Android Architecture
Last Updated :
26 Feb, 2021
Android architecture contains different number of components to support any android device needs. Android software contains an open-source Linux Kernel having collection of number of C/C++ libraries which are exposed through an application framework services.
Among all the components Linux Kernel provides main functionality of operating system functions to smartphones and Dalvik Virtual Machine (DVM) provide platform for running an android application.
The main components of android architecture are following:-
- Applications
- Application Framework
- Android Runtime
- Platform Libraries
- Linux Kernel
Pictorial representation of android architecture with several main components and their sub components –
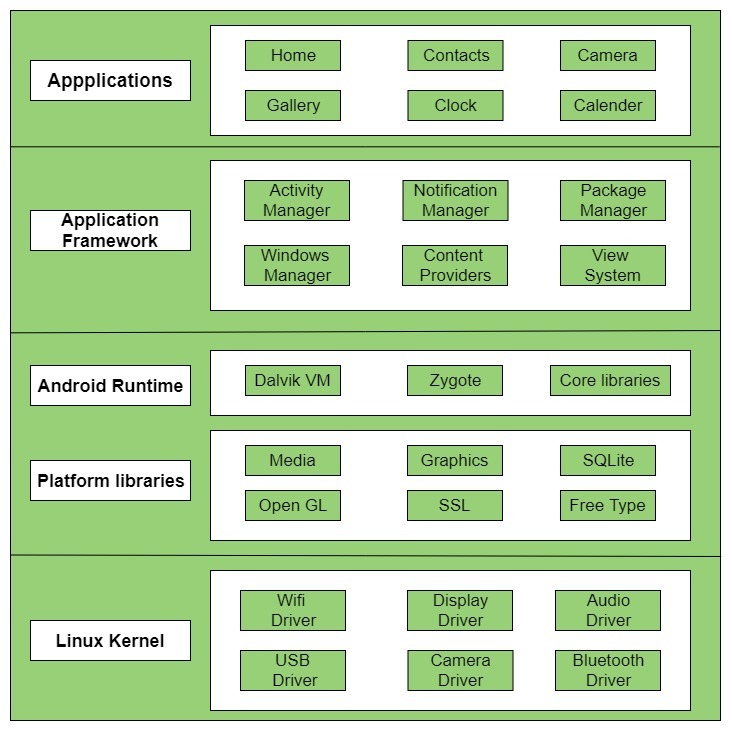
Applications –
Applications is the top layer of android architecture. The pre-installed applications like home, contacts, camera, gallery etc and third party applications downloaded from the play store like chat applications, games etc. will be installed on this layer only.
It runs within the Android run time with the help of the classes and services provided by the application framework.
Application framework –
Application Framework provides several important classes which are used to create an Android application. It provides a generic abstraction for hardware access and also helps in managing the user interface with application resources. Generally, it provides the services with the help of which we can create a particular class and make that class helpful for the Applications creation.
It includes different types of services activity manager, notification manager, view system, package manager etc. which are helpful for the development of our application according to the prerequisite.
Application runtime –
Android Runtime environment is one of the most important part of Android. It contains components like core libraries and the Dalvik virtual machine(DVM). Mainly, it provides the base for the application framework and powers our application with the help of the core libraries.
Like Java Virtual Machine (JVM), Dalvik Virtual Machine (DVM) is a register-based virtual machine and specially designed and optimized for android to ensure that a device can run multiple instances efficiently. It depends on the layer Linux kernel for threading and low-level memory management. The core libraries enable us to implement android applications using the standard JAVA or Kotlin programming languages.
Platform libraries –
The Platform Libraries includes various C/C++ core libraries and Java based libraries such as Media, Graphics, Surface Manager, OpenGL etc. to provide a support for android development.
- Media library provides support to play and record an audio and video formats.
- Surface manager responsible for managing access to the display subsystem.
- SGL and OpenGL both cross-language, cross-platform application program interface (API) are used for 2D and 3D computer graphics.
- SQLite provides database support and FreeType provides font support.
- Web-Kit This open source web browser engine provides all the functionality to display web content and to simplify page loading.
- SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is security technology to establish an encrypted link between a web server and a web browser.
Linux Kernel –
Linux Kernel is heart of the android architecture. It manages all the available drivers such as display drivers, camera drivers, Bluetooth drivers, audio drivers, memory drivers, etc. which are required during the runtime.
The Linux Kernel will provide an abstraction layer between the device hardware and the other components of android architecture. It is responsible for management of memory, power, devices etc.
The features of Linux kernel are:
- Security: The Linux kernel handles the security between the application and the system.
- Memory Management: It efficiently handles the memory management thereby providing the freedom to develop our apps.
- Process Management: It manages the process well, allocates resources to processes whenever they need them.
- Network Stack: It effectively handles the network communication.
- Driver Model: It ensures that the application works properly on the device and hardware manufacturers responsible for building their drivers into the Linux build.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...