Access Relation Databases with Python
Last Updated :
16 Jul, 2020
Databases are powerful tools for data scientists. DB-API is Python’s standard API used for accessing databases. It allows you to write a single program that works with multiple kinds of relational databases instead of writing a separate program for each one. This is how a typical user accesses databases using Python code written on a Jupyter notebook, a Web-based editor.
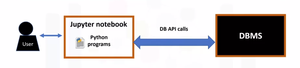
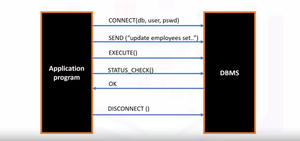
There is a mechanism by which the Python program communicates with the DBMS:
- The application program begins its database access with one or more API calls that connect the program to the DBMS.
- Then to send the SQL statement to the DBMS, the program builds the statement as a text string and then makes an API call to pass the contents to the DBMS.
- The application program makes API calls to check the status of its DBMS request and to handle errors.
- The application program ends its database access with an API call that disconnects it from the database.
The two main concepts in the Python DB-API are:
1) Connection objects used for
- Connect to a database
- Manage your transactions.
Following are a few connection methods:
- cursor(): This method returns a new cursor object using the connection.
- commit(): This method is used to commit any pending transaction to the database.
- rollback(): This method causes the database to roll back to the start of any pending transaction.
- close(): This method is used to close a database connection.
2) Query objects are used to run queries.
This is a python application that uses the DB-API to query a database.
Python3
from dbmodule import connect
connection = connect('databasename', 'username', 'pswd')
cursor = connection.cursor()
cursor.execute('select * from mytable')
results = cursor.fetchall()
cursor.close()
connection.close()
|
- First, we import the database module by using the connect API from that module. To open a connection to the database, you use the connection function and pass in the parameters that are the database name, username, and password. The connect function returns the connection object.
- After this, we create a cursor object on the connection object. The cursor is used to run queries and get the results.
- After running the queries using the cursor, we also use the cursor to fetch the results of the query.
- Finally, when the system is done running the queries, it frees all resources by closing the connection. Remember that it is always important to close connections to avoid unused connections taking up resources.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...