Amazon Interview Experience | Set 189 (For SDE-1)
Last Updated :
28 Jun, 2019
Recently, I was interviewed for Amazon SDE-1 Position. There were two telephonic rounds followed by 4 F2F rounds.
Telephonic Round 1 :
—————————
He seemed a bit unprepared for the interview. He started with some introduction and knowledge transfer about current work and then created a binary tree and asked me to write the level order, preorder, postorder and inorder traversals for that tree.
Then, the coding questions followed.
1) Flattening a multi-level linked list.
1st approach –> Using a queue : T = O(n), S = O(n). Coded it.
2nd approach –> Same as on GeeksForGeeks < Flattening a Linked List > : Didnt ask me to code. But this one requires changing the structure of data.
2) Flattening a multi-level linked list but the nodes in depth should be printed first. So, basically the 1st question resembles BFS and this one resembles DFS. Did this using recursion very easily.
3) Process vs Threads. What happens when you type in a URL? High-level design. Handshaking protocol. HTTPS protocol, etc
Telephonic Round 2 :
—————————
I must say this guy who interviewed me was really smart. This round was a little more than 1 hour and there were 3 questions.
1) BST to Singly Linked List in place. A slight modification of this problem Coded it.
2) Finding Squares on the chessboard attackable by a rook
There is an NxN chessboard. Each square on the chessboard can be either empty or can have a rook. A rook as we know can attack either horizontally or vertically. Given a 2D matrix where 0 represents an empty square and 1 represents a rook, we have to fill in all the cells in the matrix with 1 which represent squares that can be attacked by any rook present on the chessboard. One can find a much simpler version of this problem here —
Boolean Matrix Problem
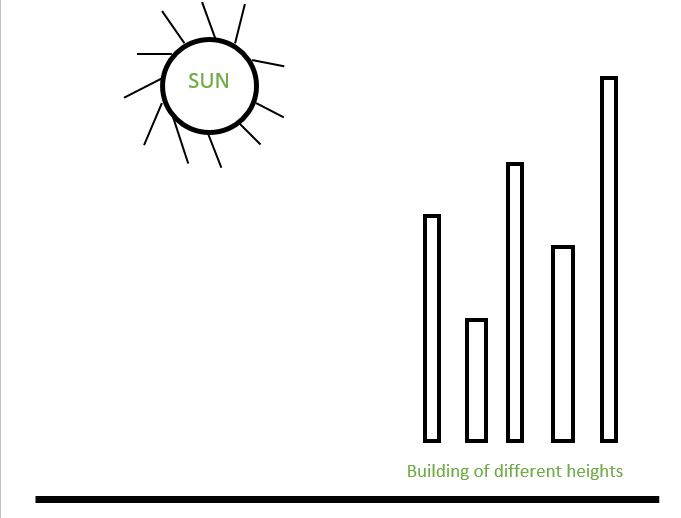
3) An array of buildings is facing the sun. The heights of the building is given in an array. You have to tell which all buildings will see the sunset. This is pretty easy. The first building will definitely see the sunset and for the rest of the buildings, just maintain a variable max_height_seen_so_far and check with the height of the current building. However, he then twisted the question and asked what my approach would be if I was to scan the buildings from back to front rather than front to end. I used a stack and applied the logic similar to that used in Next Greater Element problem.
F2F R1:
————–
Started with introduction. A lot of questions about current company, current work, current project and then a design question.
How would you design the meeting invite feature of Microsoft Outlook? Considering each meeting invite as an object and that Web server is the storage space for the invites, design a data structure to receive and send invites to user in an efficient manner. The message objects must be received in a sorted manner based on the time of meeting. I suggested using a Binary Search Tree and justified the use of this DS. I gave an O(NlogN) solution. I was then asked to code it. I coded it in C#.
Followed with a lot of HR questions.
F2F R2:
————–
1) Reverse a sub array in an array. Pretty easy.
2) Rotate a subarray in an array where start and end indices of the sub array are provided and ‘k’ is provided which is the number of rotations to be done. The interviewer behaved really dumb in this question. All he wanted was a solution. He made me dry run the code again and again and he wasn’t really bothered about the concept or the approach. I don’t think he could relate to my solution which was O(n) in time and O(1) in space.
3) Find if a linked list has a loop. Old question. Take a fast and a slow pointer. But to get this solution wasn’t really his motive. He asked why slow pointer should move by one node at a time and why the fast pointer should move at the speed of two nodes at a time. As led by the discussion, I was then asked to find the optimal speeds of slow and fast pointers for a given linked list. Again, led by the discussion, he asked if it’s given that the linked list has a loop and the size of the loop is given, can I find the optimal speeds of the slow and fast pointers?
F2F R3:
————–
1) Same question as Q3 asked in telephonic round with the only difference that the heights of the buildings was provided in a linked list. Coded it in C. Then, the interviewer twisted the question by placing the sun after the last building(previously the sun was placed before the first building). Used a stack. However, this can simply be done by the reversing the heights array and using the same function written for the first part of the problem.
2) Design a data structure to represent the hierarchy of employees in an organization. Also, the design should be such that, you can retrieve the no. of reportees of a manager(not just the direct reportees but all the employees under him) very fast(O(1) was expected). Also, insertion of a new employee and removal of an employee should be fast too.
I suggested using a n-ary tree of hash tables. Also, used an additional hash table where key was employeeId and value was the address of the hash table (or the node) in the n-ary tree. My solution did give no. of reportees in O(1) and addition and removal of employees was in O(n) time, where n is the total number of employees. There wasn’t enough time to code though.
F2F R4:
————–
This round had a lot of HR questions. Cultural info. Current project. He also asked coding questions but he wasn’t really bothered about the optimality of the solution.
1) Two nodes in a BST are swapped. Find them. Told my approach. Didn’t ask me to code it.
2) Print all the permutations of a string in lexicographic order. Coded it. Took me a lot of dry runs to make him understand that the code is correct 😀
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...