Aluminium Carbonate Formula – Structure, Properties, Uses, Sample Questions
Last Updated :
20 Dec, 2023
An alternate way to define salt is to describe it as a salt form of carbonic acid and an antacid with phosphate-binding action. Pure aluminium carbonate is extremely uncommon in nature; it is more commonly found as the sodium aluminium carbonate mineral dawsonite and the hydrated basic aluminium carbonate minerals scarbroite and hydroscarbroite.
What is Aluminium Carbonate?
Aluminium carbonate is a carbonate of an aluminium salt, which does not occur in nature. It is possible to produce it at high carbon dioxide pressure and at temperatures near to 0°C.
Aluminium carbonate storage would necessitate the development of a highly complicated mechanism that would safeguard the chemical from any external forces. Aluminium carbonate is a carbonate of aluminium. Furthermore, it is a water-insoluble Aluminium source that may readily be converted into other Aluminium compounds.
The chemical formula of Aluminium Carbonate is Al2(CO3)3.
Properties of Aluminium Carbonate
Physical Properties
The physical attributes of a chemical include its density, melting point, boiling temperature, and physical appearance. Some of the compound’s physical characteristics are also affected by the aluminium carbonate formula.
The following is a list of physical properties:
- Aluminium carbonate has a density of 1.5 g/cm3
- The compound’s molar mass is 96.09 g/mol.
- They are water-soluble.
- The melting point of aluminium carbonate is 58 °C.
- At the boiling point, it decomposes.
- The physical appearance of aluminium carbonate might be described as powdery and white. They seem like whitish powder.
Chemical Properties
The chemical properties of a compound provide information on the chemical formula of aluminium carbonate, molecular weight, reaction type, bond types involved, and other aspects of a compound.
The following are some of the compound’s chemical properties:
- Dialuminum Tricarbonate is the IUPAC term for aluminium carbonate.
- Aluminium carbonate has a molecular weight of 233.99.
- The compound’s hydrogen bond acceptor number is 9.
- The amount of hydrogen bond donors is zero. There are no bonds that can be rotated.
- The chemical compound has a complexity of 18.8.
- The characteristics of salt are basic in nature.
Structure of Aluminium Carbonate
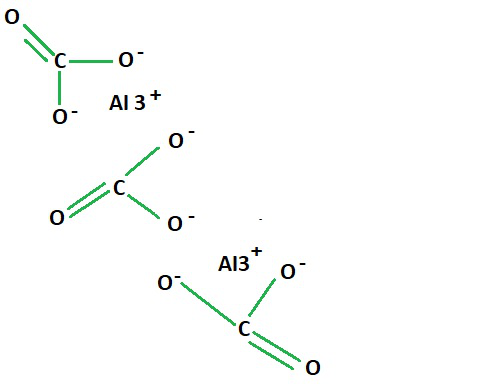
Aluminium Carbonate
Preparation of Aluminium Carbonate
There is no indication that the production of aluminium carbonate may occur in double displacement processes. Furthermore, soluble carbonates can precipitate aluminium hydroxide, resulting in the production of carbon dioxide. This is due to the fact that soluble carbonate is considered alkaline. Above all, the reaction of aluminium sulphate with sodium bicarbonate produces carbon dioxide and aluminium hydroxide. Furthermore, aluminium hydroxide inhibits foam production. This reaction was also the inspiration for the development of an early fire extinguisher.
Uses of Aluminium Carbonate
- Aluminium carbonate, like aluminium oxide and aluminium hydroxide, is a phosphate-binding medication. This medication is occasionally given to dogs and cats by veterinarians in order to bind intestinal phosphate.
- This medicine inhibits the absorption of dietary phosphate and reduces the absorption of pancreatic phosphorus. Furthermore, it is rarely used in humans. This is because of worries about its toxicity. Dogs and cats do not have a harmful reaction to their presence.
- Aluminium carbonate is useful to prevent the formation of urinary stones in humans. It is also useful as a medicinal treatment in situations of excess stomach acid. Inflammations and ulcerations may occur in some of these situations. Aluminium carbonate merely treats the symptoms of the disease; it has no impact on the disease itself.
- Furthermore, this medication can be taken as a tablet or as a liquid. Above all, caution should be exercised when taking aluminium carbonate, and it should be discussed with a medical professional before to use. Those suffering from renal problems should absolutely avoid it. Furthermore, aluminium carbonate allows for the regulation of phosphate levels in the body.
Sample Questions
Question 1: Is aluminium carbonate water soluble?
Answer:
Basic Aluminum Carbonate is a water-insoluble Aluminum source that can be easily transformed to other Aluminum compounds like the oxide by heating (calcination).
Question 2: What is the formula and valency of aluminium oxide?
Answer:
The valency of aluminum is +3 and that of oxide is -2. Therefore, the chemical formula of aluminum oxide is Al2O3.
Question 3: What is the ion content of aluminium carbonate?
Answer:
As seen in the structural formula for aluminium carbonate, two aluminium ions are present in the bonding between the three carboxylic groups that constitute the aluminium and carbonate formula.
Question 4: What is the purpose of using aluminium in water treatment?
Answer:
Aluminum is used in water treatment to eliminate disease-causing germs and other contaminants from drinking water that might harm your health. When treated appropriately, the quantity of residual aluminium remaining in the water should be comparable to or lower than that of untreated water.
Question 5: Is aluminium toxic in water?
Answer:
The EPA initially issued aluminium guidelines in 1988 in order to safeguard aquatic life from the adverse effects of aluminium toxicity in freshwaters.
Aluminum can impair an aquatic organism’s capacity to control salt concentrations and clog fish gills, potentially leading to death or impairing development and reproduction.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...