Attacks against 3G mobile networks
Last Updated :
25 Jan, 2023
There are a variety of attacks that may be launched against mobile networks, and they are two types i.e.
- Out of the mobile network: public net, private networks, other networks and,
- Inside mobile network : Smartphones, laptops, and pcs linked to the 3G network.
Attacks against 3G mobile networks are :
1. Malwares, viruses and worms –
Since many users still are shifting from 2G, 2.5G, and 3G to 3G, there is an increasing need to raise awareness about the risks that exist when using mobiles. Here are a few instances of malware that target mobile phones:
- Skull Trojan –
It is designed to infect Series 60 phones running the Symbian mobile operating system.
- Cabir worm –
It is the initially known worm in phones; It attacks mobiles which then scans remaining devices for its replica to start mobile which detects using Bluetooth.
- Mosquito Trojan –
Mosquito Trojan is a corrupted variant of the Mosquitoes mobile game targeting series 60 phones.
- Brador Trojan –
Infects the Windows Mobile operating system by making the svchost.exe file in the startup file of windows, which gives you full access to phones. Standard worm transmission vectors, including email attachments, are compatible with this executable.
- Lasco Worm –
It was initially published in 2005 and was designed to attack Symbian-based PDAs and cell phones. Lasco is built on Cabir’s code and uses Bluetooth technology to duplicate.
2. DDoS (Distributed Denial-of-Service) :
The overall purpose of this assault is to ensure that the system inaccessible to the targeted users. A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS)attack is currently one of the main prevalent cyber-security risks to wired ISPs. It assaults are a type of DoS attack. A DDoS assault entails the deployment of a bot, and that is a collection of associated gadgets that are utilized to flood a targeted system using bogus traffic.
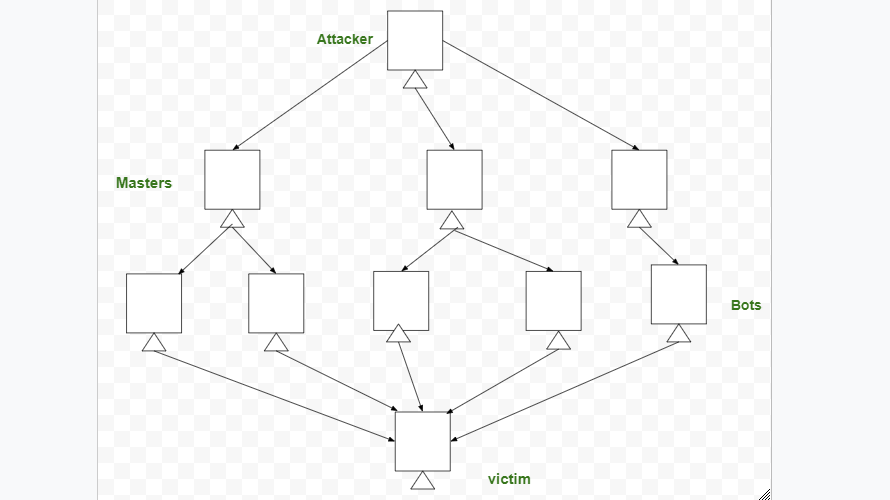
3. Overbilling attack :
An attacker hijacks a user’s IP address and then uses it to begin non-free transfers or just for own reasons. In any scenario, the transaction is charged to the real user. Whenever a lawful user’s IP address is restored to an IP pool, a hacker can intercept this and take ownership. After that, the hacker takes advantage of a user’s Cellular/mobile network services.
4. Spoofed policy development process (PDP) :
This will attack when there are flaws in GTP. Spoofing occurs when hacker pretends to be a legitimate system or client in case of theft of information, installing malicious software, or get around security measures.
5. Signaling-level attacks :
VoIP services in IMS networks are provided using signaling by Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) . SIP-based VoIP systems have a number of security flaws.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...