AKS Primality Test
Last Updated :
01 Sep, 2022
There are several primality test available to check whether the number is prime or not like Fermat’s Theorem, Miller-Rabin Primality test and alot more. But problem with all of them is that they all are probabilistic in nature. So, here comes one another method i.e AKS primality test (Agrawal–Kayal–Saxena primality test) and it is deterministically correct for any general number.
Features of AKS primality test :
1. The AKS algorithm can be used to verify the primality of any general number given.
2. The maximum running time of the algorithm can be expressed as a polynomial over the number of digits in the target number.
3. The algorithm is guaranteed to distinguish deterministically whether the target number is prime or composite.
4. The correctness of AKS is not conditional on any subsidiary unproven hypothesis.
The AKS primality test is based upon the following theorem: An integer n greater than 2 is prime if and only if the polynomial congruence relation
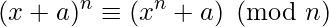
holds for some a coprime to n. Here x is just a formal symbol .
The AKS test evaluates the equality by making complexity dependent on the size of r . This is expressed as
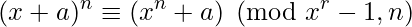
which can be expressed in simpler term as
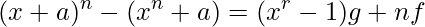
for some polynomials f and g .
This congruence can be checked in polynomial time when r is polynomial to the digits of n. The AKS algorithm evaluates this congruence for a large set of a values, whose size is polynomial to the digits of n. The proof of validity of the AKS algorithm shows that one can find r and a set of a values with the above properties such that if the congruences hold then n is a power of a prime. The brute force approach would require the expansion of the (x – a)^n polynomial and a reduction (mod n) of the resulting n + 1 coefficients .
As a should be co-prime to n. So, to implement this algorithm we can check by taking a = 1, but for large values of n we should take large values of a.
The algorithm is based on the condition that if n is any number, then it is prime if,
( x – 1 )^n – ( x^n – 1) is divisible by n.
Checking for n = 3 :
(x-1)^3 – (x^3 – 1)
= (x^3 – 3x^2 + 3x – 1) – (x^3 – 1)
= -3x^2 + 3x
As all the coefficients are divisible by n i.e. 3, so 3 (n) is prime. As the number increases, size increases.
The code here is based on this condition and can check primes till 64 .
Below is the implementation of above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
long long c[100];
void coef(int n)
{
c[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; c[0] = -c[0], i++) {
c[1 + i] = 1;
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--)
c[j] = c[j - 1] - c[j];
}
}
bool isPrime(int n)
{
coef(n);
c[0]++, c[n]--;
int i = n;
while (i-- && c[i] % n == 0)
;
return i < 0;
}
int main()
{
int n = 37;
if (isPrime(n))
cout << "Prime" << endl;
else
cout << "Not Prime" << endl;
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG {
static long c[] = new long[100];
static void coef(int n)
{
c[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; c[0] = -c[0], i++) {
c[1 + i] = 1;
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--)
c[j] = c[j - 1] - c[j];
}
}
static boolean isPrime(int n)
{
coef(n);
c[0]++;
c[n]--;
int i = n;
while ((i--) > 0 && c[i] % n == 0)
;
return i < 0;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int n = 37;
if (isPrime(n))
System.out.println("Prime");
else
System.out.println("Not Prime");
}
}
|
Python3
c = [0] * 100;
def coef(n):
c[0] = 1;
for i in range(n):
c[1 + i] = 1;
for j in range(i, 0, -1):
c[j] = c[j - 1] - c[j];
c[0] = -c[0];
def isPrime(n):
coef(n);
c[0] = c[0] + 1;
c[n] = c[n] - 1;
i = n;
while (i > -1 and c[i] % n == 0):
i = i - 1;
return True if i < 0 else False;
n = 37;
if (isPrime(n)):
print("Prime");
else:
print("Not Prime");
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static long []c = new long[100];
static void coef(int n)
{
c[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; c[0] = -c[0], i++)
{
c[1 + i] = 1;
for (int j = i; j > 0; j--)
c[j] = c[j - 1] - c[j];
}
}
static bool isPrime(int n)
{
coef(n);
c[0]++;
c[n]--;
int i = n;
while ((i--) > 0 && c[i] % n == 0)
;
return i < 0;
}
public static void Main()
{
int n = 37;
if (isPrime(n))
Console.WriteLine("Prime");
else
Console.WriteLine("Not Prime");
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
global $c;
function coef($n)
{
$c[0] = 1;
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $c[0] = -$c[0], $i++)
{
$c[1 + $i] = 1;
for ($j = $i; $j > 0; $j--)
$c[$j] = $c[$j - 1] - $c[$j];
}
}
function isPrime($n)
{
global $c;
coef($n);
$i = $n;
while ($i-- && $c[$i] % $n == 0)
return $i < 0;
}
$n = 37;
if (isPrime($n))
echo "Not Prime", "\n";
else
echo "Prime", "\n";
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
let c = [];
function coef(n)
{
c[0] = 1;
for (let i = 0; i < n; c[0] = -c[0], i++) {
c[1 + i] = 1;
for (let j = i; j > 0; j--)
c[j] = c[j - 1] - c[j];
}
}
function isPrime(n)
{
coef(n);
c[0]++;
c[n]--;
let i = n;
while ((i--) > 0 && c[i] % n == 0)
;
return i < 0;
}
let n = 37;
if (isPrime(n))
document.write("Prime");
else
document.write("Not Prime");
</script>
|
Output:
Prime
Time complexity: O(n2)
Auxiliary space: O(1) as space taken is constant.
References:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/AKS_primality_test
https://rosettacode.org/wiki/AKS_test_for_primes#C
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HvMSRWTE2mI
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...