Find all reachable nodes from every node present in a given set
Last Updated :
10 Mar, 2023
Given an undirected graph and a set of vertices, find all reachable nodes from every vertex present in the given set.
Consider below undirected graph with 2 disconnected components.
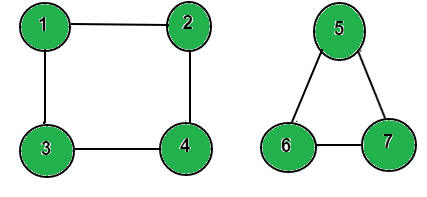
arr[] = {1 , 2 , 5}
Reachable nodes from 1 are 1, 2, 3, 4
Reachable nodes from 2 are 1, 2, 3, 4
Reachable nodes from 5 are 5, 6, 7
Method 1 (Simple)
One straight forward solution is to do a BFS traversal for every node present in the set and then find all the reachable nodes.
Assume that we need to find reachable nodes for n nodes, the time complexity for this solution would be O(n*(V+E)) where V is number of nodes in the graph and E is number of edges in the graph.
Please note that we need to call BFS as a separate call for every node without using the visited array of previous traversals because a same vertex may need to be printed multiple times. This seems to be an effective solution but consider the case when E = ?(V2) and n = V, time complexity becomes O(V3).
Method 2 (Efficient)
Since the given graph is undirected, all vertices that belong to same component have same set of reachable nodes. So we keep track of vertex and component mappings. Every component in the graph is assigned a number and every vertex in this component is assigned this number. We use the visit array for this purpose, the array which is used to keep track of visited vertices in BFS.
For a node u,
if visit[u] is 0 then
u has not been visited before
else // if not zero then
visit[u] represents the component number.
For any two nodes u and v belonging to same
component, visit[u] is equal to visit[v]
To store the reachable nodes, use a map m with key as component number and value as a vector which stores all the reachable nodes.
To find reachable nodes for a node u return m[visit[u]]
Look at the pseudo code below in order to understand how to assign component numbers.
componentNum = 0
for i=1 to n
If visit[i] is NOT 0 then
componentNum++
// bfs() returns a list (or vector)
// for given vertex 'i'
list = bfs(i, componentNum)
m[visit[i]]] = list
For the graph shown in the example the visit array would be.
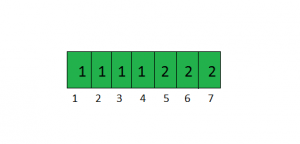
For the nodes 1, 2, 3 and 4 the component number is 1. For nodes 5, 6 and 7 the component number is 2.
Implementation of above idea
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class Graph
{
public:
int V;
list<int> *adj;
Graph(int );
void addEdge(int, int);
vector<int> BFS(int, int, int []);
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list<int>[V+1];
}
void Graph::addEdge(int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v);
adj[v].push_back(u);
}
vector<int> Graph::BFS(int componentNum, int src,
int visited[])
{
queue<int> queue;
queue.push(src);
visited[src] = componentNum;
vector<int> reachableNodes;
while(!queue.empty())
{
int u = queue.front();
queue.pop();
reachableNodes.push_back(u);
for (auto itr = adj[u].begin();
itr != adj[u].end(); itr++)
{
if (!visited[*itr])
{
visited[*itr] = componentNum;
queue.push(*itr);
}
}
}
return reachableNodes;
}
void displayReachableNodes(int n,
unordered_map <int, vector<int> > m)
{
vector<int> temp = m[n];
for (int i=0; i<temp.size(); i++)
cout << temp[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
void findReachableNodes(Graph g, int arr[], int n)
{
int V = g.V;
int visited[V+1];
memset(visited, 0, sizeof(visited));
unordered_map <int, vector<int> > m;
int componentNum = 0;
for (int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++)
{
int u = arr[i];
if (!visited[u])
{
componentNum++;
m[visited[u]] = g.BFS(componentNum, u, visited);
}
cout << "Reachable Nodes from " << u <<" are\n";
displayReachableNodes(visited[u], m);
}
}
int main()
{
int V = 7;
Graph g(V);
g.addEdge(1, 2);
g.addEdge(2, 3);
g.addEdge(3, 4);
g.addEdge(3, 1);
g.addEdge(5, 6);
g.addEdge(5, 7);
int arr[] = {2, 4, 5};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int);
findReachableNodes(g, arr, n);
return 0;
}
|
Python3
from collections import deque
def addEdge(v, w):
global visited, adj
adj[v].append(w)
adj[w].append(v)
def BFS(componentNum, src):
global visited, adj
queue = deque()
queue.append(src)
visited[src] = 1
reachableNodes = []
while (len(queue) > 0):
u = queue.popleft()
reachableNodes.append(u)
for itr in adj[u]:
if (visited[itr] == 0):
visited[itr] = 1
queue.append(itr)
return reachableNodes
def displayReachableNodes(m):
for i in m:
print(i, end = " ")
print()
def findReachableNodes(arr, n):
global V, adj, visited
a = []
componentNum = 0
for i in range(n):
u = arr[i]
if (visited[u] == 0):
componentNum += 1
a = BFS(componentNum, u)
print("Reachable Nodes from ", u, " are")
displayReachableNodes(a)
if __name__ == '__main__':
V = 7
adj = [[] for i in range(V + 1)]
visited = [0 for i in range(V + 1)]
addEdge(1, 2)
addEdge(2, 3)
addEdge(3, 4)
addEdge(3, 1)
addEdge(5, 6)
addEdge(5, 7)
arr = [ 2, 4, 5 ]
n = len(arr)
findReachableNodes(arr, n)
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class ReachableNodes {
private static int V;
private static List<List<Integer> > adj;
private static boolean[] visited;
public static void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj.get(v).add(w);
adj.get(w).add(v);
}
public static List<Integer> BFS(int componentNum,
int src)
{
List<Integer> queue = new ArrayList<>();
queue.add(src);
visited[src] = true;
List<Integer> reachableNodes = new ArrayList<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int u = queue.remove(0);
reachableNodes.add(u);
for (int itr : adj.get(u)) {
if (visited[itr] == false) {
visited[itr] = true;
queue.add(itr);
}
}
}
return reachableNodes;
}
public static void
displayReachableNodes(List<Integer> m)
{
for (int i : m) {
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void findReachableNodes(int[] arr, int n)
{
List<Integer> a = new ArrayList<>();
int componentNum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int u = arr[i];
if (visited[u] == false) {
componentNum++;
a = BFS(componentNum, u);
}
System.out.println("Reachable Nodes from " + u
+ " are");
displayReachableNodes(a);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
V = 7;
adj = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < V + 1; i++) {
adj.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
visited = new boolean[V + 1];
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(2, 3);
addEdge(3, 4);
addEdge(3, 1);
addEdge(5, 6);
addEdge(5, 7);
int[] arr = { 2, 4, 5 };
int n = arr.length;
findReachableNodes(arr, n);
}
}
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class ReachableNodes {
private static int V;
private static List<List<int> > adj;
private static bool[] visited;
public static void AddEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].Add(w);
adj[w].Add(v);
}
public static List<int> BFS(int componentNum, int src)
{
List<int> queue = new List<int>();
queue.Add(src);
visited[src] = true;
List<int> reachableNodes = new List<int>();
while (queue.Count > 0) {
int u = queue[0];
queue.RemoveAt(0);
reachableNodes.Add(u);
foreach(int itr in adj[u])
{
if (visited[itr] == false) {
visited[itr] = true;
queue.Add(itr);
}
}
}
return reachableNodes;
}
public static void DisplayReachableNodes(List<int> m)
{
foreach(int i in m) { Console.Write(i + " "); }
Console.WriteLine();
}
public static void FindReachableNodes(int[] arr, int n)
{
List<int> a = new List<int>();
int componentNum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int u = arr[i];
if (visited[u]
== false) {
componentNum++;
a = BFS(componentNum, u);
}
Console.WriteLine("Reachable Nodes from " + u
+ " are");
DisplayReachableNodes(a);
}
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
V = 7;
adj = new List<List<int> >();
for (int i = 0; i < V + 1; i++) {
adj.Add(new List<int>());
}
visited = new bool[V + 1];
AddEdge(1, 2);
AddEdge(2, 3);
AddEdge(3, 4);
AddEdge(3, 1);
AddEdge(5, 6);
AddEdge(5, 7);
int[] arr = { 2, 4, 5 };
int n = arr.Length;
FindReachableNodes(arr, n);
}
}
|
Javascript
function addEdge(v, w) {
adj[v].push(w);
adj[w].push(v);
}
function BFS(componentNum, src) {
let queue = [];
queue.push(src);
visited[src] = true;
let reachableNodes = [];
while (queue.length != 0) {
let u = queue.shift();
reachableNodes.push(u);
for (let itr of adj[u]) {
if (visited[itr] == false) {
visited[itr] = true;
queue.push(itr);
}
}
}
return reachableNodes;
}
function displayReachableNodes(m) {
for (let i of m) {
console.log(i + " ");
}
console.log();
}
function findReachableNodes(arr, n) {
let a = [];
let componentNum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
let u = arr[i];
if (visited[u] == false) {
componentNum++;
a = BFS(componentNum, u);
}
console.log("Reachable Nodes from " + u + " are");
displayReachableNodes(a);
}
}
let V = 7;
let adj = new Array(V + 1);
for (let i = 0; i < V + 1; i++) {
adj[i] = new Array();
}
let visited = new Array(V + 1).fill(false);
addEdge(1, 2);
addEdge(2, 3);
addEdge(3, 4);
addEdge(3, 1);
addEdge(5, 6);
addEdge(5, 7);
let arr = [2, 4, 5];
let n = arr.length;
findReachableNodes(arr, n);
|
Output
Reachable Nodes from 2 are
2 1 3 4
Reachable Nodes from 4 are
2 1 3 4
Reachable Nodes from 5 are
5 6 7
Time Complexity Analysis:
n = Size of the given set
E = Number of Edges
V = Number of Nodes
O(V+E) for BFS
In worst case all the V nodes are displayed for each node present in the given, i.e only one component in the graph so it takes O(n*V) time.
Worst Case Time Complexity : O(V+E) + O(n*V)
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...