Reverse a Linked List
Last Updated :
02 Apr, 2024
Given a pointer to the head node of a linked list, the task is to reverse the linked list. We need to reverse the list by changing the links between nodes.
Examples:
Input: Head of following linked list
1->2->3->4->NULL
Output: Linked list should be changed to,
4->3->2->1->NULL
Input: Head of following linked list
1->2->3->4->5->NULL
Output: Linked list should be changed to,
5->4->3->2->1->NULL
Input: NULL
Output: NULL
Input: 1->NULL
Output: 1->NULL
Reverse a linked list by Iterative Method:
The idea is to use three pointers curr, prev, and next to keep track of nodes to update reverse links.
Illustration:
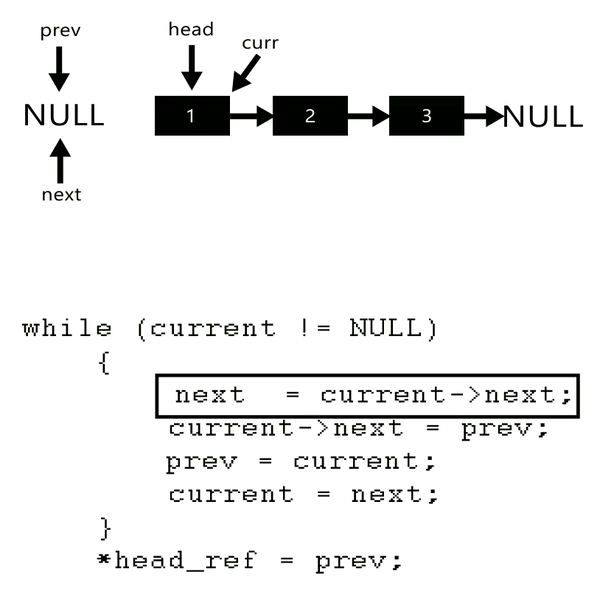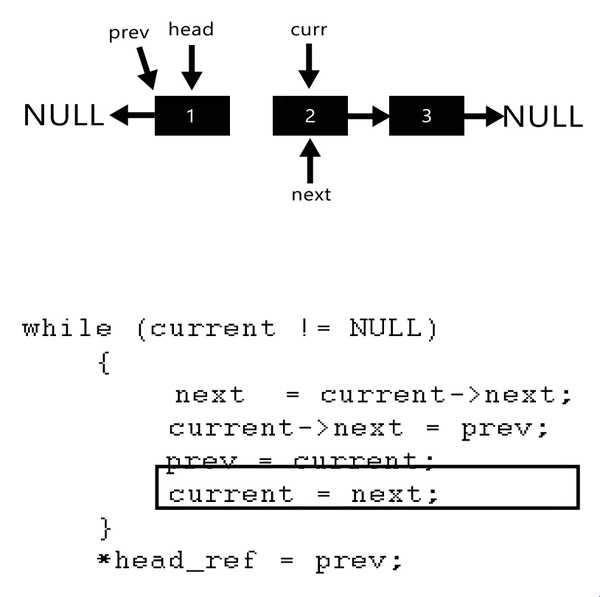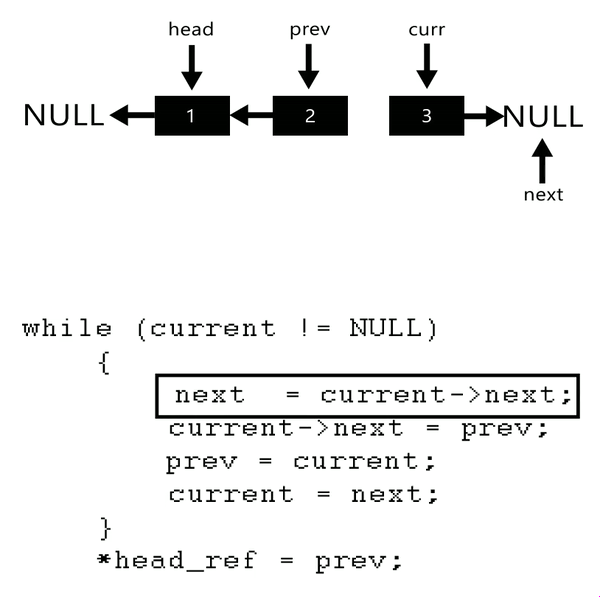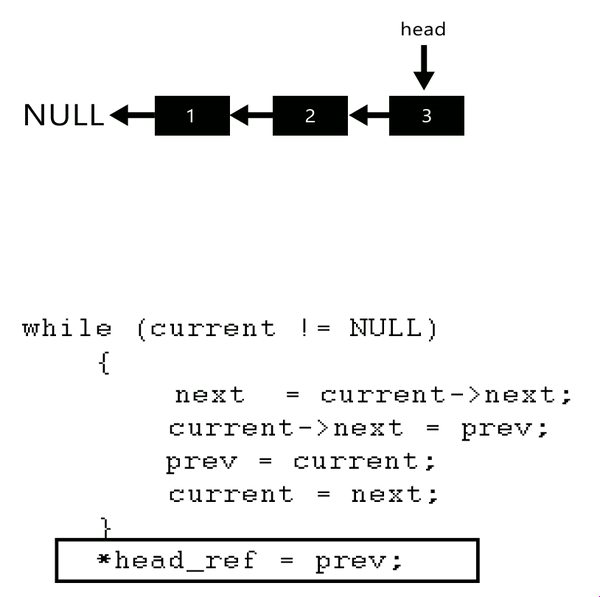
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Initialize three pointers prev as NULL, curr as head, and next as NULL.
- Iterate through the linked list. In a loop, do the following:
- Before changing the next of curr, store the next node
- Now update the next pointer of curr to the prev
- Update prev as curr and curr as next
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// Iterative C++ program to reverse a linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
next = NULL;
}
};
struct LinkedList {
Node* head;
LinkedList() { head = NULL; }
/* Function to reverse the linked list */
void reverse()
{
// Initialize current, previous and next pointers
Node* current = head;
Node *prev = NULL, *next = NULL;
while (current != NULL) {
// Store next
next = current->next;
// Reverse current node's pointer
current->next = prev;
// Move pointers one position ahead.
prev = current;
current = next;
}
head = prev;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void print()
{
struct Node* temp = head;
while (temp != NULL) {
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
}
void push(int data)
{
Node* temp = new Node(data);
temp->next = head;
head = temp;
}
};
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
LinkedList ll;
ll.push(20);
ll.push(4);
ll.push(15);
ll.push(85);
cout << "Given linked list\n";
ll.print();
ll.reverse();
cout << "\nReversed linked list \n";
ll.print();
return 0;
}
// Iterative C program to reverse a linked list
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
/* Function to reverse the linked list */
static void reverse(struct Node** head_ref)
{
struct Node* prev = NULL;
struct Node* current = *head_ref;
struct Node* next = NULL;
while (current != NULL) {
// Store next
next = current->next;
// Reverse current node's pointer
current->next = prev;
// Move pointers one position ahead.
prev = current;
current = next;
}
*head_ref = prev;
}
/* Function to push a node */
void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
struct Node* new_node
= (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
new_node->data = new_data;
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void printList(struct Node* head)
{
struct Node* temp = head;
while (temp != NULL) {
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
}
}
/* Driver code*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
struct Node* head = NULL;
push(&head, 20);
push(&head, 4);
push(&head, 15);
push(&head, 85);
printf("Given linked list\n");
printList(head);
reverse(&head);
printf("\nReversed linked list \n");
printList(head);
getchar();
}
// Java program for reversing the linked list
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
/* Function to reverse the linked list */
Node reverse(Node node)
{
Node prev = null;
Node current = node;
Node next = null;
while (current != null) {
next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
node = prev;
return node;
}
// prints content of double linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(85);
list.head.next = new Node(15);
list.head.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(20);
System.out.println("Given linked list");
list.printList(head);
head = list.reverse(head);
System.out.println("");
System.out.println("Reversed linked list ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
// This code has been contributed by Mayank Jaiswal
// C# program for reversing the linked list
using System;
class GFG {
// Driver Code
static void Main(string[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.AddNode(new LinkedList.Node(85));
list.AddNode(new LinkedList.Node(15));
list.AddNode(new LinkedList.Node(4));
list.AddNode(new LinkedList.Node(20));
// List before reversal
Console.WriteLine("Given linked list ");
list.PrintList();
// Reverse the list
list.ReverseList();
// List after reversal
Console.WriteLine("Reversed linked list ");
list.PrintList();
}
}
class LinkedList {
Node head;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// function to add a new node at
// the end of the list
public void AddNode(Node node)
{
if (head == null)
head = node;
else {
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) {
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = node;
}
}
// function to reverse the list
public void ReverseList()
{
Node prev = null, current = head, next = null;
while (current != null) {
next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
head = prev;
}
// function to print the list data
public void PrintList()
{
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
Console.Write(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Mayank Sharma
<script>
// JavaScript program for reversing the linked list
var head;
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
/* Function to reverse the linked list */
function reverse(node) {
var prev = null;
var current = node;
var next = null;
while (current != null) {
next = current.next;
current.next = prev;
prev = current;
current = next;
}
node = prev;
return node;
}
// prints content of double linked list
function printList(node) {
while (node != null) {
document.write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver Code
head = new Node(85);
head.next = new Node(15);
head.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next = new Node(20);
document.write("Given linked list<br/>");
printList(head);
head = reverse(head);
document.write("<br/>");
document.write("Reversed linked list<br/> ");
printList(head);
// This code is contributed by todaysgaurav
</script>
# Python program to reverse a linked list
# Time Complexity : O(n)
# Space Complexity : O(1)
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Function to reverse the linked list
def reverse(self):
prev = None
current = self.head
while(current is not None):
next = current.next
current.next = prev
prev = current
current = next
self.head = prev
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to print the LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print(temp.data, end=" ")
temp = temp.next
# Driver code
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(20)
llist.push(4)
llist.push(15)
llist.push(85)
print ("Given linked list")
llist.printList()
llist.reverse()
print ("\nReversed linked list")
llist.printList()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
OutputGiven linked list
85 15 4 20
Reversed linked list
20 4 15 85
Time Complexity: O(N), Traversing over the linked list of size N.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Reverse a linked list using Recursion:
The idea is to reach the last node of the linked list using recursion then start reversing the linked list.
Illustration:
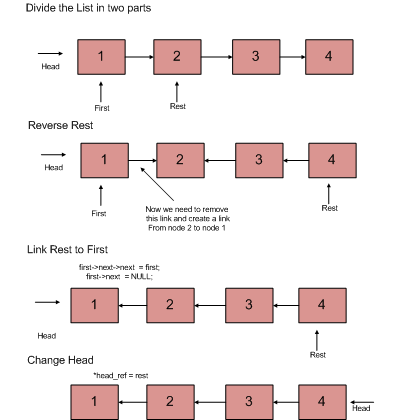
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Divide the list in two parts – first node and rest of the linked list.
- Call reverse for the rest of the linked list.
- Link the rest linked list to first.
- Fix head pointer to NULL
Below is the implementation of above approach:
C++
// Recursive C++ program to reverse
// a linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* Link list node */
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
Node(int data)
{
this->data = data;
next = NULL;
}
};
struct LinkedList {
Node* head;
LinkedList() { head = NULL; }
Node* reverse(Node* head)
{
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL)
return head;
/* reverse the rest list and put
the first element at the end */
Node* rest = reverse(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
/* tricky step -- see the diagram */
head->next = NULL;
/* fix the head pointer */
return rest;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
void print()
{
struct Node* temp = head;
while (temp != NULL) {
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
}
void push(int data)
{
Node* temp = new Node(data);
temp->next = head;
head = temp;
}
};
/* Driver program to test above function*/
int main()
{
/* Start with the empty list */
LinkedList ll;
ll.push(20);
ll.push(4);
ll.push(15);
ll.push(85);
cout << "Given linked list\n";
ll.print();
ll.head = ll.reverse(ll.head);
cout << "\nReversed linked list \n";
ll.print();
return 0;
}
// Recursive Java program to reverse
// a linked list
import java.io.*;
class recursion {
static Node head; // head of list
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
static Node reverse(Node head)
{
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
/* reverse the rest list and put
the first element at the end */
Node rest = reverse(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
/* tricky step -- see the diagram */
head.next = null;
/* fix the head pointer */
return rest;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
static void print()
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
static void push(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node(data);
temp.next = head;
head = temp;
}
/* Driver program to test above function*/
public static void main(String args[])
{
/* Start with the empty list */
push(20);
push(4);
push(15);
push(85);
System.out.println("Given linked list");
print();
head = reverse(head);
System.out.println("Reversed linked list");
print();
}
}
// This code is contributed by Prakhar Agarwal
// Recursive C# program to
// reverse a linked list
using System;
class recursion {
// Head of list
static Node head;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
static Node reverse(Node head)
{
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
// Reverse the rest list and put
// the first element at the end
Node rest = reverse(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
// Tricky step --
// see the diagram
head.next = null;
// Fix the head pointer
return rest;
}
// Function to print linked list
static void print()
{
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
Console.WriteLine();
}
static void push(int data)
{
Node temp = new Node(data);
temp.next = head;
head = temp;
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
// Start with the
// empty list
push(20);
push(4);
push(15);
push(85);
Console.WriteLine("Given linked list");
print();
head = reverse(head);
Console.WriteLine("Reversed linked list");
print();
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
<script>
// Recursive javascript program to reverse
// a linked list
var head; // head of list
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
function reverse(head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
/*
* reverse the rest list and put the first element at the end
*/
var rest = reverse(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
/* tricky step -- see the diagram */
head.next = null;
/* fix the head pointer */
return rest;
}
/* Function to print linked list */
function print() {
var temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
document.write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
document.write();
}
function push(data) {
var temp = new Node(data);
temp.next = head;
head = temp;
}
/* Driver program to test above function */
/* Start with the empty list */
push(20);
push(4);
push(15);
push(85);
document.write("Given linked list<br/>");
print();
head = reverse(head);
document.write("<br/>Reversed Linked list<br/>");
print();
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
"""Python3 program to reverse linked list
using recursive method"""
# Linked List Node
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
# Create and Handle list operations
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None # Head of list
# Method to reverse the list
def reverse(self, head):
# If head is empty or has reached the list end
if head is None or head.next is None:
return head
# Reverse the rest list
rest = self.reverse(head.next)
# Put first element at the end
head.next.next = head
head.next = None
# Fix the header pointer
return rest
# Returns the linked list in display format
def __str__(self):
linkedListStr = ""
temp = self.head
while temp:
linkedListStr = (linkedListStr +
str(temp.data) + " ")
temp = temp.next
return linkedListStr
# Pushes new data to the head of the list
def push(self, data):
temp = Node(data)
temp.next = self.head
self.head = temp
# Driver code
linkedList = LinkedList()
linkedList.push(20)
linkedList.push(4)
linkedList.push(15)
linkedList.push(85)
print("Given linked list")
print(linkedList)
linkedList.head = linkedList.reverse(linkedList.head)
print("Reversed linked list")
print(linkedList)
# This code is contributed by Debidutta Rath
OutputGiven linked list
85 15 4 20
Reversed linked list
20 4 15 85
Time Complexity: O(N), Visiting over every node one time
Auxiliary Space: O(N), Function call stack space
Reverse a linked list by Tail Recursive Method:
The idea is to maintain three pointers previous, current and next, recursively visit every node and make links using these three pointers.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- First update next with next node of current i.e. next = current->next
- Now make a reverse link from current node to previous node i.e. curr->next = prev
- If the visited node is the last node then just make a reverse link from the current node to previous node and update head.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// A simple and tail recursive C++ program to reverse
// a linked list
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
};
void reverseUtil(Node* curr, Node* prev, Node** head);
// This function mainly calls reverseUtil()
// with prev as NULL
void reverse(Node** head)
{
if (!head)
return;
reverseUtil(*head, NULL, head);
}
// A simple and tail-recursive function to reverse
// a linked list. prev is passed as NULL initially.
void reverseUtil(Node* curr, Node* prev, Node** head)
{
/* If last node mark it head*/
if (!curr->next) {
*head = curr;
/* Update next to prev node */
curr->next = prev;
return;
}
/* Save curr->next node for recursive call */
Node* next = curr->next;
/* and update next ..*/
curr->next = prev;
reverseUtil(next, curr, head);
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printlist(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
cout << head->data << " ";
head = head->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node* head1 = new Node(1);
head1->next = new Node(2);
head1->next->next = new Node(3);
head1->next->next->next = new Node(4);
head1->next->next->next->next = new Node(5);
head1->next->next->next->next->next = new Node(6);
head1->next->next->next->next->next->next = new Node(7);
head1->next->next->next->next->next->next->next
= new Node(8);
cout << "Given linked list\n";
printlist(head1);
reverse(&head1);
cout << "Reversed linked list\n";
printlist(head1);
return 0;
}
// A simple and tail recursive C program to reverse a linked
// list
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
} Node;
void reverseUtil(Node* curr, Node* prev, Node** head);
// This function mainly calls reverseUtil()
// with prev as NULL
void reverse(Node** head)
{
if (!head)
return;
reverseUtil(*head, NULL, head);
}
// A simple and tail-recursive function to reverse
// a linked list. prev is passed as NULL initially.
void reverseUtil(Node* curr, Node* prev, Node** head)
{
/* If last node mark it head*/
if (!curr->next) {
*head = curr;
/* Update next to prev node */
curr->next = prev;
return;
}
/* Save curr->next node for recursive call */
Node* next = curr->next;
/* and update next ..*/
curr->next = prev;
reverseUtil(next, curr, head);
}
// A utility function to create a new node
Node* newNode(int key)
{
Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
temp->data = key;
temp->next = NULL;
return temp;
}
// A utility function to print a linked list
void printlist(Node* head)
{
while (head != NULL) {
printf("%d ", head->data);
head = head->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
Node* head1 = newNode(1);
head1->next = newNode(2);
head1->next->next = newNode(3);
head1->next->next->next = newNode(4);
head1->next->next->next->next = newNode(5);
head1->next->next->next->next->next = newNode(6);
head1->next->next->next->next->next->next = newNode(7);
head1->next->next->next->next->next->next->next
= newNode(8);
printf("Given linked list\n");
printlist(head1);
reverse(&head1);
printf("Reversed linked list\n");
printlist(head1);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
// Java program for reversing the Linked list
class LinkedList {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// A simple and tail recursive function to reverse
// a linked list. prev is passed as NULL initially.
Node reverseUtil(Node curr, Node prev)
{
/*If head is initially null OR list is empty*/
if (head == null)
return head;
/* If last node mark it head*/
if (curr.next == null) {
head = curr;
/* Update next to prev node */
curr.next = prev;
return head;
}
/* Save curr->next node for recursive call */
Node next1 = curr.next;
/* and update next ..*/
curr.next = prev;
reverseUtil(next1, curr);
return head;
}
// prints content of double linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(1);
list.head.next = new Node(2);
list.head.next.next = new Node(3);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
list.head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
list.head.next.next.next.next.next.next
= new Node(7);
list.head.next.next.next.next.next.next.next
= new Node(8);
System.out.println("Given linked list ");
list.printList(head);
Node res = list.reverseUtil(head, null);
System.out.println("\nReversed linked list ");
list.printList(res);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
// C# program for reversing the Linked list
using System;
public class LinkedList {
Node head;
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
// A simple and tail-recursive function to reverse
// a linked list. prev is passed as NULL initially.
Node reverseUtil(Node curr, Node prev)
{
/* If last node mark it head*/
if (curr.next == null) {
head = curr;
/* Update next to prev node */
curr.next = prev;
return head;
}
/* Save curr->next node for recursive call */
Node next1 = curr.next;
/* and update next ..*/
curr.next = prev;
reverseUtil(next1, curr);
return head;
}
// prints content of double linked list
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
Console.Write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
list.head = new Node(1);
list.head.next = new Node(2);
list.head.next.next = new Node(3);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
list.head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
list.head.next.next.next.next.next.next
= new Node(7);
list.head.next.next.next.next.next.next.next
= new Node(8);
Console.WriteLine("Given linked list ");
list.printList(list.head);
Node res = list.reverseUtil(list.head, null);
Console.WriteLine("\nReversed linked list ");
list.printList(res);
}
}
// This code contributed by Rajput-Ji
<script>
// javascript program for reversing the Linked list
var head;
class Node {
constructor(d) {
this.data = d;
this.next = null;
}
}
// A simple and tail recursive function to reverse
// a linked list. prev is passed as NULL initially.
function reverseUtil(curr, prev)
{
/* If head is initially null OR list is empty */
if (head == null)
return head;
/* If last node mark it head */
if (curr.next == null) {
head = curr;
/* Update next to prev node */
curr.next = prev;
return head;
}
/* Save curr->next node for recursive call */
var next1 = curr.next;
/* and update next .. */
curr.next = prev;
reverseUtil(next1, curr);
return head;
}
// prints content of var linked list
function printList(node) {
while (node != null) {
document.write(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
// Driver Code
var head = new Node(1);
head.next = new Node(2);
head.next.next = new Node(3);
head.next.next.next = new Node(4);
head.next.next.next.next = new Node(5);
head.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(6);
head.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(7);
head.next.next.next.next.next.next.next = new Node(8);
document.write("Original Linked list<br/> ");
printList(head);
var res = reverseUtil(head, null);
document.write("<br/>");
document.write("Reversed linked list <br/>");
printList(res);
// This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji
</script>
# Simple and tail recursive Python program to
# reverse a linked list
# Node class
class Node:
# Constructor to initialize the node object
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
# Function to initialize head
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def reverseUtil(self, curr, prev):
# If last node mark it head
if curr.next is None:
self.head = curr
# Update next to prev node
curr.next = prev
return
# Save curr.next node for recursive call
next = curr.next
# And update next
curr.next = prev
self.reverseUtil(next, curr)
# This function mainly calls reverseUtil()
# with previous as None
def reverse(self):
if self.head is None:
return
self.reverseUtil(self.head, None)
# Function to insert a new node at the beginning
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
# Utility function to print the linked LinkedList
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
while(temp):
print (temp.data, end=" ")
temp = temp.next
# Driver code
llist = LinkedList()
llist.push(8)
llist.push(7)
llist.push(6)
llist.push(5)
llist.push(4)
llist.push(3)
llist.push(2)
llist.push(1)
print ("Given linked list")
llist.printList()
llist.reverse()
print ("\nReversed linked list")
llist.printList()
# This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007)
OutputGiven linked list
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Reversed linked list
8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1
Time Complexity: O(N), Visiting every node of the linked list of size N.
Auxiliary Space: O(N), Function call stack space
Reverse a linked list using Stack:
The idea is to store the all the nodes in the stack then make a reverse linked list.
Follow the steps below to solve the problem:
- Store the nodes(values and address) in the stack until all the values are entered.
- Once all entries are done, Update the Head pointer to the last location(i.e the last value).
- Start popping the nodes(value and address) and store them in the same order until the stack is empty.
- Update the next pointer of last Node in the stack by NULL.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program for above approach
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Create a class Node to enter values and address in the
// list
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node* next;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = NULL;
}
};
// Function to reverse the linked list
void reverseLL(Node** head)
{
// Create a stack "s" of Node type
stack<Node*> s;
Node* temp = *head;
while (temp->next != NULL) {
// Push all the nodes in to stack
s.push(temp);
temp = temp->next;
}
*head = temp;
while (!s.empty()) {
// Store the top value of stack in list
temp->next = s.top();
// Pop the value from stack
s.pop();
// update the next pointer in the list
temp = temp->next;
}
temp->next = NULL;
}
// Function to Display the elements in List
void printlist(Node* temp)
{
while (temp != NULL) {
cout << temp->data << " ";
temp = temp->next;
}
}
// Program to insert back of the linked list
void insert_back(Node** head, int value)
{
// we have used insertion at back method to enter values
// in the list.(eg: head->1->2->3->4->Null)
Node* temp = new Node(value);
temp->next = NULL;
// If *head equals to NULL
if (*head == NULL) {
*head = temp;
return;
}
else {
Node* last_node = *head;
while (last_node->next != NULL)
last_node = last_node->next;
last_node->next = temp;
return;
}
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
Node* head = NULL;
insert_back(&head, 1);
insert_back(&head, 2);
insert_back(&head, 3);
insert_back(&head, 4);
cout << "Given linked list\n";
printlist(head);
reverseLL(&head);
cout << "\nReversed linked list\n";
printlist(head);
return 0;
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
// Java program for above approach
import java.util.*;
class GFG {
// Create a class Node to enter values and address in
// the list
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int x) {
data = x;
next = null;
}
};
static Node head = null;
// Function to reverse the linked list
static void reverseLL()
{
// Create a stack "s" of Node type
Stack<Node> s = new Stack<>();
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) {
// Push all the nodes in to stack
s.add(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
head = temp;
while (!s.isEmpty()) {
// Store the top value of stack in list
temp.next = s.peek();
// Pop the value from stack
s.pop();
// update the next pointer in the list
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = null;
}
// Function to Display the elements in List
static void printlist(Node temp)
{
while (temp != null) {
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
}
// Program to insert back of the linked list
static void insert_back(int value)
{
// we have used insertion at back method to enter
// values in the list.(eg: head.1.2.3.4.Null)
Node temp = new Node(value);
temp.next = null;
// If *head equals to null
if (head == null) {
head = temp;
return;
}
else {
Node last_node = head;
while (last_node.next != null)
last_node = last_node.next;
last_node.next = temp;
return;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void main(String[] args)
{
insert_back(1);
insert_back(2);
insert_back(3);
insert_back(4);
System.out.print("Given linked list\n");
printlist(head);
reverseLL();
System.out.print("\nReversed linked list\n");
printlist(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by Aditya Kumar (adityakumar129)
// C# program for above approach
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class GFG {
// Create a class Node to enter
// values and address in the list
public class Node {
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int x) {
data = x;
}
};
static Node head = null;
// Function to reverse the
// linked list
static void reverseLL()
{
// Create a stack "s"
// of Node type
Stack<Node> s = new Stack<Node>();
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null) {
// Push all the nodes
// in to stack
s.Push(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
head = temp;
while (s.Count != 0) {
// Store the top value of
// stack in list
temp.next = s.Peek();
// Pop the value from stack
s.Pop();
// Update the next pointer in the
// in the list
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = null;
}
// Function to Display
// the elements in List
static void printlist(Node temp)
{
while (temp != null) {
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
}
// Function to insert back of the
// linked list
static void insert_back(int val)
{
// We have used insertion at back method
// to enter values in the list.(eg:
// head.1.2.3.4.Null)
Node temp = new Node(val);
temp.next = null;
// If *head equals to null
if (head == null) {
head = temp;
return;
}
else {
Node last_node = head;
while (last_node.next != null) {
last_node = last_node.next;
}
last_node.next = temp;
return;
}
}
// Driver Code
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
insert_back(1);
insert_back(2);
insert_back(3);
insert_back(4);
Console.Write("Given linked list\n");
printlist(head);
reverseLL();
Console.Write("\nReversed linked list\n");
printlist(head);
}
}
// This code is contributed by gauravrajput1
<script>
// javascript program for above approach
// Create a class Node to enter
// values and address in the list
class Node
{
constructor(x){
this.data = x;
this.next = null;
}
}
var head = null;
// Function to reverse the
// linked list
function reverseLL()
{
// Create a stack "s"
// of Node type
var s = [];
var temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
{
// Push all the nodes
// in to stack
s.push(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
head = temp;
while (s.length!=0)
{
// Store the top value of
// stack in list
temp.next = s.pop();
// update the next pointer in the
// in the list
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = null;
}
// Function to Display
// the elements in List
function printlist(temp)
{
while (temp != null)
{
document.write(temp.data+ " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
}
// Program to insert back of the
// linked list
function insert_back( value)
{
// we have used insertion at back method
// to enter values in the list.(eg:
// head.1.2.3.4.Null)
var temp = new Node(value);
temp.next = null;
// If *head equals to null
if (head == null)
{
head = temp;
return;
}
else
{
var last_node = head;
while (last_node.next != null)
{
last_node = last_node.next;
}
last_node.next = temp;
return;
}
}
// Driver Code
insert_back(1);
insert_back(2);
insert_back(3);
insert_back(4);
document.write("Given linked list\n");
printlist(head);
reverseLL();
document.write("<br/>Reversed linked list\n");
printlist(head);
// This code is contributed by umadevi9616
</script>
# Python code for the above approach
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val = 0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
# Program to reverse the linked list
# using stack
def reverseLLUsingStack(self, head):
# Initialise the variables
stack, temp = [], head
while temp:
stack.append(temp)
temp = temp.next
head = temp = stack.pop()
# Until stack is not
# empty
while len(stack) > 0:
temp.next = stack.pop()
temp = temp.next
temp.next = None
return head
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
head = ListNode(1, ListNode(2, ListNode(3, ListNode(4))))
print("Given linked list")
temp = head
while temp:
print(temp.val, end=' ')
temp = temp.next
obj = Solution()
print("\nReversed linked list")
head = obj.reverseLLUsingStack(head)
while head:
print(head.val, end=' ')
head = head.next
OutputGiven linked list
1 2 3 4
Reversed linked list
4 3 2 1
Time Complexity: O(N), Visiting every node of the linked list of size N.
Auxiliary Space: O(N), Space is used to store the nodes in the stack.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...