Applying Lambda functions to Pandas Dataframe
Last Updated :
24 Nov, 2023
In Python Pandas, we have the freedom to add different functions whenever needed like lambda function, sort function, etc. We can apply a lambda function to both the columns and rows of the Pandas data frame.
Syntax: lambda arguments: expression
An anonymous function which we can pass in instantly without defining a name or any thing like a full traditional function.
Applying Lambda Functions to Pandas
Below are some methods and ways by which we can apply lambda functions to Pandas:
- Dataframe.assign() on a Single Column
- Dataframe.assign() on Multiple Columns
- Dataframe.apply() on a Single Row
- Dataframe.apply() on Multiple Rows
- Lambda Function on Multiple Rows and Columns Simultaneously
Dataframe.assign() on a Single Column
In this example, we will apply the lambda function Dataframe.assign() to a single column. The function is applied to the ‘Total_Marks’ column, and a new column ‘Percentage’ is formed with its help.
Python3
import pandas as pd
values= [['Rohan',455],['Elvish',250],['Deepak',495],
['Soni',400],['Radhika',350],['Vansh',450]]
df = pd.DataFrame(values,columns=['Name','Total_Marks'])
df = df.assign(Percentage = lambda x: (x['Total_Marks'] /500 * 100))
df
|
Output:
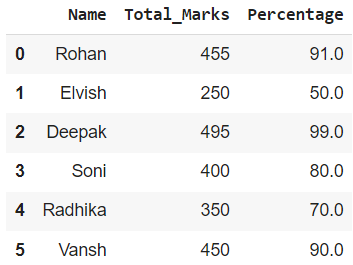
Dataframe.assign() on a Single Column
Dataframe.assign() on Multiple Columns
In this example, we will apply the lambda function Dataframe.assign() to multiple columns. The lambda function is applied to 3 columns i.e., ‘Field_1’, ‘Field_2’, and ‘Field_3’.
Python3
import pandas as pd
values_list = [[15, 2.5, 100], [20, 4.5, 50], [25, 5.2, 80],
[45, 5.8, 48], [40, 6.3, 70], [41, 6.4, 90],
[51, 2.3, 111]]
df = pd.DataFrame(values_list, columns=['Field_1', 'Field_2', 'Field_3'])
df = df.assign(Product=lambda x: (x['Field_1'] * x['Field_2'] * x['Field_3']))
df
|
Output:
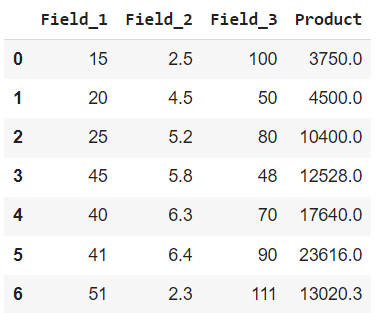
Dataframe.assign() on Multiple Columns
Dataframe.apply() on a Single Row
In this example, we will apply the lambda function Dataframe.apply() to single row. The lambda function is applied to a row starting with ‘d’ and hence square all values corresponding to it.
Python3
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
values_list = [[15, 2.5, 100], [20, 4.5, 50], [25, 5.2, 80],
[45, 5.8, 48], [40, 6.3, 70], [41, 6.4, 90],
[51, 2.3, 111]]
df = pd.DataFrame(values_list, columns=['Field_1', 'Field_2', 'Field_3'],
index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g'])
df = df.apply(lambda x: np.square(x) if x.name == 'd' else x, axis=1)
df
|
Output:
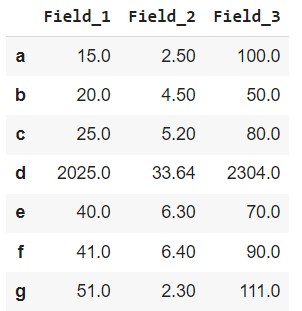
Dataframe.apply() on a Single Row
Dataframe.apply() on Multiple Rows
In this example, we will apply the lambda function to multiple rows using Dataframe.apply(). The lambda function is applied to 3 rows starting with ‘a’, ‘e’, and ‘g’.
Python3
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
values_list = [[15, 2.5, 100], [20, 4.5, 50], [25, 5.2, 80],
[45, 5.8, 48], [40, 6.3, 70], [41, 6.4, 90],
[51, 2.3, 111]]
df = pd.DataFrame(values_list, columns=['Field_1', 'Field_2', 'Field_3'],
index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g'])
df = df.apply(lambda x: np.square(x) if x.name in [
'a', 'e', 'g'] else x, axis=1)
df
|
Output:
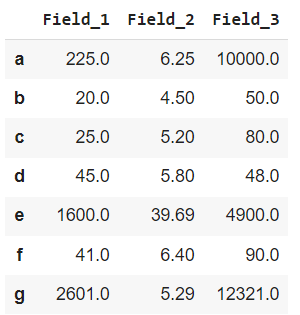
Dataframe.apply() on Multiple Rows
Lambda Function on Multiple Rows and Columns Simultaneously
In this example, we will apply the lambda function simultaneously to multiple columns and rows using dataframe.assign() and dataframe.apply().
Python3
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
values_list = [[1.5, 2.5, 10.0], [2.0, 4.5, 5.0], [2.5, 5.2, 8.0],
[4.5, 5.8, 4.8], [4.0, 6.3, 70], [4.1, 6.4, 9.0],
[5.1, 2.3, 11.1]]
df = pd.DataFrame(values_list, columns=['Field_1', 'Field_2', 'Field_3'],
index=['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g'])
df = df.apply(lambda x: np.square(x) if x.name in ['b', 'f'] else x, axis=1)
df = df.assign(Product=lambda x: (x['Field_1'] * x['Field_2'] * x['Field_3']))
df
|
Output
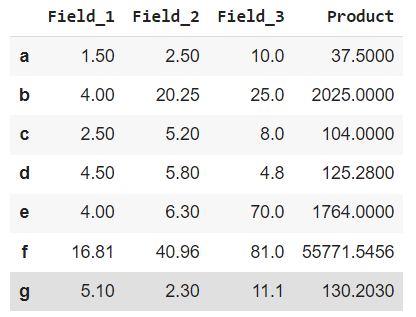
Lambda Function on Multiple Rows and Columns Simultaneously
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...