Program for Method Of False Position
Last Updated :
02 Dec, 2022
Given a function f(x) on floating number x and two numbers ‘a’ and ‘b’ such that f(a)*f(b) < 0 and f(x) is continuous in [a, b]. Here f(x) represents algebraic or transcendental equation. Find root of function in interval [a, b] (Or find a value of x such that f(x) is 0).
Input: A function of x, for example x3 – x2 + 2.
And two values: a = -200 and b = 300 such that
f(a)*f(b) < 0, i.e., f(a) and f(b) have
opposite signs.
Output: The value of root is : -1.00
OR any other value close to root.
We strongly recommend to refer below post as a prerequisite of this post.
Solution of Algebraic and Transcendental Equations | Set 1 (The Bisection Method)
In this post The Method Of False Position is discussed. This method is also known as Regula Falsi or The Method of Chords.
Similarities with Bisection Method:
- Same Assumptions: This method also assumes that function is continuous in [a, b] and given two numbers ‘a’ and ‘b’ are such that f(a) * f(b) < 0.
- Always Converges: like Bisection, it always converges, usually considerably faster than Bisection–but sometimes very much more slowly than Bisection.
Differences with Bisection Method:
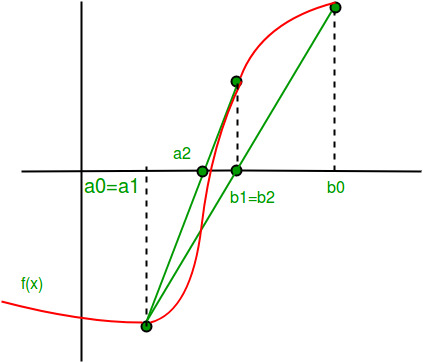
It differs in the fact that we make a chord joining the two points [a, f(a)] and [b, f(b)]. We consider the point at which the chord touches the x axis and named it as c.
Steps:
- Write equation of the line connecting the two points.
y – f(a) = ( (f(b)-f(a))/(b-a) )*(x-a)
Now we have to find the point which touches x axis.
For that we put y = 0.
so x = a - (f(a)/(f(b)-f(a))) * (b-a)
x = (a*f(b) - b*f(a)) / (f(b)-f(a))
This will be our c that is c = x.
- If f(c) == 0, then c is the root of the solution.
- Else f(c) != 0
- If value f(a)*f(c) < 0 then root lies between a and c. So we recur for a and c
- Else If f(b)*f(c) < 0 then root lies between b and c. So we recur b and c.
- Else given function doesn’t follow one of assumptions.
Since root may be a floating point number and may converge very slow in worst case, we iterate for a very large number of times such that the answer becomes closer to the root.
Following is the implementation.
C++
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_ITER 1000000
double func(double x)
{
return x*x*x - x*x + 2;
}
void regulaFalsi(double a, double b)
{
if (func(a) * func(b) >= 0)
{
cout << "You have not assumed right a and b\n";
return;
}
double c = a;
for (int i=0; i < MAX_ITER; i++)
{
c = (a*func(b) - b*func(a))/ (func(b) - func(a));
if (func(c)==0)
break;
else if (func(c)*func(a) < 0)
b = c;
else
a = c;
}
cout << "The value of root is : " << c;
}
int main()
{
double a =-200, b = 300;
regulaFalsi(a, b);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int MAX_ITER = 1000000;
static double func(double x)
{
return (x * x * x - x * x + 2);
}
static void regulaFalsi(double a, double b)
{
if (func(a) * func(b) >= 0)
{
System.out.println("You have not assumed right a and b");
}
double c = a;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_ITER; i++)
{
c = (a * func(b) - b * func(a))
/ (func(b) - func(a));
if (func(c) == 0)
break;
else if (func(c) * func(a) < 0)
b = c;
else
a = c;
}
System.out.println("The value of root is : " + (int)c);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double a = -200, b = 300;
regulaFalsi(a, b);
}
}
|
Python3
MAX_ITER = 1000000
def func( x ):
return (x * x * x - x * x + 2)
def regulaFalsi( a , b):
if func(a) * func(b) >= 0:
print("You have not assumed right a and b")
return -1
c = a
for i in range(MAX_ITER):
c = (a * func(b) - b * func(a))/ (func(b) - func(a))
if func(c) == 0:
break
elif func(c) * func(a) < 0:
b = c
else:
a = c
print("The value of root is : " , '%.4f' %c)
a =-200
b = 300
regulaFalsi(a, b)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int MAX_ITER = 1000000;
static double func(double x)
{
return (x * x * x - x * x + 2);
}
static void regulaFalsi(double a, double b)
{
if (func(a) * func(b) >= 0)
{
Console.WriteLine("You have not assumed right a and b");
}
double c = a;
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_ITER; i++)
{
c = (a * func(b) - b * func(a))
/ (func(b) - func(a));
if (func(c) == 0)
break;
else if (func(c) * func(a) < 0)
b = c;
else
a = c;
}
Console.WriteLine("The value of root is : " + (int)c);
}
public static void Main(String []args)
{
double a = -200, b = 300;
regulaFalsi(a, b);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let MAX_ITER = 1000000
function func(x){
return x*x*x - x*x + 2;
}
function regulaFalsi( a, b){
if (func(a) * func(b) >= 0){
document.write("You have not assumed right a and b\n");
return;
}
let c = a;
for (let i=0; i < MAX_ITER; i++)
{
c = Math.floor((a*func(b) - b*func(a))/ (func(b) - func(a)));
if (func(c)==0){
break;
}
else if (func(c)*func(a) < 0){
b = c;
}
else{
a = c;
}
}
document.write("The value of root is : " + c);
}
let a =-200;
let b = 300;
regulaFalsi(a, b);
</script>
|
Output
The value of root is : -1
This method always converges, usually considerably faster than Bisection. But worst case can be very slow.
We will soon be discussing other methods to solve algebraic and transcendental equations.
References:
Introductory Methods of Numerical Analysis by S.S. Sastry
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/False_position_method
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...