agetty command in Linux with Examples
Last Updated :
08 Oct, 2021
agetty is a Linux version of getty. getty short for “get tty” is a Unix program running on a host computer that manages physical or virtual terminals to allow multi-user access. Linux provides virtual terminal(tty) which is similar to the regular Linux terminal. agetty command opens a virtual terminal(tty port), prompts for a login name and invokes the /bin/login command.
Syntax:
agetty [options] port [baud_rate...] [term]
Arguments:
- port: It is a pathname relative to the /dev directory. If a “-” is specified, then this command considers that its standard input is already connected to a tty port and that a connection to a remote user has already been established.
- baud_rate, … : It is a comma-separated list of one or more baud rates. It should be specified in the descending order.
- term : It is the value to be used for the TERM environment variable.
Options:
- -8, –8bits: Assume 8-bit tty.
- -a, –autologin: Automatic login for the specified user.
- -c, –noreset: Do not reset control mode.
- -E, –remote: Typically the login(1) command is given a remote hostname when called by something such as telnetd(8). This option allows agetty to pass what it is using for a hostname to login(1) for use in utmp(5).
- -h, –flow-control: Enables CTS/RTS handshaking (flow control).
- -i, –noissue: Do not display issue file.
- -J –noclear: Do not clear the screen before prompt.
- -m, –extract-baud: Use extract baud rate during connect.
- -n, –skip-login: Do not prompt for login.
- -p, –login-pause: Wait for the user to press any key before the login prompt.
- -R, –hangup: Call vhangup() to do a virtual hangup of the specified terminal.
- -s, –keep-baud: Try to keep previously used baud rate.
- -t, –timeout: It will terminate the login session if no user name can be read within timeout seconds.
- -U, –detect-case: This is used to turn on the support for detecting uppercase-only terminal.
For more details about the options you can run the following command on the terminal:
agetty --help
Examples:
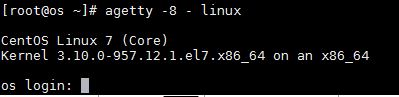
1) agetty -8 – linux
- -8 option for 8-bit tty.
- ‘-‘ for specifies that standard input is already connected to a tty port.
- baud rate is optional so not used here.
- ‘linux’ is value of TERM environment variable.
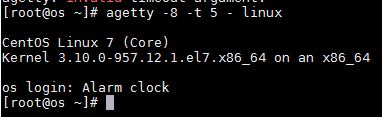
2) agetty -8 -t 5 – linux
- -t 5 is the login process timeout.
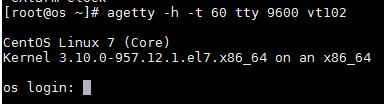
3) agetty -h -t 60 tty 9600 vtxxx
- tty refers to the device /dev/tty.
- 9600 is the bits per second bound rate.
- vtxxx is the TERM environment variable to indicate that a VTxxx terminal is connecting, in the previous example ‘linux’ is used as TERM env.
- -h activates CTS/RTS handshaking (flow control).
- -t 60 allows 60 seconds for someone to attempt to log in before the modem is hung up.
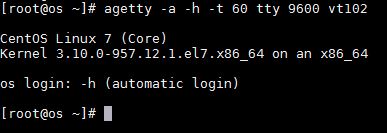
4) agetty -a -h -t 60 tty 9600 vt102
5) agetty –version To display the version information.

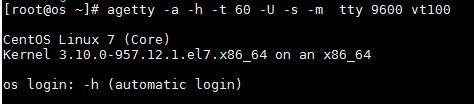
6) agetty -a -h -t 60 -U -s -m tty 9600 vt100
- -U detects the uppercase terminal.
- -s try to use existing baud rate.
- -m use exact baud rate specified in the command.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...