Balanced Binary Tree
Last Updated :
21 Dec, 2022
A binary tree is balanced if the height of the tree is O(Log n) where n is the number of nodes. For Example, the AVL tree maintains O(Log n) height by making sure that the difference between the heights of the left and right subtrees is at most 1. Red-Black trees maintain O(Log n) height by making sure that the number of Black nodes on every root-to-leaf path is the same and that there are no adjacent red nodes. Balanced Binary Search trees are performance-wise good as they provide O(log n) time for search, insert and delete.
A balanced binary tree is a binary tree that follows the 3 conditions:
- The height of the left and right tree for any node does not differ by more than 1.
- The left subtree of that node is also balanced.
- The right subtree of that node is also balanced.
A single node is always balanced. It is also referred to as a height-balanced binary tree.
Example:
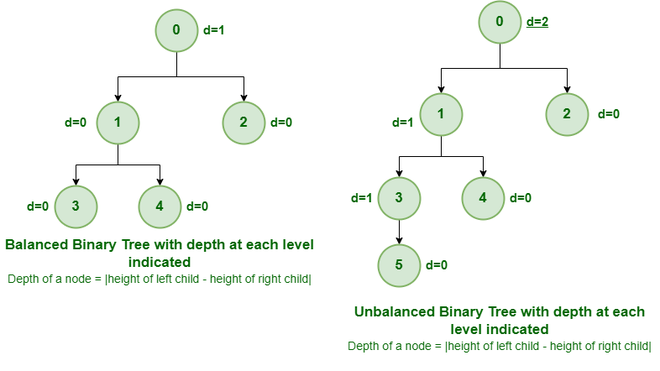
Balanced and Unbalanced Binary Tree
It is a type of binary tree in which the difference between the height of the left and the right subtree for each node is either 0 or 1. In the figure above, the root node having a value 0 is unbalanced with a depth of 2 units.
Application of Balanced Binary Tree:
Advantages of Balanced Binary Tree:
- Non Destructive updates are supported by a Balanced Binary Tree with the same asymptotic effectiveness.
- Range queries and iteration in the right sequence are made feasible by the balanced binary tree.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...