myqueue.push(1);
myqueue.push(8);
myqueue.push(3);
myqueue.push(6);
myqueue.push(2);
cout << myqueue.size();
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int sum = 0;
Queue<Integer> myqueue = new LinkedList<>();
myqueue.add(1);
myqueue.add(8);
myqueue.add(3);
myqueue.add(6);
myqueue.add(2);
System.out.println(myqueue.size());
}
}
|
Python
from collections import deque
def main():
sum = 0
myqueue = deque()
myqueue.append(1)
myqueue.append(8)
myqueue.append(3)
myqueue.append(6)
myqueue.append(2)
print(len(myqueue))
main()
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace ConsoleApp1 {
class MainClass {
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
int sum = 0;
Queue<int> myqueue = new Queue<int>();
myqueue.Enqueue(1);
myqueue.Enqueue(8);
myqueue.Enqueue(3);
myqueue.Enqueue(6);
myqueue.Enqueue(2);
Console.WriteLine(myqueue.Count);
}
}
}
|
Javascript
let sum = 0;
let myqueue=[];
myqueue.push(1);
myqueue.push(8);
myqueue.push(3);
myqueue.push(6);
myqueue.push(2);
console.log(myqueue.length);
|
Complexity Analysis:
Time Complexity: O(1)
Space Complexity: O(N)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...