Arrays asList() method in Java with Examples
Last Updated :
24 Nov, 2021
The asList() method of java.util.Arrays class is used to return a fixed-size list backed by the specified array. This method acts as a bridge between array-based and collection-based APIs, in combination with Collection.toArray(). The returned list is serializable and implements RandomAccess.
Tip: This runs in O(1) time.
Syntax:
public static List asList(T... a)
Parameters: This method takes the array a which is required to be converted into a List. Here … is known as varargs which is an array of parameters and works similar to an object array parameter.
Special Note: The type of array must be a Wrapper Class(Integer,Float, etc) in case of primitive data types(int, float,etc) , i.e you can’t pass int a[] but you can pass Integer a[]. If you pass int a[], this function will return a List <int a[]> and not List <Integer> , as “autoboxing” doesn’t happen in this case and int a[] is itself identified as an object and a List of int array is returned, instead of list of integers , which will give error in various Collection functions .
Return Value: This method returns a list view of the specified array.
Example 1:
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
try {
String a[]
= new String[] { "A", "B", "C", "D" };
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(a);
System.out.println("The list is: " + list);
}
catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("Exception thrown : " + e);
}
}
}
|
Output
The list is: [A, B, C, D]
Example 2:
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
try {
Integer a[] = new Integer[] { 10, 20, 30, 40 };
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(a);
System.out.println("The list is: " + list);
}
catch (NullPointerException e) {
System.out.println("Exception thrown : " + e);
}
}
}
|
Output
The list is: [10, 20, 30, 40]
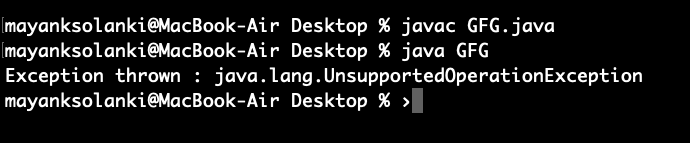
Example 3:
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
public static void main(String[] argv) throws Exception
{
try {
Integer a[] = new Integer[] { 10, 20, 30, 40 };
List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(a);
list.add(50);
System.out.println("The list is: " + list);
}
catch (UnsupportedOperationException e) {
System.out.println("Exception thrown : " + e);
}
}
}
|
Output:
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...