A Quick Overview to Computer Vision
Last Updated :
10 Jul, 2020
Computer vision means the extraction of information from images, text, videos, etc. Sometimes computer vision tries to mimic human vision. It’s a subset of computer-based intelligence or Artificial intelligence which collects information from digital images or videos and analyze them to define the attributes.
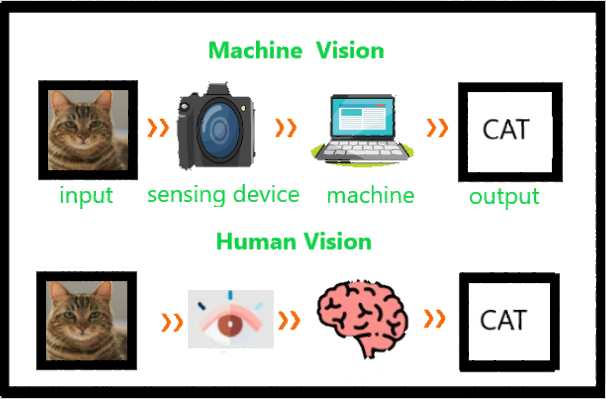
The entire process involves image acquiring, screening, analyzing, identifying, and extracting information. This extensive processing helps computers to understand any visual content and act on it accordingly. Computer vision projects translate digital visual content into precise descriptions to gather multi-dimensional data. This data is then turned into a computer-readable language to aid the decision-making process. The main objective of this branch of Artificial intelligence is to teach machines to collect information from images.
Applications of Computer Vision
- Medical Imaging: Computer vision helps in MRI reconstruction, automatic pathology, diagnosis, and computer aided surgeries and more.
- AR/VR: Object occlusion, outside-in tracking, and inside-out tracking for virtual and augmented reality.
- Smartphones: All the photo filters (including animation filters on social media), QR code scanners, panorama construction, Computational photography, face detectors, image detectors like (Google Lens, Night Sight) that we use are computer vision applications.
- Internet: Image search, Mapping, photo captioning, Ariel imaging for maps, video categorization and more.
Computer Vision with OpenCV
OpenCV (Open Source Computer Vision), a cross-platform and free to use library of functions is based on real-time Computer Vision which supports Deep Learning frameworks that aids in image and video processing. In Computer Vision, the principal element is to extract the pixels from the image to study the objects and thus understand what it contains. Below are a few key aspects that Computer Vision seeks to recognize in the photographs:
- Object Detection: The location of the object.
- Object Recognition: The objects in the image, and their positions.
- Object Classification: The broad category that the object lies in.
- Object Segmentation: The pixels belonging to that object.
Need of Computer Vision
From selfies to landscape images, we are flooded with all kinds of photos today. A report by Internet Trends says people upload more than 1.8 billion photos daily, and that’s just the number of uploaded images. Consider what the number would come to if you count the images stored in phones. We consume more than 4, 146, 600 videos on YouTube and send 103, 447, 520 spam mails daily. Again, that’s just a part of it – communication, media, and entertainment, the IoT are all actively contributing to this number. This abundantly available visual content demands analyzing and understanding and Computer vision helps in doing that by way of teaching machines to “see” these images and videos.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...