It is a well established fact that merge sort runs faster than insertion sort. Using asymptotic analysis. we can prove that merge sort runs in O(nlogn) time and insertion sort takes O(n^2). It is obvious because merge sort uses a divide-and-conquer approach by recursively solving the problems where as insertion sort follows an incremental approach. If we scrutinize the time complexity analysis even further, we’ll get to know that insertion sort isn’t that bad enough. Surprisingly, insertion sort beats merge sort on smaller input size. This is because there are few constants which we ignore while deducing the time complexity. On larger input sizes of the order 10^4 this doesn’t influence the behavior of our function. But when input sizes fall below, say less than 40, then the constants in the equation dominate the input size ‘n’. So far, so good. But I wasn’t satisfied with such mathematical analysis. As a computer science undergrad we must believe in writing code. I’ve written a C program to get a feel of how the algorithms compete against each other for various input sizes. And also, why such rigorous mathematical analysis is done on establishing running time complexities of these sorting algorithms.
Implementation:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <time.h>
#define MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY 1000000001
int cmpfunc(const void *a, const void *b)
{
// Compare function used by qsort
return (*(int *)a - *(int *)b);
}
int *generate_random_array(int n)
{
srand(time(NULL));
int *a = malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
a[i] = rand() % MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY;
return a;
}
int *copy_array(int a[], int n)
{
int *arr = malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
arr[i] = a[i];
return arr;
}
// Code for Insertion Sort
void insertion_sort_asc(int a[], int start, int end)
{
int i;
for (i = start + 1; i <= end; ++i)
{
int key = a[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= start && a[j] > key)
{
a[j + 1] = a[j];
--j;
}
a[j + 1] = key;
}
}
// Code for Merge Sort
void merge(int a[], int start, int end, int mid)
{
int i = start, j = mid + 1, k = 0;
int *aux = malloc(sizeof(int) * (end - start + 1));
while (i <= mid && j <= end)
{
if (a[i] <= a[j])
aux[k++] = a[i++];
else
aux[k++] = a[j++];
}
while (i <= mid)
aux[k++] = a[i++];
while (j <= end)
aux[k++] = a[j++];
j = 0;
for (i = start; i <= end; ++i)
a[i] = aux[j++];
free(aux);
}
void _merge_sort(int a[], int start, int end)
{
if (start < end)
{
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
_merge_sort(a, start, mid);
_merge_sort(a, mid + 1, end);
merge(a, start, end, mid);
}
}
void merge_sort(int a[], int n)
{
return _merge_sort(a, 0, n - 1);
}
void insertion_and_merge_sort_combine(int a[], int start, int end, int k)
{
// Performs insertion sort if size of array is less than or equal to k
// Otherwise, uses mergesort
if (start < end)
{
int size = end - start + 1;
if (size <= k)
{
return insertion_sort_asc(a, start, end);
}
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
insertion_and_merge_sort_combine(a, start, mid, k);
insertion_and_merge_sort_combine(a, mid + 1, end, k);
merge(a, start, end, mid);
}
}
void test_sorting_runtimes(int size, int num_of_times)
{
// Measuring the runtime of the sorting algorithms
int number_of_times = num_of_times;
int t = number_of_times;
int n = size;
double insertion_sort_time = 0, merge_sort_time = 0;
double merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time = 0, qsort_time = 0;
while (t--)
{
clock_t start, end;
int *a = generate_random_array(n);
int *b = copy_array(a, n);
start = clock();
insertion_sort_asc(b, 0, n - 1);
end = clock();
insertion_sort_time += ((double)(end - start)) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
free(b);
int *c = copy_array(a, n);
start = clock();
merge_sort(c, n);
end = clock();
merge_sort_time += ((double)(end - start)) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
free(c);
int *d = copy_array(a, n);
start = clock();
insertion_and_merge_sort_combine(d, 0, n - 1, 40);
end = clock();
merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time += ((double)(end - start)) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
free(d);
start = clock();
qsort(a, n, sizeof(int), cmpfunc);
end = clock();
qsort_time += ((double)(end - start)) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC;
free(a);
}
insertion_sort_time /= number_of_times;
merge_sort_time /= number_of_times;
merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time /= number_of_times;
qsort_time /= number_of_times;
printf("\nTime taken to sort:\n"
"%-35s %f\n"
"%-35s %f\n"
"%-35s %f\n"
"%-35s %f\n\n",
"(i)Insertion sort: ",
insertion_sort_time,
"(ii)Merge sort: ",
merge_sort_time,
"(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: ",
merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time,
"(iv)Qsort library function: ",
qsort_time);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int t;
scanf("%d", &t);
while (t--)
{
int size, num_of_times;
scanf("%d %d", &size, &num_of_times);
test_sorting_runtimes(size, num_of_times);
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class SortingAlgorithms {
// Maximum element in array
static final int MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int t = scanner.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < t; i++) {
int size = scanner.nextInt();
int num_of_times = scanner.nextInt();
testSortingRuntimes(size, num_of_times);
}
scanner.close();
}
static int[] generateRandomArray(int n) {
// Generate an array of n random integers.
int[] arr = new int[n];
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i] = random.nextInt(MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY);
}
return arr;
}
static void insertionSortAsc(int[] a, int start, int end) {
// Perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end.
for (int i = start + 1; i <= end; i++) {
int key = a[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= start && a[j] > key) {
a[j + 1] = a[j];
j--;
}
a[j + 1] = key;
}
}
static void merge(int[] a, int start, int end, int mid) {
// Merge two sorted sublists of a.
// The first sublist is a[start:mid+1], and the second sublist is a[mid+1:end+1].
int[] aux = new int[end - start + 1];
int i = start, j = mid + 1, k = 0;
while (i <= mid && j <= end) {
if (a[i] <= a[j]) {
aux[k++] = a[i++];
} else {
aux[k++] = a[j++];
}
}
while (i <= mid) {
aux[k++] = a[i++];
}
while (j <= end) {
aux[k++] = a[j++];
}
System.arraycopy(aux, 0, a, start, aux.length);
}
static void mergeSort(int[] a) {
// Perform an in-place merge sort on a.
mergeSortHelper(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
static void mergeSortHelper(int[] a, int start, int end) {
// Recursive merge sort function.
if (start < end) {
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
mergeSortHelper(a, start, mid);
mergeSortHelper(a, mid + 1, end);
merge(a, start, end, mid);
}
}
static void insertionAndMergeSortCombine(int[] a, int start, int end, int k) {
/*
Perform an in-place sort on a from start to end.
If the size of the list is less than or equal to k, use insertion sort.
Otherwise, use merge sort.
*/
if (start < end) {
int size = end - start + 1;
if (size <= k) {
insertionSortAsc(a, start, end);
} else {
int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
insertionAndMergeSortCombine(a, start, mid, k);
insertionAndMergeSortCombine(a, mid + 1, end, k);
merge(a, start, end, mid);
}
}
}
static void testSortingRuntimes(int size, int num_of_times) {
// Test the runtime of the sorting algorithms.
double insertionSortTime = 0;
double mergeSortTime = 0;
double mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime = 0;
double qsortTime = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < num_of_times; i++) {
int[] a = generateRandomArray(size);
int[] b = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
insertionSortAsc(b, 0, b.length - 1);
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
insertionSortTime += end - start;
int[] c = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
mergeSort(c);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
mergeSortTime += end - start;
int[] d = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
insertionAndMergeSortCombine(d, 0, d.length - 1, 40);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime += end - start;
int[] e = Arrays.copyOf(a, a.length);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
Arrays.sort(e);
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
qsortTime += end - start;
}
insertionSortTime /= num_of_times;
mergeSortTime /= num_of_times;
mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime /= num_of_times;
qsortTime /= num_of_times;
System.out.println("\nTime taken to sort:\n"
+ "(i) Insertion sort: " + insertionSortTime + "\n"
+ "(ii) Merge sort: " + mergeSortTime + "\n"
+ "(iii) Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: " + mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime + "\n"
+ "(iv) Qsort library function: " + qsortTime + "\n");
}
}
import time
import random
import copy
from typing import List
# Maximum element in array
MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001
def generate_random_array(n: int) -> List[int]:
#Generate a list of n random integers.
return [random.randint(0, MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY) for _ in range(n)]
def insertion_sort_asc(a: List[int], start: int, end: int) -> None:
#Perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end.
for i in range(start + 1, end + 1):
key = a[i]
j = i - 1
while j >= start and a[j] > key:
a[j + 1] = a[j]
j -= 1
a[j + 1] = key
def merge(a: List[int], start: int, end: int, mid: int) -> None:
#Merge two sorted sublists of a.
#The first sublist is a[start:mid+1], and the second sublist is a[mid+1:end+1].
aux = []
i = start
j = mid + 1
while i <= mid and j <= end:
if a[i] <= a[j]:
aux.append(a[i])
i += 1
else:
aux.append(a[j])
j += 1
while i <= mid:
aux.append(a[i])
i += 1
while j <= end:
aux.append(a[j])
j += 1
a[start:end+1] = aux
def _merge_sort(a: List[int], start: int, end: int) -> None:
#Recursive merge sort function.
if start < end:
mid = start + (end - start) // 2
_merge_sort(a, start, mid)
_merge_sort(a, mid + 1, end)
merge(a, start, end, mid)
def merge_sort(a: List[int]) -> None:
#Perform an in-place merge sort on a.
_merge_sort(a, 0, len(a) - 1)
def insertion_and_merge_sort_combine(a: List[int], start: int, end: int, k: int) -> None:
"""
Perform an in-place sort on a from start to end.
If the size of the list is less than or equal to k, use insertion sort.
Otherwise, use merge sort.
"""
if start < end:
size = end - start + 1
if size <= k:
insertion_sort_asc(a, start, end)
else:
mid = start + (end - start) // 2
insertion_and_merge_sort_combine(a, start, mid, k)
insertion_and_merge_sort_combine(a, mid + 1, end, k)
merge(a, start, end, mid)
def test_sorting_runtimes(size: int, num_of_times: int) -> None:
#Test the runtime of the sorting algorithms.
insertion_sort_time = 0
merge_sort_time = 0
merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time = 0
qsort_time = 0
for _ in range(num_of_times):
a = generate_random_array(size)
b = copy.deepcopy(a)
start = time.time()
insertion_sort_asc(b, 0, len(b) - 1)
end = time.time()
insertion_sort_time += end - start
c = copy.deepcopy(a)
start = time.time()
merge_sort(c)
end = time.time()
merge_sort_time += end - start
d = copy.deepcopy(a)
start = time.time()
insertion_and_merge_sort_combine(d, 0, len(d) - 1, 40)
end = time.time()
merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time += end - start
start = time.time()
a.sort()
end = time.time()
qsort_time += end - start
insertion_sort_time /= num_of_times
merge_sort_time /= num_of_times
merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time /= num_of_times
qsort_time /= num_of_times
print(f"\nTime taken to sort:\n"
f"(i)Insertion sort: {insertion_sort_time}\n"
f"(ii)Merge sort: {merge_sort_time}\n"
f"(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: {merge_sort_and_insertion_sort_mix_time}\n"
f"(iv)Qsort library function: {qsort_time}\n")
def main() -> None:
t = int(input())
for _ in range(t):
size, num_of_times = map(int, input().split())
test_sorting_runtimes(size, num_of_times)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
// Importing required modules
const { performance } = require('perf_hooks');
// Maximum element in array
const MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY = 1000000001;
// Function to generate a list of n random integers
function generateRandomArray(n) {
return Array.from({length: n}, () => Math.floor(Math.random() * MAX_ELEMENT_IN_ARRAY));
}
// Function to perform an in-place insertion sort on a from start to end
function insertionSortAsc(a, start, end) {
for (let i = start + 1; i <= end; i++) {
let key = a[i];
let j = i - 1;
while (j >= start && a[j] > key) {
a[j + 1] = a[j];
j -= 1;
}
a[j + 1] = key;
}
}
// Function to merge two sorted sublists of a
function merge(a, start, end, mid) {
let aux = [];
let i = start;
let j = mid + 1;
while (i <= mid && j <= end) {
if (a[i] <= a[j]) {
aux.push(a[i]);
i += 1;
} else {
aux.push(a[j]);
j += 1;
}
}
while (i <= mid) {
aux.push(a[i]);
i += 1;
}
while (j <= end) {
aux.push(a[j]);
j += 1;
}
for (let i = start; i <= end; i++) {
a[i] = aux[i - start];
}
}
// Recursive merge sort function
function _mergeSort(a, start, end) {
if (start < end) {
let mid = start + Math.floor((end - start) / 2);
_mergeSort(a, start, mid);
_mergeSort(a, mid + 1, end);
merge(a, start, end, mid);
}
}
// Function to perform an in-place merge sort on a
function mergeSort(a) {
_mergeSort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
}
// Function to perform an in-place sort on a from start to end
function insertionAndMergeSortCombine(a, start, end, k) {
if (start < end) {
let size = end - start + 1;
if (size <= k) {
insertionSortAsc(a, start, end);
} else {
let mid = start + Math.floor((end - start) / 2);
insertionAndMergeSortCombine(a, start, mid, k);
insertionAndMergeSortCombine(a, mid + 1, end, k);
merge(a, start, end, mid);
}
}
}
// Function to test the runtime of the sorting algorithms
function testSortingRuntimes(size, numOfTimes) {
let insertionSortTime = 0;
let mergeSortTime = 0;
let mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime = 0;
let qsortTime = 0;
for (let _ = 0; _ < numOfTimes; _++) {
let a = generateRandomArray(size);
let b = [...a];
let start = performance.now();
insertionSortAsc(b, 0, b.length - 1);
let end = performance.now();
insertionSortTime += end - start;
let c = [...a];
start = performance.now();
mergeSort(c);
end = performance.now();
mergeSortTime += end - start;
let d = [...a];
start = performance.now();
insertionAndMergeSortCombine(d, 0, d.length - 1, 40);
end = performance.now();
mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime += end - start;
start = performance.now();
a.sort((a, b) => a - b);
end = performance.now();
qsortTime += end - start;
}
insertionSortTime /= numOfTimes;
mergeSortTime /= numOfTimes;
mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime /= numOfTimes;
qsortTime /= numOfTimes;
console.log(`\nTime taken to sort:\n(i)Insertion sort: ${insertionSortTime}\n(ii)Merge sort: ${mergeSortTime}\n(iii)Insertion-mergesort-hybrid: ${mergeSortAndInsertionSortMixTime}\n(iv)Qsort library function: ${qsortTime}\n`);
}
// Main function
function main() {
let t = parseInt(prompt("Enter the number of test cases: "));
for (let _ = 0; _ < t; _++) {
let size = parseInt(prompt("Enter the size of the array: "));
let numOfTimes = parseInt(prompt("Enter the number of times to run the test: "));
testSortingRuntimes(size, numOfTimes);
}
}
// Call the main function
main();
I have compared the running times of the following algorithms:
- Insertion sort: The traditional algorithm with no modifications/optimisation. It performs very well for smaller input sizes. And yes, it does beat merge sort
- Merge sort: Follows the divide-and-conquer approach. For input sizes of the order 10^5 this algorithm is of the right choice. It renders insertion sort impractical for such large input sizes.
- Combined version of insertion sort and merge sort: I have tweaked the logic of merge sort a little bit to achieve a considerably better running time for smaller input sizes. As we know, merge sort splits its input into two halves until it is trivial enough to sort the elements. But here, when the input size falls below a threshold such as ’n’ < 40 then this hybrid algorithm makes a call to traditional insertion sort procedure. From the fact that insertion sort runs faster on smaller inputs and merge sort runs faster on larger inputs, this algorithm makes best use both the worlds.
- Quick sort: I have not implemented this procedure. This is the library function qsort() which is available in . I have considered this algorithm in order to know the significance of implementation. It requires a great deal of programming expertise to minimize the number of steps and make at most use of the underlying language primitives to implement an algorithm in the best way possible. This is the main reason why it is recommended to use library functions. They are written to handle anything and everything. They optimize to the maximum extent possible. And before I forget, from my analysis qsort() runs blazingly fast on virtually any input size!
The Analysis:
- Input: The user has to supply the number of times he/she wants to test the algorithm corresponding to number of test cases. For each test case the user must enter two space separated integers denoting the input size ’n’ and the ‘num_of_times’ denoting the number of times he/she wants to run the analysis and take average. (Clarification: If ‘num_of_times’ is 10 then each of the algorithm specified above runs 10 times and the average is taken. This is done because the input array is generated randomly corresponding to the input size which you specify. The input array could be all sorted. Our it could correspond to the worst case .i.e. descending order. In order to avoid running times of such input arrays. The algorithm is run ‘num_of_times‘ and the average is taken.) clock() routine and CLOCKS_PER_SEC macro from is used to measure the time taken. Compilation: I have written the above code in Linux environment (Ubuntu 16.04 LTS). Copy the code snippet above. Compile it using gcc, key in the inputs as specified and admire the power of sorting algorithms!
- Results: As you can see for small input sizes, insertion sort beats merge sort by 2 * 10^-6 sec. But this difference in time is not so significant. On the other hand, the hybrid algorithm and qsort() library function, both perform as good as insertion sort.
 The input size is now increased by approximately 100 times to n = 1000 from n = 30. The difference is now tangible. Merge sort runs 10 times faster than insertion sort. There is again a tie between the performance of the hybrid algorithm and the qsort() routine. This suggests that the qsort() is implemented in a way which is more or less similar to our hybrid algorithm i.e., switching between different algorithms to make the best out of them.
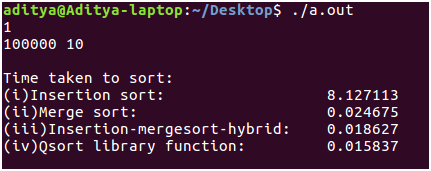
The input size is now increased by approximately 100 times to n = 1000 from n = 30. The difference is now tangible. Merge sort runs 10 times faster than insertion sort. There is again a tie between the performance of the hybrid algorithm and the qsort() routine. This suggests that the qsort() is implemented in a way which is more or less similar to our hybrid algorithm i.e., switching between different algorithms to make the best out of them. 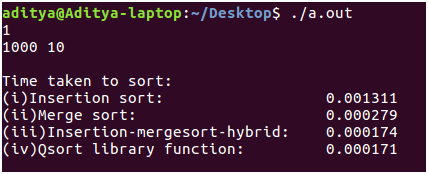 Finally, the input size is increased to 10^5 (1 Lakh!) which is most probably the ideal size used in practical scenario’s. Compared to the previous input n = 1000 where merge sort beat insertion sort by running 10 times faster, here the difference is even more significant. Merge sort beats insertion sort by 100 times! The hybrid algorithm which we have written in fact does out perform the traditional merge sort by running 0.01 sec faster. And lastly, qsort() the library function, finally proves us that implementation also plays a crucial role while measuring the running times meticulously by running 3 milliseconds faster! :D
Finally, the input size is increased to 10^5 (1 Lakh!) which is most probably the ideal size used in practical scenario’s. Compared to the previous input n = 1000 where merge sort beat insertion sort by running 10 times faster, here the difference is even more significant. Merge sort beats insertion sort by 100 times! The hybrid algorithm which we have written in fact does out perform the traditional merge sort by running 0.01 sec faster. And lastly, qsort() the library function, finally proves us that implementation also plays a crucial role while measuring the running times meticulously by running 3 milliseconds faster! :D
Note: Do not run the above program with n >= 10^6 since it will take a lot of computing power. Thank you and Happy coding! :)