2D Transformation | Rotation of objects
Last Updated :
17 Mar, 2023
We have to rotate an object by a given angle about a given pivot point and print the new co-ordinates.
Examples:
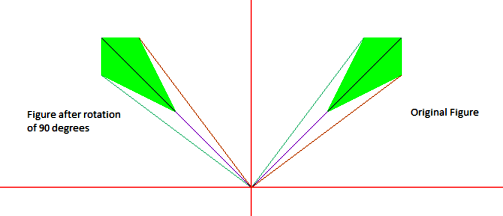
Input : {(100, 100), (150, 200), (200, 200),
(200, 150)} is to be rotated about
(0, 0) by 90 degrees
Output : (-100, 100), (-200, 150), (-200, 200), (-150, 200)
Input : {(100, 100), (100, 200), (200, 200)}
is to be rotated about (50, -50) by
-45 degrees
Output : (191.421, 20.7107), (262.132, 91.4214),
(332.843, 20.7107)

In order to rotate an object we need to rotate each vertex of the figure individually.
On rotating a point P(x, y) by an angle A about the origin we get a point P'(x’, y’). The values of x’ and y’ can be calculated as follows:-

We know that,
x = rcosB, y = rsinB
x’ = rcos(A+B) = r(cosAcosB – sinAsinB) = rcosBcosA – rsinBsinA = xcosA – ysinA
y’ = rsin(A+B) = r(sinAcosB + cosAsinB) = rcosBsinA + rsinBcosA = xsinA + ycosA
Rotational Matrix Equation:-
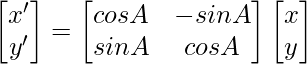
CPP
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
#define SIN(x) sin(x * 3.141592653589 / 180)
#define COS(x) cos(x * 3.141592653589 / 180)
void rotate(float a[][2], int n, int x_pivot, int y_pivot,
int angle)
{
int i = 0;
while (i < n) {
int x_shifted = a[i][0] - x_pivot;
int y_shifted = a[i][1] - y_pivot;
a[i][0] = x_pivot
+ (x_shifted * COS(angle)
- y_shifted * SIN(angle));
a[i][1] = y_pivot
+ (x_shifted * SIN(angle)
+ y_shifted * COS(angle));
cout << "(" << a[i][0] << ", " << a[i][1] << ") ";
i++;
}
}
int main()
{
int size1 = 4;
float points_list1[][2] = { { 100, 100 },
{ 150, 200 },
{ 200, 200 },
{ 200, 150 } };
rotate(points_list1, size1, 0, 0, 90);
return 0;
}
|
Java
public class rotation {
static void rotate(double a[][], int n, int x_pivot,
int y_pivot, int angle)
{
int i = 0;
while (i < n)
{
int x_shifted = (int)a[i][0] - x_pivot;
int y_shifted = (int)a[i][1] - y_pivot;
double x = Math.toRadians(angle);
a[i][0] = x_pivot
+ (x_shifted * Math.cos(x)
- y_shifted * Math.sin(x));
a[i][1] = y_pivot
+ (x_shifted * Math.sin(x)
+ y_shifted * Math.cos(x));
System.out.printf("(%f, %f) ", a[i][0],
a[i][1]);
i++;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int size1 = 4;
double points_list1[][] = { { 100, 100 },
{ 150, 200 },
{ 200, 200 },
{ 200, 150 } };
rotate(points_list1, size1, 0, 0, 90);
}
}
|
Python3
import math
SIN=lambda x: int(math.sin(x * 3.141592653589 / 180))
COS=lambda x: int(math.cos(x * 3.141592653589 / 180))
def rotate(a, n, x_pivot, y_pivot, angle):
i = 0
while (i < n) :
x_shifted = a[i][0] - x_pivot
y_shifted = a[i][1] - y_pivot
a[i][0] = x_pivot + (x_shifted * COS(angle) - y_shifted * SIN(angle))
a[i][1] = y_pivot + (x_shifted * SIN(angle) + y_shifted * COS(angle))
print("({}, {}) ".format(a[i][0], a[i][1]),end=" ")
i+=1
if __name__=='__main__':
size1 = 4
points_list1 = [[ 100, 100],
[ 150, 200],
[ 200, 200],
[ 200, 150],]
rotate(points_list1, size1, 0, 0, 90)
|
Javascript
const SIN = (x) => Math.sin(x * Math.PI / 180);
const COS = (x) => Math.cos(x * Math.PI / 180);
function rotate(a, n, x_pivot, y_pivot, angle) {
let i = 0;
while (i < n) {
const x_shifted = a[i][0] - x_pivot;
const y_shifted = a[i][1] - y_pivot;
a[i][0] = x_pivot + (x_shifted * COS(angle) - y_shifted * SIN(angle));
a[i][1] = y_pivot + (x_shifted * SIN(angle) + y_shifted * COS(angle));
console.log(`(${a[i][0]}, ${a[i][1]}) `);
i++;
}
}
const size1 = 4;
const points_list1 = [[ 100, 100],
[ 150, 200],
[ 200, 200],
[ 200, 150],];
rotate(points_list1, size1, 0, 0, 90);
|
C#
using System;
class rotation
{
static void rotate(double[,] a, int n,
int x_pivot, int y_pivot, int angle)
{
int i = 0;
while (i < n)
{
int x_shifted = (int)a[i, 0] - x_pivot;
int y_shifted = (int)a[i, 1] - y_pivot;
double x = Math.PI * angle / 180.0;
a[i, 0] = x_pivot + (x_shifted *
Math.Cos(x) - y_shifted *
Math.Sin(x));
a[i, 1] = y_pivot + (x_shifted *
Math.Sin(x) + y_shifted *
Math.Cos(x));
Console.Write("({0}, {1}) ",
a[i, 0], a[i, 1]);
i++;
}
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
int size1 = 4;
double[,] points_list1 = { { 100, 100 },
{ 150, 200 },
{ 200, 200 },
{ 200, 150 } };
rotate(points_list1, size1, 0, 0, 90);
}
}
|
Output:
(-100, 100), (-200, 150), (-200, 200), (-150, 200)
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
References: Rotation matrix
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...