Sorted insert for circular linked list
Last Updated :
10 Jan, 2023
Difficulty Level: Rookie
Write a C function to insert a new value in a sorted Circular Linked List (CLL). For example, if the input CLL is following.
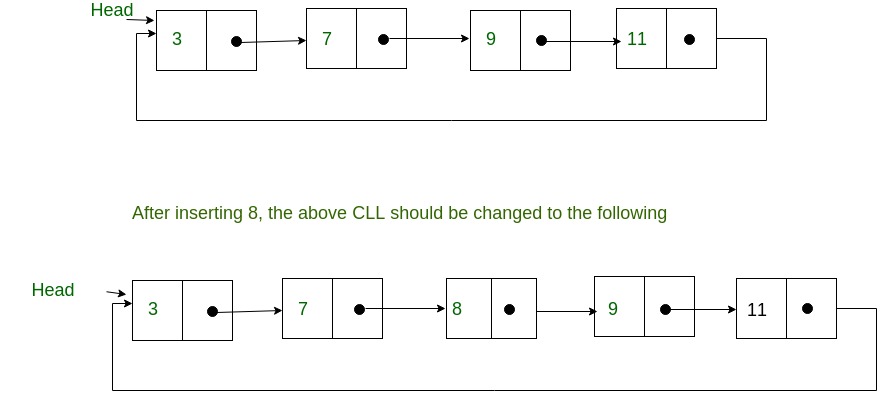
Algorithm:
Allocate memory for the newly inserted node and put data in the newly allocated node. Let the pointer to the new node be new_node. After memory allocation, following are the three cases that need to be handled.
1) Linked List is empty:
a) since new_node is the only node in CLL, make a self loop.
new_node->next = new_node;
b) change the head pointer to point to new node.
*head_ref = new_node;
2) New node is to be inserted just before the head node:
(a) Find out the last node using a loop.
while(current->next != *head_ref)
current = current->next;
(b) Change the next of last node.
current->next = new_node;
(c) Change next of new node to point to head.
new_node->next = *head_ref;
(d) change the head pointer to point to new node.
*head_ref = new_node;
3) New node is to be inserted somewhere after the head:
(a) Locate the node after which new node is to be inserted.
while ( current->next!= *head_ref &&
current->next->data < new_node->data)
{ current = current->next; }
(b) Make next of new_node as next of the located pointer
new_node->next = current->next;
(c) Change the next of the located pointer
current->next = new_node;
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Node
{
public:
int data;
Node *next;
};
void sortedInsert(Node** head_ref, Node* new_node)
{
Node* current = *head_ref;
if (current == NULL)
{
new_node->next = new_node;
*head_ref = new_node;
}
else if (current->data >= new_node->data)
{
while(current->next != *head_ref)
current = current->next;
current->next = new_node;
new_node->next = *head_ref;
*head_ref = new_node;
}
else
{
while (current->next!= *head_ref &&
current->next->data < new_node->data)
current = current->next;
new_node->next = current->next;
current->next = new_node;
}
}
void printList(Node *start)
{
Node *temp;
if(start != NULL)
{
temp = start;
do {
cout<<temp->data<<" ";
temp = temp->next;
} while(temp != start);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {12, 56, 2, 11, 1, 90};
int list_size, i;
Node *start = NULL;
Node *temp;
for (i = 0; i< 6; i++)
{
temp = new Node();
temp->data = arr[i];
sortedInsert(&start, temp);
}
printList(start);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct Node
{
int data;
struct Node *next;
};
void sortedInsert(struct Node** head_ref, struct Node* new_node)
{
struct Node* current = *head_ref;
if (current == NULL)
{
new_node->next = new_node;
*head_ref = new_node;
}
else if (current->data >= new_node->data)
{
while(current->next != *head_ref)
current = current->next;
current->next = new_node;
new_node->next = *head_ref;
*head_ref = new_node;
}
else
{
while (current->next!= *head_ref &&
current->next->data < new_node->data)
current = current->next;
new_node->next = current->next;
current->next = new_node;
}
}
void printList(struct Node *start)
{
struct Node *temp;
if(start != NULL)
{
temp = start;
printf("\n");
do {
printf("%d ", temp->data);
temp = temp->next;
} while(temp != start);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = {12, 56, 2, 11, 1, 90};
int list_size, i;
struct Node *start = NULL;
struct Node *temp;
for (i = 0; i< 6; i++)
{
temp = (struct Node *)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
temp->data = arr[i];
sortedInsert(&start, temp);
}
printList(start);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class Node
{
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList
{
Node head;
LinkedList() { head = null; }
void sortedInsert(Node new_node)
{
Node current = head;
if (current == null)
{
new_node.next = new_node;
head = new_node;
}
else if (current.data >= new_node.data)
{
while (current.next != head)
current = current.next;
current.next = new_node;
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
else
{
while (current.next != head &&
current.next.data < new_node.data)
current = current.next;
new_node.next = current.next;
current.next = new_node;
}
}
void printList()
{
if (head != null)
{
Node temp = head;
do
{
System.out.print(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != head);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
int arr[] = new int[] {12, 56, 2, 11, 1, 90};
Node temp = null;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
temp = new Node(arr[i]);
list.sortedInsert(temp);
}
list.printList();
}
}
|
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def push(self, new_data):
new_node = Node(new_data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def printList(self):
temp = self.head
print(temp.data,end=' ')
temp = temp.next
while(temp != self.head):
print (temp.data,end=' ')
temp = temp.next
def sortedInsert(self, new_node):
current = self.head
if current is None:
new_node.next = new_node
self.head = new_node
elif (current.data >= new_node.data):
while current.next != self.head :
current = current.next
current.next = new_node
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
else:
while (current.next != self.head and
current.next.data < new_node.data):
current = current.next
new_node.next = current.next
current.next = new_node
arr = [12, 56, 2, 11, 1, 90]
list_size = len(arr)
start = LinkedList()
for i in range(list_size):
temp = Node(arr[i])
start.sortedInsert(temp)
start.printList()
|
C#
using System;
class LinkedList
{
public class Node
{
public int data;
public Node next;
public Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
Node head;
LinkedList()
{
head = null;
}
void sortedInsert(Node new_node)
{
Node current = head;
if (current == null)
{
new_node.next = new_node;
head = new_node;
}
else if (current.data >= new_node.data)
{
while (current.next != head)
current = current.next;
current.next = new_node;
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
else
{
while (current.next != head &&
current.next.data < new_node.data)
current = current.next;
new_node.next = current.next;
current.next = new_node;
}
}
void printList()
{
if (head != null)
{
Node temp = head;
do
{
Console.Write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
}
while (temp != head);
}
}
public static void Main(String []args)
{
LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
int []arr = {12, 56, 2, 11, 1, 90};
Node temp = null;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++)
{
temp = new Node(arr[i]);
list.sortedInsert(temp);
}
list.printList();
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
class Node {
constructor(val) {
this.data = val;
this.next = null;
}
}
var head = null;
function sortedInsert(new_node) {
var current = head;
if (current == null) {
new_node.next = new_node;
head = new_node;
}
else if (current.data >= new_node.data) {
while (current.next != head)
current = current.next;
current.next = new_node;
new_node.next = head;
head = new_node;
}
else {
while (current.next != head && current.next.data < new_node.data)
current = current.next;
new_node.next = current.next;
current.next = new_node;
}
}
function printList() {
if (head != null) {
var temp = head;
do {
document.write(temp.data + " ");
temp = temp.next;
} while (temp != head);
}
}
var arr = [ 12, 56, 2, 11, 1, 90 ];
var temp = null;
for (i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
temp = new Node(arr[i]);
sortedInsert(temp);
}
printList();
</script>
|
Output:
1 2 11 12 56 90
Time Complexity: O(n)
Here n is the number of nodes in the given linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(1).
As constant extra space is used.
Case 2 of the above algorithm/code can be optimized. To implement the suggested change we need to modify case 2 to follow.
C
else if (current->data >= new_node->data)
{
swap(&(current->data), &(new_node->data));
new_node->next = (*head_ref)->next;
(*head_ref)->next = new_node;
}
|
C++
else if (current->data >= new_node->data)
{
swap(&(current->data), &(new_node->data));
new_node->next = (*head_ref)->next;
(*head_ref)->next = new_node;
}
|
Java
else if (current.data >= new_node.data)
{
Node tmp = current.data;
current.data = new_node.data;
new_node.data = tmp;
new_node.next = (head_ref).next;
(head_ref).next = new_node;
}
|
Python3
elif (current.data >= new_node.data):
tmp = current.data;
current.data = new_node.data;
new_node.data = tmp;
new_node.next = (head_ref).next;
(head_ref).next = new_node;
|
C#
else if (current.data >= new_node.data)
{
Node tmp = current.data;
current.data = new_node.data;
new_node.data = tmp;
new_node.next = (head_ref).next;
(head_ref).next = new_node;
}
|
Javascript
<script>
else if (current.data >= new_node.data)
{
let tmp = current.data;
current.data = new_node.data;
new_node.data = tmp;
new_node.next = (head_ref).next;
(head_ref).next = new_node;
}
</script>
|
In the previous approach the time complexity of case 2 was O(n) which is reduced to O(1) using this approach.
The auxiliary space used here is O(1) which is same as previous approach.
Please write comments if you find the above code/algorithm incorrect, or find other ways to solve the same problem.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...