Animal cell forms the basic structural and functional unit of organisms. Unlike plant cells, it lacks a cell wall and chloroplasts but consists of various membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, etc. In animal cells, these organelles function together to perform essential cellular processes like energy production, immune response, protein synthesis, and cellular communication.
Animal Cell Definition
Animal cells are eukaryotic cells that don’t have a cell wall but have nucleus where genetic material is stored.
An animal cell forms the fundamental unit of organism that belong to the animal kingdom. Its size ranges from microscopic microns to a few millimeters. The largest known animal cell, the ostrich egg, ranges from over 5.1 inches and weighs about 1.4 kilograms, while human neurons are just 100 microns across.
What is an Animal Cell?
Robert Hook discovered the animal cell in 1665. Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden gave the cell theory, which states that cells are the basic units of life in both plants and animals. It help us understanding the animal cell in detail.
Animal cells perform multiple functions essential for the survival and adaptation of organisms. Animal cell is eukaryotic in nature and exhibit DNA within the nucleus. It also contains various cellular structure and organelles like the cytoplasm, Golgi apparatus, ribosomes, mitochondria, etc. Animal cells function together to carry out various cellular processes and sustains life.
Animal Cell Diagram
The mentioned diagram shows the various organelles present in an animal cell.
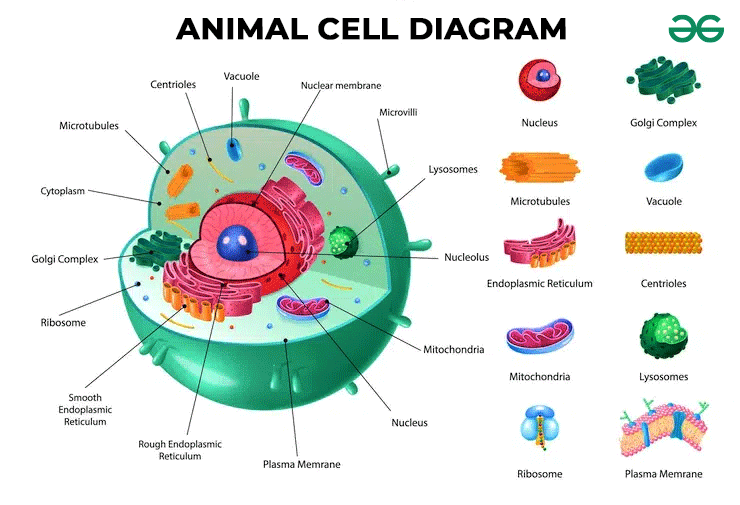
Animal Cell Structure
Animal cells consists of cellular structure and various organelles that carry out are the basic function of life. The various organelles present in animal cells are as follows:
Cell Membrane
A thin, lipid and protein-rich membrane covering the outer layer of the cell called as cell membrane. It is semi-permeable and protects the cell from its environment. It also regulates the passage of material in and out of the cell.
Nucleus
The nucleus is referred to as the cell’s control center. It contains genetic material (DNA) that regulates various cell activities and protein synthesis.
Nuclear Membrane
The nucleus is surrounded by double membrane. It controls the passage of substances between the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Centrosome
A centrosome is a small organelle present close to the nucleus. Its have a dense center, which is surrounded by radiating tubules. Microtubules are formed at the centrosomes.
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are spherical organelles membrane-bound organelles. The enzymes present in the lysosome break down cellular debris, waste products, and foreign substances.
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm is a gel- like substance that contains various cell organelles. It is protected by the cell membrane and contains nucleoplasm.
Golgi Apparatus
Golgi Apparatus is a flat, layered, sac-like organelle present close to the nucleus. It produces, transport, stores, and packs lipids and proteins.
Mitochondria
The mitochondrion is a double-membrane organelle present in both plant and animal cell.. It is spherical or rod-shaped. They are a cell’s powerhouse responsible for producing ATP (energy) through cellular respiration.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are small organelles present in ER. It helps in protein synthesis in plant and animal cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum is of two types rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum. Rough ER consists of ribosomes and takes part in protein synthesis, and smooth ER is involved in lipid metabolism.
Vacuole
Vacoules are membrane-bound sac that stores water, food, ions, nutrients, and waste products. Unlike plant cell, they’re smaller and less prominent in animal cells.
Nucleopore
The passage of nucleic acids and proteins through the nuclear membrane is facilitated by these microscopic holes present on the membrane.
Animal Cell Types
Animal cells can be categorised into various types. Each animal cell is having a specific function. The various type of animal cell are as follows:
Skin Cells
The animal cell that forms the epidermis is referred to as “skin cells.” These are the Langerhans cells, Merkel cells, keratinocytes, and melanocytes. The cells can be squamous, columnar, or cuboidal in shape. It performs the specific functions like protection, absorption, and secretion.
Muscle Cells
Muscle cells are of three types skeletal muscle cells, smooth muscle cells, and cardiac muscle cells. They are also known as muscle fibers and perform contraction and movement of muscles.
Blood Cells
Blood cells are of three types red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Function of red blood cells is to transport oxygen, white blood cells provide immune response, and platelets aid in blood clotting.
Nerve Cells
Nerve cells carry signals in the form of electrical impulses. It is divided into different parts as cell body, dendrites, and an axon.
Fat Cells
Fats cells are also known as fat cells and store energy in the form of fat. It plays an important role in insulation, protection, and hormone regulation.
Functions of Animal Cell
Animal cells perform multiple functions essential for the survival and adaptation of organisms. Important functions of animal cells are:
- Mitochondria present in the animal cell produce energy through cellular respiration, that is, ATP the energy currency of the cell.
- The plasma membrane of the animal cell regulates the entry and exit of substances and maintains cellular homeostasis.
- The nucleus contains DNA, which regulates cellular activities through transcription and translation.
- The ER helps in protein synthesis, and the Golgi apparatus packs the molecules for transport.
- Centrioles in the cell organizes microtubules during cell division, which ensures chromosome separation.
- Animal cells work together to maintain a stable internal environment, which is necessary for overall organism health.
Also Read: Difference between Animal and Plant Cell
Important Points about Animal cell
The important points about animal cell are as follows:
- A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. There are two primary types of cells: Prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells.
- Plant and animal cells are examples of eukaryotic cells. Therefore, they both share similarities.
- Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not have a rigid cell wall. This absence of rigid walls allows animal cells to be more flexible in shape and movement.
- Animal cell lack chloroplasts and cannot perform photosynthesis.
- Animal cells vary in structure and function to perform specific tasks in different tissues and organs of the body.
Animal cells is an important topic taught in class 9 biology to provide an understanding of their structure and functions.
FAQs on Animal Cells
1. What is an Animal Cell?
Answer:
Animal cell is a basic unit of life in animals. It lacks a cell wall but is surrounded by a plasma membrane. Organelles like the nucleus, mitochondria, and endoplasmic reticulum, which perform functions like producing energy, and help in protein synthesis are present.
2. State the various types of animal cells..
Answer:
The various type of animal cell are:
- Blood Cells
- Nerve cells
- Skin Cells
- Muscle Cells
- Fat Cells
3. What is the role of lysosomes?
Answer:
Lysosomes are spherical organelles enclosed by a membrane. It contains enzymes that aid in breaking down cellular waste, debris, and foreign materials through a process called hydrolysis. This helps maintain cellular cleanliness and recycles useful components.
4. What is the size of an animal cell?
Answer:
Animal cells generally have diameters ranging from 10 to 30 micrometers. However, this size can vary based on cell type and function. Like nerve cells can extend to over a meter in length, while red blood cells are usually around 7 micrometers in diameter.
5. Who invented animal cell?
Answer:
Robert Hook discovered the animal cell in 1665. Theodor Schwann and Matthias Schleiden gave the cell theory, which states that cells are the basic units of life in both plants and animals. It help us understanding the animal cell in detail.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...