8085 program to access and exchange the content of Flag register with register B
Last Updated :
11 Apr, 2023
Problem – Write an assembly language program in 8085 microprocessor to access Flag register and exchange the content of flag register F with register B.
Example –
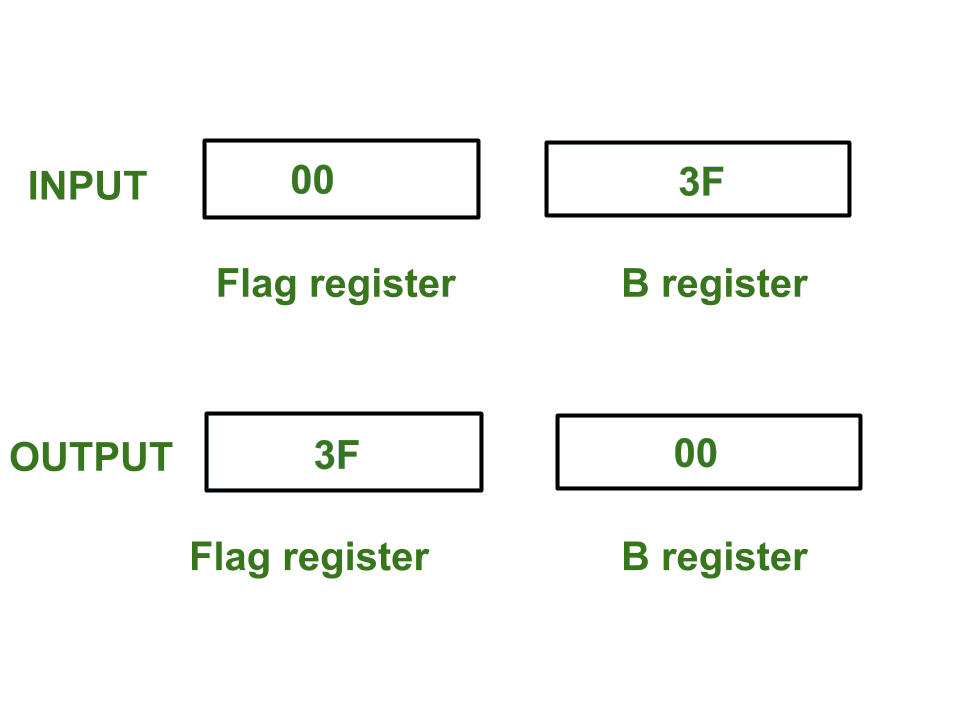
Assumptions – Initial values of flag register, register B and stack pointer are is 00, 3F, and 3FFF respectively.
PSW stands for PROGRAM STATUS WORD. PSW combines accumulator A and flag register F.
Algorithm –
- Push the value of PSW in-memory stack with the help of PUSH instruction
- Pop the value of the Flag register and store it in register H with help of POP instruction
- Move the value of register L in register C [ H -> ACCUMULATOR VALUE, L-> FLAG REGISTER VALUE]
- Move the value of register B in register L
- Move the value of register C in register B
- Push the value of register H in-memory stack with the help of PUSH instruction
- Pop the value of PSW from the memory stack using POP instruction
Program –
MVI B , 3FH
PUSH PSW
POP H
MOV C , L
MOV L , B
MOV B , C
PUSH H
POP PSW
HLT
| MEMORY ADDRESS |
MNEMONICS |
COMMENT |
| 2000 |
PUSH PSW |
Push value of accumulator and flag in stack |
| 2001 |
POP H |
Pop value from TOP of memory stack in H |
| 2002 |
MOV C, L |
C <- L |
| 2003 |
MOV H, L |
L <- B |
| 2004 |
MOV B, L |
B <- C |
| 2005 |
PUSH H |
Push the value of register H |
| 2006 |
POP PSW |
Pop value of flag register and Accumulator |
| 2007 |
HLT |
END |
Explanation – Registers used A, B, C, H, F
- PUSH PSW instruction performs the following task:
SP <- SP - 1
M[SP] <- A
SP <- SP - 1
M[SP] <- F
- POP H instruction performs the following task:
H <- M[SP]
SP <- SP + 1
- MOV C, L – moves the value of L in register C as we know that H contains the accumulator value and L contains flag register value
- MOV L, B – moves the value of B in register L, hence L is updated
- MOV B, C – moves the value of C in register B, hence B is updated
- PUSH H performs the following task:
SP <- SP - 1
M[SP] <- H
- POP PSW performs the following task:
F <- M[SP]
SP <- SP + 1
A <- M[SP]
SP <- SP + 1
- HLT – stops executing the program and halts any further execution
Advantages:
- The program is a useful utility program for accessing and exchanging the contents of the Flag register with another register.
- It can be customized to exchange the Flag register contents with other registers as well, by modifying the instructions to load and store the register values.
Disadvantages:
- The program is not optimized for speed, as it uses multiple instructions to move each byte of data and push/pop the stack.
- The program requires the use of a stack, which can be a limited resource in some applications.
- The program does not check for errors or boundary conditions, such as when the register contents exceed the valid range or when the stack overflows.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...