Append to JSON file using Python
Last Updated :
26 Mar, 2024
The full form of JSON is JavaScript Object Notation. It means that a script (executable) file which is made of text in a programming language, is used to store and transfer the data. Python supports JSON through a built-in package called JSON. To use this feature, we import the JSON package in Python script. The text in JSON is done through quoted-string which contains the value in key-value mapping within { }.
Functions Used:
- json.loads(): json.loads() function is present in python built-in ‘json’ module. This function is used to parse the JSON string.
Syntax: json.loads(json_string)
Parameter: It takes JSON string as the parameter.
Return type: It returns the python dictionary object.
- json.dumps(): json.dumps() function is present in python built-in ‘json’ module. This function is used to convert Python object into JSON string.
Syntax: json.dumps(object)
Parameter: It takes Python Object as the parameter.
Return type: It returns the JSON string.
- update(): This method updates the dictionary with elements from another dictionary object or from an iterable key/value pair.
Syntax: dict.update([other])
Parameters: Takes another dictionary or an iterable key/value pair.
Return type: Returns None.
Example 1: Updating a JSON string.
Python3
# Python program to update
# JSON
import json
# JSON data:
x = '{ "organization":"GeeksForGeeks","city":"Noida","country":"India"}'
# python object to be appended
y = {"pin":110096}
# parsing JSON string:
z = json.loads(x)
# appending the data
z.update(y)
# the result is a JSON string:
print(json.dumps(z))
Output:
{“organization”: “GeeksForGeeks”, “city”: “Noida”, “country”: “India”, “pin”: 110096}
Example 2: Updating a JSON file. Suppose the JSON file looks like this.
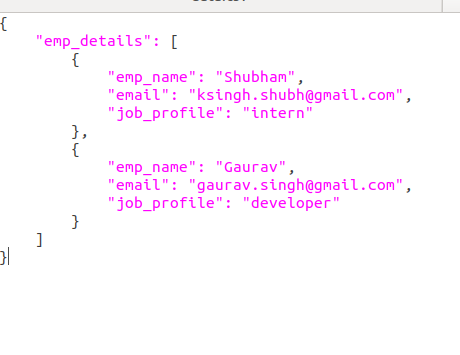
We want to add another JSON data after emp_details. Below is the implementation.
Python3
# Python program to update
# JSON
import json
# function to add to JSON
def write_json(new_data, filename='data.json'):
with open(filename,'r+') as file:
# First we load existing data into a dict.
file_data = json.load(file)
# Join new_data with file_data inside emp_details
file_data["emp_details"].append(new_data)
# Sets file's current position at offset.
file.seek(0)
# convert back to json.
json.dump(file_data, file, indent = 4)
# python object to be appended
y = {"emp_name":"Nikhil",
"email": "nikhil@geeksforgeeks.org",
"job_profile": "Full Time"
}
write_json(y)
Output:

Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...